Motion and Time Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 9
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Motion and Time? |

|
| Speed: |

|
| Units |

|
| Measurement of Speed |

|
| Practice Questions |

|
What is Motion and Time?
The connection between motion and time is that the speed of an object depends on how far it travels within a certain time frame. Speed is calculated by dividing the distance covered by the time taken. The basic unit for measuring speed is metre per second (m/s).
Speed = Distance/Time
What is Motion?
The speed of an object refers to how much distance it covers in a given time. An object is considered to be in motion when it changes its position over time in relation to a stationary object, such as a building or an electric pole.
Types of Motion:
1. Slow and Fast Motion: If an object ‘A’ covers a distance in less time and another object covers the same distance in more time, the object A is called a faster moving object and object B is called a slower moving object. In other words, object A has faster motion and object B has slower motion.
2. Rectilinear Motion: Motion along a straight line is known as rectilinear motion or motion along a straight line. For example: Motion of a car along a straight line
3. Curvilinear Motion: Motion along a curve line is known as curvilinear motion. For example: Motion of car or any moving object along a curve line
4. Circular Motion: Motion along a circle is known as circular motion. For example: Motion of cyclist along a circular park.
5. Periodic Motion: This type of motion repeats itself at regular intervals. For example, the swinging of a pendulum is periodic and is used in clocks and watches to measure time.

Speed:
Distance covered by an object in unit time is called speed.
Speed may be divided into three types: Uniform speed, Non-Uniform Speed and Average Speed
Uniform Speed: If an object covers a fixed distance in each unit of time the motion is known as uniform motion or uniform speed.
Non-uniform Speed: If an object does not cover a fixed distance in each unit of time the motion is known as non-uniform motion or non-uniform speed.
Average Speed: Total distance covered divided by total time taken is known as average speed.
Periodic Motion or Oscillatory Motion: When an object repeats its motion after every fixed interval of time, the motion of the object is called periodic motion or osscillatory motion.
In many wall clocks pendulum is used even today. A device having a string suspended with a fixed point with a bob at bottom is called pendulum.
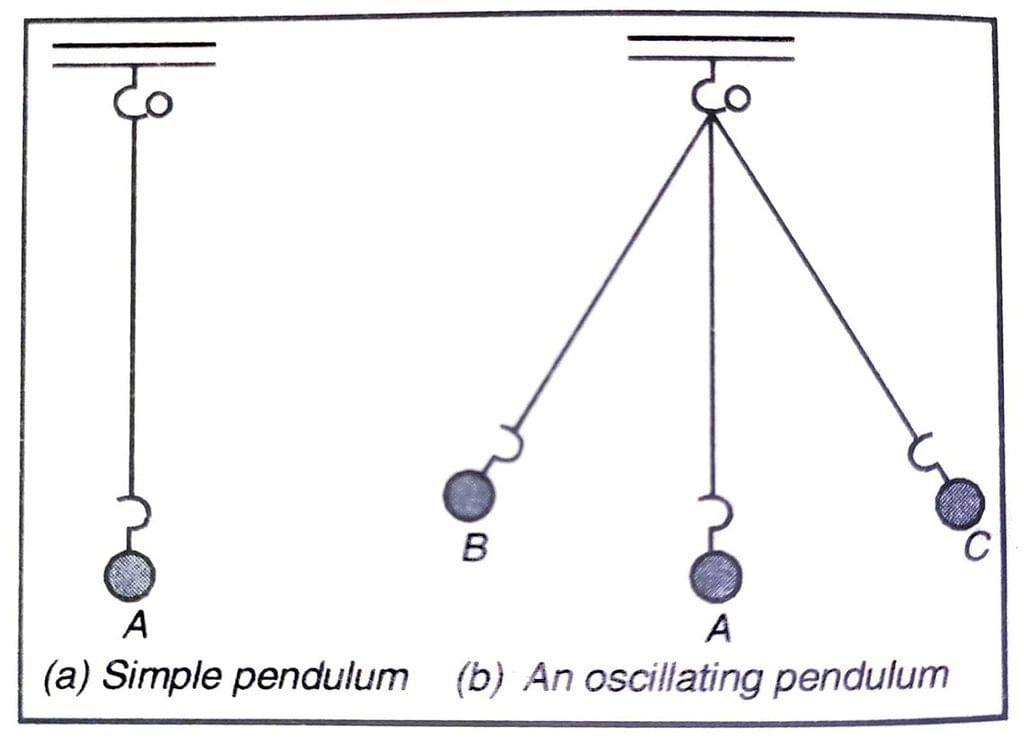
The motion of pendulum starting from one extreme end to another extreme end and back to the first extreme end is called one oscillation. Similarly, the motion of a simple pendulum from its mean position to extreme left and extreme right and back to the mean position is called one oscillation.
Time Period: Time taken to complete one oscillation by the pendulum is called time period.
Units
Unit of Time: Time is measured in second. Thus, unit of time is second. Second is denoted by ‘s’.
60 second = 1 minute
60 minute = 1 hour
24 hour = 1 day
7 day = 1 week
365 days = 1 year
Unit of speed: Unit of speed is meter/second (m/s), or metre/minute (m/min) or kilometer/hour (km/h).
1000 metre (m) = 1 kilometer (km)
Measurement of Speed
Speedometer: A device used to measure the speed of a vehicle is called SPEEDOMETER.
Odometer: A device used to measure the distance covered by a vehicle.
Distance Time Graph: When distance covered by an object and time taken to cover the distance is represented on a graph, the graph is called distance time graph.
If a vehicle cover a distance of 5 km every hour and travels for 5 hours, the time distance time graph for the given vehicle can be plotted as follows using the table given below:
Distance time graph of a moving vehicle with a constant speed is a straight slanting line.
Speed-time graph for the same vehicle will be a straight line parallel to x-axis.
Practice Questions
Question: 1 – A car covers a distance of 100 km in 5 hour, calculate its speed.
Solution:
Given,
Total distance = 100 km
Total time taken = 5 hour
We know that
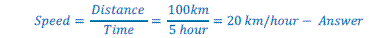
Question: 2 – A car covers 20 km in the first hour and cover 30 km in the last 4 hours. Find its average speed.
Solution:
Given,
Total distance covered = 20 km + 30 km = 50 km
Total time taken = 1 hour + 4 hour = 5 hour
We know that,

Question: 3 – A pendulum takes 20 second to complete 10 oscillations, calculate its time period.
Solution:
Given, Number of oscillations = 10
Time taken = 20 second
We know that,
|
111 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Motion and Time Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 9
| 1. What is the difference between speed and velocity? |  |
| 2. How is speed measured? |  |
| 3. What is the formula to calculate speed? |  |
| 4. How can you determine the average speed of an object in motion? |  |
| 5. Can an object have a constant speed but changing velocity? |  |
















