Hydrocarbons, Class 11, Chemistry Detailed Chapter Notes PDF Download
Alkanes (Properties and Nomenclature) - Hydrocarbons, Class 11, Chemistry
Hydrocarbons
Alkane
Alkane are the saturated non polar hydrocarbon having general formula CnH2n+2.
Hydrocarbon - Those organic compounds which contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms are known as hydrocarbons.
1.2 General method of preparation
1.2.1 By catalytic reduction of alkenes and alkynes
R - C º ≡ C - R' R - CH2 - CH2 - R'
R - CH = CH - R' R - CH2 - CH2 - R'
Hydrogenation → Addition of H2 to unsaturated bond.
Hydrogenation is of two kind
(a) Heterogeneous and (b) Homogeneous
(a) Heterogeneous It is two phase hydrogenation the catalyst is finely divided metal like Ni, Pt or Pd and a solution of alkene.
(b) Homogeneous It is one phase hydrogenation both catalyst and alkenes are solution. In this hydrogenation catalyst are organic complex of transition metal like Rh or Ir.
Hydrogenation is exothermic, qualitative and during the hydrogenation, total heat evolved to hydrogenate one mole of unsaturated compound is called heat of hydrogenation. Heat of hydrogenation is the measurement of stability of isomeric alkenes.
stability of alkene
1.2.2 From alkyl halide
(A) From organometallic compound compound having bond. (M
metal)
(i) By wurtz reaction
2R - X + 2Na R → R + 2NaX
R - X + R' - X R - R, R- R', R' - R'
Mechanism Two mechanisms are suggested
(a) Ionic mechanism
2Na 2Na 2e
(b) Free radical mechanism
Na
Note : The alkyl halide should be 1º or 2º, with 3º R - X SN2 and free radical coupling is not possible due to steric hinderance so in that case elimination or disproportionation is possible.
In the ionic mechanism alkyl sodium gives
strong base as well as nucleophile which gives SN2 with R - X, ether should be dry otherwise, if moisture is present then
forms R - H instead of R - R with H2O.
(ii) By G.R.
(iii) By corey house alkane synthesis
Mechanism
R2CuLi is the source of
R2 CuLi do not reacts with -NO2, - CN, > C = O etc.
Ex.1
if C is CH3 - CH2 - (CH2)5 - CH3, than what is Y.
Ans. CH3 - (CH2)6 - Br
Q.1
(iv) By Franklande reagent
R - X Zn R - X R - R Zn X2
Mechanism
R - X
(B) By reduction of alkyl halides
(i) with metal-acid
Reducing agent
Zn / acid, Zn - Cu / H2O or Zn - Cu acid
Zn - Cu / C2H5OH, Na - Hg / acid, Al - Hg / H2O etc.
Mechanism
(ii) With Metal hydrides
(a) TPH (Ph3SnH) : It reduces 1º, 2º & 3º R - X
R - X R - H
(b) NaBH4
(c) ,
1.2.3 By red P & HI
Red P & HI is strong reducing agent
R - COOH R - CH3
R - CH3
R - CH3
R - X R - H
R - OH R - H H2O
1.2.4 By soda lime → Fatty acids are good source of hydrocarbon, correction, heating of sodium salt of carboxylic acid (R - COONa) with soda lime (NaOH - CaO) gives hydrocarbon, which is known as decarboxylation (e.g. replacement of - COOH group by -H) decarboxylation also takes place on heating only, when compound is gem dicarboxylic acid or there is keto group or double bond on b carbon.
Ex.2
What are A and B
Ans. A is
Q.2
Write the structure of A and mention its stereochemistry
1.2.5 By Kolbe's electrolysis
2RCOOK 2HOH RR 2CO2 H2 2KOH
e.g. 2CH3 - COOK 2H2O CH3CH3 2CO2 H2 2KOH.
If n is the number of carbon atoms in the salt of carboxylic acid, the alkane formed has 2(n - 1) carbon atoms.
1.2.6 Reduction of aldehydes, ketones :
(a) By Clemmensen's reduction : with Zn - Hg / conc. HCl
R - CHO RCH3 H2O
RCH2R' H2O
e.g. CH3 - CHO CH3CH3 H2O
CH3CH2C2H5 H2O
Clemmensen reduction is not used for compound which have acid sensitive group.
(b) By Wolff-kishner reduction with NH2NH2 / KOH
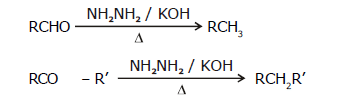
Wolff-kishner reduction is not used for compounds which have base sensitive groups.
1.3 Physical Properties of Alkanes :
3.3.1 Physical State :
The first four members (C1 to C4) are gases : the next thirteen members, (C5 to C17) are liquids while the higher members are waxy solids.
1.3.2 Boiling points :
The boiling points of n-alkanes increase regularly with the increase in the number of carbon atoms
Among the isomeric alkanes, the branched chain isomers have relatively low boiling points as compared to their corresponding straight chain isomers. Greater the branching of the chain, lower is the boiling point. This is due to the fact that branching of the chain makes the molecules more compact and brings it close to a sphere, so the magnitude of vander wall forces decreases.
1.3.3. Melting Points
It is the evident that the increase in melting point is relatively more in moving from an alkane having odd number of carbon atoms to the higher alkane with even no. of `C' while it is relatively less in moving from an alkane with even number of carbon atoms to the higher alkane.
Explanation : The alkanes with even no. of `C' atoms are more closely packed.
1.3.4 Solubility
In keeping with the popular rule "like dissolves like" hydrocarbons are insoluble in polar solvent like water because they are predominantly non-polar in nature.
1.3.5 Density
The densities of alkanes increase with increasing molecular weight but become constant at about 0.8 g cm-3. This means that all alkanes are lighter than water so they floats over water.
1.4.1 Chemical Reaction of Alkanes :
Characteristic reaction of alkanes are free radical substitution reaction, these reaction are generally chain reactions which are completed in three steps mainely.
(i) chain initiation (ii) chain propagation, (iii) chain termination
Examples of free radical substitution reaction →
R - H + X2 R - X + HX
Exp. CH4
When equimolar amount of methane and Cl2 are taken, a mixture of four possible products are formed, but if we take excess of CH4 then yield of CH3Cl will be the major product.
Reactivity of X2 : F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
Reactivity of H : 3ºH > 2ºH > 1ºH
with F2 alkanes reacts so vigorously that, even in the dark and at room temp, reactant diluted with an inert gas.
Iodination is reversible reaction, since HI formed as a by-product is a strong reducing agent and reduces alkyl iodide back to alkane. Hence iodination can be done only in presence of strong oxidizing agent like HIO3, HNO3 or HgO
R - H + I2 R - I + HI
HI + HIO3 H2O + I2
Mechanism of halogenation of CH4 →
(i) Chain initiation it is a endothermic step
X2
(ii) Chain propagation
(iii) Chain termination → it is always exothermic
Each photon of light cleaves one chlorine molecule to form two chlorine redicals, each chlorine atom starts a chain and on an average each chain contains 5000 repetitions of the chain propagating cycle so about 10,000 molecules of CH3Cl are formed by one photon of light.
Some reagent affects the rate of halogenation : For example
Q.3 In the given ways which is feasible
Q.4 Which of the following reaction has zero activation energy
(A)
(B) Cl2 2 Cl
(C)
(D)
Q.5 If the Eact for a forward reaction is given
the Eact for backward reaction will be
(A) 1 kcal
(B) 4 kcal
(C) -4 kcal
(D) 3 kcal
Halogenations of higher alkane :
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
Relative amounts of the various isomers differ remarkably depending upon the halogen used from the above reaction, it is observed that chlorination gives mixture in which no isomer greatly dominates while, in bromination gives mixture in which one isomer dominates greatly (97% - 99%).
Factors determining the relative yields of the isomeric products.
(i) Probability factor This factor is based on the number of each kind of H atom in the molecule.
(ii) Reactivity of hydrogen The order of reactivity is 3º > 2º > 1º
1.4.2 Aromatisation:
1.4.3 Combustion : (i.e. complete oxidation)
O2
nCO2 (n 1) H2O (DHcombustion = -ve)
O2
xCO2
H2O
C5H12 8O2 5CO2 6H2O
Heat of combustion : Amount of heat i.e. liberated when 1 mole of hydrocarbon is completely burnt into CO2 & H2O.
Heat of combustion as a measure of stability of alkane :
Combustion is used as a measurements of stability.
More branched alkanes are more stable and have lower heat of combustion.
e.g. (I) CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH3 (II)
stability : II > I
DHcomb. : I > II
More branched alkane has more no. of primary C - H bonds. (therefore it has more bond energy).
Homologues : Higher homologues have higher heat of combustion.
Isomers : Branched isomer has lower heat of combustion.
(i) Initiators they initiate the chain reaction, initiators are R2O2, Perester's etc.
R - O - O - R
(ii) Inhibitors A substance that slow down or stop the reaction are known as inhibitors
For example O2 is a good inhibitor
all reactive alkyl free radicals are consumed so reaction become stop for a period of time.
Relative reactivity of halogen toward methane
Order of reactivity is F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 which can be explained by the value of DH (energy change)
Steps of halogenation, value of DH for each step. (Kcal/mole)
F Cl Br I
(i) X2 2 X 38 58 46 38
(ii) -32 1 16 33
(iii) - 70 - 26 - 24 - 20
Ex.3 Explain why the chain initiating step in thermal chlorination of CH4 is
Cl2 and not CH4
Ans. Because Eact of Cl2 is less than Eact of CH4
Ex.4 Chlorination of CH4 involves following steps :
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Which of the following is rate determining ?
(A) Step (i)
(B) Step (ii)
(C) Step (iii)
(D) Step (ii) and (iii) both
Ans. (B)
Reactivity of hydrogen 3º > 2º > 1º
Because formation of alkyl free radical is Rds so, that H is more reactive which produce more stable free radical (less Eact)
order of stability of F.R.
=================================================================
Alkenes (Properties and Nomenclature) - Hydrocarbons,Class 11, Chemistry
Alkene
1. Introduction
Alkenes are hydrocarbons with carbon-carbon double bonds, Alkenes are sometimes called olefins, a term derived from olefinic gas, meaning "oil forming gas". Alkenes are among the most important industrial compound and many alkenes are also found in plants and animals. Ethylene is the largest - volume industrial organic compound, used to make polyethylene and a variety of other industrial and consumer chemicals.
2. Structure and bonding in Alkenes
(1) Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons having at least one double bond.
(2) They are represented by general Formula (G.F.) CnH2n (one double bond)
(3) In Ethene C = C bond length is 1.34 Å
(4) Its bond energy is 146 kcal.mol-1
(5) The hybridization of (C = C) alkenic carbon is sp2
(6) The πe- cloud is present above and below the plane of s-bonded skeleton.
(7) They are also known as olefins since ethene, the first member of the homologous series forms oily liquid substance when treated with halogens.
(8) Compounds may exist as conjugated polyenes or as cumulated polyenes or as isolated polyenes
Note : That angle a > b since repulsion due to p electrons (double bond - single bond repulsion > single bond single bond repulsion according to VSEPR theory.
Ex.1 Write IUPAC names of
(a) (b)
Ans. (a) 2, 3-Dimethylcyclohexene
(b) 1-(2-butenyl) cyclohex -1-ene
Ex.2 Give the structure for each of the following
(a) 4-Methyl-1, 3-hexadiene
(b) 1-Isopropenylcyclopentene
Ans. (a) (b)
3. Physical Properties of Alkenes / Hydrocarbons
Table : III
4. Laboratory test of Alkene
Table - IV
5. Methods of preparation of alkenes
(I) BY PARTIAL REDUCTION OF ALKYNES
(a) By Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkynes in presence of poisoned catalyst(A Syn Addition of Hydrogen : Synthesis of cis-Alkenes : This is performed by)
(i) Lindlar's catalyst : Metallic palladium deposited on calcium carbonate with lead acetate and quinoline.
(ii) P-2 catalyst (Ni2B nickel boride)
General Reaction R - C º C - R
Mechanism of hydrogenation :
Steps : The reactant alkyne molecules and hydrogen molecules get adsorbed at the surface of metal catalyst. It is chemical adsorption (chemisorption).
In this state, the reactants lie very close to each other and so the hydrogen atoms start forming bond with carbon. Two hydrogen atoms are added to two triply bonded carbon atom from the same side of p bond and a cis or syn addition product is formed. The product alkene now escapes away from the surface of the catalyst. Quinoline occupies the metal surface inhibiting further reduction to alkanes Quinoline therefore is called catalyst poison and palladium is called deactivated catalyst or poisoned catalyst.
e.g.
(b) Birch Reduction : (Anti Addition of Hydrogen : Synthesis of trans-Alkenes)
General Reaction
e.g. CH3 - CH2 - C = C - CH2 - CH3
Note : This process of reduction is not eligible when terminal alkynes are taken. (R - C º CH) because terminal alkynes form sodium salt with Na metal.
CH3 - C = CH Na / NH3 CH3 - CH = C- Na [H]
Ex.3 Identify the reagent for following synthesis.
Ans. H2 / Lindiar's catalyst.
Ex.4 Identify the products in the following reaction :
Ans.
(II) BY DEHAL OGENATION OF VICINAL DIHALIDES
There are two types of dihalides namely gem (or geminal) dihalides in which the two halogen atoms are attached to the same carbon atom and vicinal dihalides in which the two halogen atoms are attached to the adjacent carbon atoms.
Dehalogenation of vicinal dihalides can be effect either by NaI in acetone or zinc in presence of acetic acid or ethanol.
General Reaction
(i)
(ii) CH3 - CHBr - CH2Br CH3 - CH = CH2
Remarks
(1) Both are E2 elimination.
(2) Both are stereospecific anti elimination.
(III) DEHYDRO HALOGENATION OF ALKYL HALIDES
Dehydro halogenation is the elimination of a hydrogen and a halogen from an alkyl halide to form an alkene.
Dehydro halogenation can take place by E1 and E2 mechanism.
(i) Hot alcoholic solution of KOH EtO- / EtOH (ii) NaNH2
(iii) t-BuO-K in t-BuOH
(i) Dehydrohalogenation by the E2 mechanism : Second-order elimination is a reliable synthetic reaction, especially if the alkyl halide is a poor SN2 substrate. E2 dehydrohalogenation takes place in one step, in which a strong base abstracts a proton from one carbon atoms as the leaving group leaves the adjacent carbon.
General reaction :
e.g.
Here b - H is eliminated by base hence called b elimination following Saytzeff rule.
i.e, (Highly substituted alkene is major product). It also involves an anti elimination of HX.
e.g.
e.g.
e.g.
e.g.
(ii) Formation of the Hoffmann product
Bulky bases can also accomplish dehydro halogenation that do not follow the saytzeff rule. Due to steric hindrance, a bulky base abstracts the proton that leads to the most highly substituted alkene. In these cases, it abstracts a less hindered proton, often the one that leads to formation of the least highly substituted product, called the Hoffmann product.
Stereospecific E2 reactions
The E2 is stereospecific because it normally goes through an anti and coplanar transition state. The products are alkene, and different diastereomers of starting materials commonly give different diastereomers of alkenes.
Ex.5 What alkyl halide would yield each of the following pure alkene on reaction with alcoholic KOH ?
(i)
(ii) CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH = CH2
Ans. (i)
(ii) CH3CH2CH2CH2 CH2Cl
(iii)
Ex.6 What are the various product due to loss of HBr from
Ans.
(IV) DEHYDRATION OF ALCOHOLS
Alcohols when heated in presence of following reagents undergo loss of water molecule and form alkenes. The elimination is b elimination.
(i) H2SO4 / 160ºC
(ii) H3PO4 / Δ
(iii) P2O5 / Δ
(iv) Al2O3 / 350ºC undergo loss of water molecule and form alkenes
General Reaction RCHCH2OH R - CH = CH2 H2O
e.g.
(V) BY PYROLYSIS OF ESTERS
Thermal cleavage of an ester involves formations of a six membered ring in the transition state leading to the elimination of an acid leaving behind an alkene.
As a direct consequence of cyclic transition state, both the leaving groups namely proton and carboxylate ion are eliminated from the cis position. This is an example of syn elimination.
(VI) BY HOFMANN ELIMINATION METHOD
Alkenes can be prepared by heating quaternary ammonium hydroxide under reduced pressure at a temperature between 100ºC and 200ºC.
Less substituted alkenes are formed as major product in this case, which are defined as Hofmann alkenes.
(VII) BY WITTIG REACTION
The aldehydes and ketones are converted into alkenes by using a special class of compounds called phosphorus ylides, also called Wittig reagents.
The Triphenyl group of phosphorane has a strong tendency to pull oxygen atom of the aldehyde or ketone via a cyclic transition state forming an alkene.
(R, R', R" and R"' may be hydrogen or any alkyl group)
e.g.
Ex.7 Complete the following reaction :
Ans.
Ex.8 Identify the (X), (Y), and (Z) in the following reactions
(i) PhCH2Br CH3 - - CH3
(X)
(ii) CH3I PhCOCH3 (Y)
(iii) PhCH2Br PhCH = CHCHO (Z)
Ans. (X) = Ph - CH = C(CH3)2
(Y) = Ph - C(CH3) = CH2
(Z) = Ph - CH = CH - CH = CH - Ph
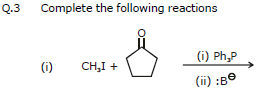
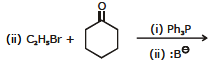
6. Chemical reactions of alkenes
(I) CATALYTIC HYDROGENATION OF ALKENES : (HETEROGENEOUS HYDROGENATION)
Hydrogenation : The function of catalyst
Hydrogenation of a alkene is exothermic reaction (DHº = - 120 kJ mol-1)
R - CH = CH - R H2 R - CH2 - CH2 - R heat
As a consequence ,both hydrogen atoms usually add from the same side of the molecule. This mode of addition is called a syn addition.
Hydrogenation of an alkene is formally a reduction, with H2 adding across the double bond to give an alkane.
The process usually requires a catalyst containing Pt, Pd or Ni.
e.g. CH3 - CH - = CH - CH3 H2 CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH3
e.g.
Ex.9 Complete the following reactions :
CH3CH = CH2 H2 ?
Sol. CH3CH2CH3
(II) ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION REACTIONS :
Mechanism
Step 1 : Attack of the electrophile on p bond forms a carbocation.
Step 2 : Attack by a nucleophile gives the product of addition
(i) Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes
Alkenes add water in the presence of an acid catalyst to yield alcohols. The addition takes place with Markovnikov regioselectivity. The reaction is reversible, and the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is simply the reverse of that for the dehydration of an alcohol.
The carbocation intermediate may rearrange if a more stable carbocation is possible by hydride or alkanide migration. Thus, a mixture of isomeric alcohol products may result.
General Reaction
e.g.
e.g.
Ex.10 Identify the product in following reaction
Ans.
(ii) (a) Oxymercuration - Demercuration
Alkenes react with mercuric acetate in a mixture of water and tetrahydrofuran (THF) to produce (hydroxyalkyl) mercury compounds. These can be reduced to alcohols with sodium borohydride and water :
Oxymercuration
General Reaction
In the oxymercuration step, water and mercuric acetate add to the double bond; in the demercuration step, sodium borohydride reduces the acetoxymercury group and replaces in with hydrogen. Then net addition of H -and -OH takes place with Markovnikov regioselectivity and generally takes place without the complication of rearrangements.
e.g.
(b) Alkoxymercuration - demercuration
General reaction
e.g.
Ex.11 Supply the structures for (X) and (Y) in the following two - step reaction :
C3H7CH = CH2
Sol. (X) = C3H7CH(OH)CH2-HgOAC (Y) = C3H7CH(OH)CH3
(An organomercurial alcohol)
Ex.12 Identify final product in the following :
(a)
(b)
Ans. (a) (b)
(iii) Hydroboration-oxidation (SYN ADDITION)
General Reaction
An alkene reacts with BH3 : THF of diborane to produce an alkylborane. Oxidation and hydrolysis of the alkylborane with hydrogen peroxide and base yields an alcohol.
e.g.
Oxidation
In the first step, boron and hydrogen undergo syn addition to the alkene in the second step, treatment with hydrogen peroxide and base replaces the boron with -OH with retention of configuration. The net addition of -H and -OH occurs with anti Markovnikov regioselectivity and syn stereoselectivity. Hydrogboration -oxidation therefore, serves as a useful regiochemical complement to oxymercuration demercuration
e.g.
e.g.
(i) Hydration with dil. H2SO4 proceeds via carbocation rearrangement
(ii) Hydration with Hg(OAc)2, H2O, following by NaBH4 proceeds via Markonikov's rule
(ii) Hydration with (BH3)2 followed by H2O2 / OH- proceeds via Anti Markonikov's rule
(iv) Addition of hydrogen halides
General Reaction
e.g.
e.g.
Ex.13 Predict the major products of the following reactions and propose mechanism to support your predictions.
(A)
(B) CH3 - CH2 - O - O - CH2 - CH3
(C)
Sol. (A) (B)
(C)
Ex.14 Identify the products in the following reactions :
(a) F3C - CH = CH2 HCl (b) O2N - CH = CH2 HCl
(c) CH3O - CH = CH2 HCl (d) PhCH = CHCH3 HCl
(e)
Q.6 Give the products of the following reactions : -
Q.7 Give the reactant (alkene) of the following products.
(v) Addition of halogen
Halogen add to alkenes to form vicinal dihalides.
General Reaction
(X2 = Cl2, Br2)
The nucleophile attacks the electrophilic nucleus of one halogen atom, and the other halogen serves as the leaving group, departing as halide ion. Many reactions fit this general pattern.
Note : (i) F2 is not added because F is never generated. Morever reaction is explosive giving CO2 & H2O
(ii) I2 is not added because reaction is reversible with equilibrium in backward direction.
(iii) Reaction with bromine is basis for test of alkenes.
(iv) Halogen addition is stereospecific anti addition
(v) Halogens can also be added in presence of sun light and give free radical addition.
(Reactivity of halogen addition in sunlight is F2 (explosive) > Cl2 > Br2 > I2)
Mech.
Step-1 Formation of a halonium ion
Step-2 Opening of the halonium ion
X attacks from the back side of halonium ion.
e.g.
e.g.
Ex.15 Give the product of the following reaction.
Me2C = CH2 ICl ?
Sol. Cl is more electronegative than I making I the E that, according to the Markovnikov rule, adds to the C with the greater number of H's. The product is 2-chloro-1-iodo-2-methylpropane, (Me2CClCH2I).
Ex.16 What are the products and (type of isomers) when Br2 adds to : -
(a) (b)
Ans. (a) (b)
(vi) Hydroxylation of Alkenes
(a) Syn Hydroxylation : (Reaction with Bayer's reagent, (cold dilute alkaline KMnO4 solution).
Both OH groups are added from same stereochemical side. This addition is example of syn addition
General Reaction
e.g.
The same function of syn addition of 2 - OH groups is performed by OsO4 / H2O2
e.g.
(b) Anti hydroxylation
General Reaction
e.g.
Ex.17 Identify the product in the following reaction :
Ans.
Ex.18 Identify the product (X) in the following reaction :
Ans. (x) :
Since C = C bond in ring is more substituted than that in open chain.
(vii) Addition of carbenes to Alkenes :
Methylene is the simplest of the carbenes : uncharged, reactive intermediates that have a carbon atom with two bonds and two nonbonding electrons. Like borane (BH2), methylene is a potent electrophile because it has an unfilled octet. It adds to the electrons rich pi-bond of an alkene to form a cyclopropane.
General Reactions
Heating or photolysis of diazomethane (CH2N2) gives nitrogen gas and methylene.
There are two difficulties with using CH2N2 to cyclopropene double bonds. First, it is extremely toxic and explosive. A safer reagent would be more convenient for routine use. Second, methylene generated from CH2N2 is so reactive that it inserts into C - H bonds as well as C = C bonds.
e.g.
Ex.19 Identify the product in the following reactions
(a)
(b)
Ans. (a) (b)
(III) EPOXIDATION OF ALKENES :
An alkene is converted to an epoxide by a peroxyacid, a carboxylic acid that has an extra oxygen atom in a -O - O - (peroxy) linkage.
General Reaction
The epoxidation of an alkene is clearly an oxidation, since an oxidation, since an oxygen atom is added Peroxyacids are highly selective oxidizing agents. Some simple peroxyacids (sometimes called per acids) and their corresponding carboxylic acids are shown below :
Mech.
e.g.
Ex.20 Complete the following reaction
Ans.
Ex.21 Predict the product, including stereochemistry where appropriate, for the m-chloroperoxy-benzoic acid expoxidations of the following alkenes.
(a) (b)
(c) Cis-cyclodecene (D) Trans-cyclodecene
(IV) HALOHYDRIN FORMATION
General Reaction
X' and H2O are generated as attacking species from X2 H2O
e.g.
Ex.22 Predict the product in the following reactions
(a)
(b)
Ans. (a) (b)
(V) OXIDATIVE CLEAVAGE OF ALKENES
(i) Cleavage by permanganate
In a KMnO4 hydroxylation, if the solution is warm or acidic or too concentrated, oxidative cleavage of the glycol may occur. Mixtures of Ketones and carboxylic acids are formed, depending on whether there are any oxidizable aldehydes in the initial fragments. A terminal = CH2 group is oxidized to CO2 and water.
General Reaction
e.g.
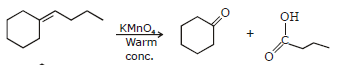
e.g
.
Ex.23 What is the main utility of this reaction and why is it superior to KMnO4cleavage for this purpose
Sol. It locates the position of C = C's in molecules. KMnO4 cleavage is more vigorous and can oxidiz other groups, i.e., OH.
Ex.24 Give the products of the following reactions : -
(i) (ii)
(iii)
Sol. X = Cis-1, 2-Cyclopentanediol Y = meso - CH3 - CHOH - CHOH - CH3
Z = rac - CH3CHOHCHOHCH3
(ii) Ozonolysls : Like permanganate ozone cleaves double bonds to give ketones and aldehydes. However, ozonolysis is milder, and both ketones and aldehydes can be recovered without further oxidation.
General Reaction
Mech.
e.g.
e.g. CH3CH2CHO CH3(CH2)4CHO (65%)
e.g.
(VI) HALOGENATION, ALLYLIC SUBSTITUTION
General Reaction
NBS = N-Bromosuccinimide
NCS = N-Chlorosuccinimide
e.g.
Ex.25 CH2 = CHCH2CH = CH2 (X), (X) is
(A) (B) CH2 = CHC = CHCH2Br
(C) CH2 = CHCH2CH = CHBr (D)
Ans. A
Ex.26 Assertion (A) : Propene (CH3CH = CH2) undergoes allylic substitution.
Reason (R) : CH2 = CHCH2 (allylic) free radical is stabilised by resonance.
Ans. (A)
Ex.27 Identify the product in the following reactions
(a) (b)
Ans. (a) (b)
Ex.28 Identify the products (x, y) of following reaction : -
Ans. (X) : (Y) :
(VII) ADDITION OF FREE RADICALS
General Reaction
e.g.
Ex.29 Which of the following reactions are correct ?
(a)
(b) RCH = CH2 BrCCl3
(A) only (a) (B) only (b) (C) both are correct (D) None of these
Ans. (C)
Ex.30 Isobutylene product is :
(A) Tertiary butyl bromide (B) Isobutyl bromide
(C) Tertiary butyl alcohol (D) Isobutyl alcohol
Ans. (B)
=============================================================
Alkynes (Properties and Nomenclature) - Hydrocarbons, CBSE, Class 11, Chemistry
Alkynes
1. Introduction
A triple bond gives an alkyne four fewer hydrogen atoms than the corresponding alkane. There fore the triple bond contributes two degree of unsaturation (DU).
Alkynes are not as common in nature as alkenes, but some plants do use alkynes to protect themselves against disease or predators. Acetylene is by far the most important commercial alkyne. Acetylene is an important industrial feedstock but its largest use is as the fuel for the oxyacetylene welding torch.
2. Structure and Bonding in Alkynes
(1) Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain carbon -carbon triple bond.
(2) Alkynes are also called acetylenes because they are derivatives of acetylene.
(3) The general formula is : CnH2n-2. (one triple bond)
(4) In alkyne C º C bond length is 1.20 Å.
(5) Its bond energy is 192 kcal. mol-1
(6) The hybridization of carbon atoms having triple bond (C º C) in alkynes is sp
(7) Overlapping of these sp hybrid orbitals with each other and with the hydrogen orbitals gives the sigma bond framework which is linear (180º) structure.
(8) Two p bonds result from overlap of the two remaining unhybridized p orbitals on each carbon atom. These orbitals overlap at right angles (90º) to each other, forming one p bond with electron density above and below the C - C sigma bond, and the other with electron density in front and in back of the sigma bond. This result in a cylindrical p electron cloud around s bonded structure
Note : Any type of stereoisomerism does not arise in acetylenic bond due to linearity of C º C bond.
Ex.1 Cis-trans isomerism is not possible in alkynes because of :
Ans. 180º bond-angle at the carbon-carbon triple bond.
Ex.2 Draw the geometrical isomers of hept -2-en-5-yne?
Ans.
3. Physical Properties of Alkynes
(1) Alkynes are relatively nonpolar (w.r.t. alkyl halides and alcohols) and are nearly insoluble in water (but they are more polar than alkenes and alkanes). They are quite soluble in most organic solvents, (acetone, ether, methylene chloride, chloroform and alcohols).
(2) Acetylene, propyne, and the butynes are gases at room temperature, just like the corresponding alkanes and alkenes. In fact, the boiling point of alkynes are nearly the same as those of alkanes and alkenes with same number of carbon atoms.
4. Table
5. TABLE - COMPARATIVE STUDY OF ALKANES, ALKENES, ALKYNES
Ex.3 Which has a longer carbon-methyl bond, 1-butyne or 2-butyne. Explain?
Ans. The bond from the methyl group in 1-butyne is to an sp3-hybridised carbon and so is longer than the bond from the methyl group in 2-butyne, which is to an sp-hybridised carbon.

Ex.4 Arrange the following bond-lengths in increasing order.
Ans. (d) < (b) < (c) < (e) < (a)
Q.3 Arrange C - H bond -lengths (a,b,g) in increasing order as shown : -
6. Laboratory test of Alkyne
7. Laboratory test of terminal alkynes
When triple bond comes at the end of a carbon chain. The alkyne is called a terminal alkyne.
1-Butyne, terminal alkyne
8. Acidity of Terminal Alkynes
Terminal alkynes are much acidic than other hydrocarbons due to more electronegative sp hybridised carbon. The polarity (acidity) of a C - H bond varies with its hydridization, increasing with the increase in precentage's character of the orbitals.
sp3 < sp2 < sp
The hydrogen bonded to the carbon of a terminal alkyne is considerably more acidic than those bonded to carbons of an alkene and alkane (see section). The pKa values for ethyne, ethene & ethane illustrate this point
pKa = 25 pKa=44 pKa=50
The order of basicity of their anions is opposite to that of their relative acidity:
Relative Basicity
CH3CH!2: > H2C = CH:- > HC º C:-
Relative acidity
pKa 15.7 16-17 25 38 44 50
Relative Basicity
9. General methods of preparation :
(I) By dehydro halogenation of gem and vic dihalide:
General Reaction: RCH = CHR + Br2 →
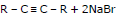
A vic - dibromide
The dehydrohalogenations occur in two steps, the first yielding a bromoalkene and the second alkyne.
Mechanism :
Step 1
Amide ion Vic-Dibromide Bromoalkene Ammonia Bromide
(The strongly ion
basic amide ion
brings about an
E2 reaction.)
Step 2
e.g. CH3CH2CH = CH2
CH3CH2C º CH
e.g.
[CH3CH2C º CH]
CH3CH2C º C!NaÅ
CH3CH2C º C:-Na CH3CH2C º CH NH3 NaCl
General Reaction
Ex.5 Give the structure of three isomeric dibromides that could be used as starting materials for the preparation of 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne.
Sol. (I) (II)
(III)
Ex.6 Show the product in the following reaction
? Sol.
Q.4 1,1-dibromopentane on reaction with fused KOH at 470 K gives 2-pentyne
1,1-dibromo pentane 2-pentyne
Give the mechanism of this rearrangement.
(II) By Dehalogenation of Tetrahaloalkane:
General Reaction
(III) Replacement of The Acetylenic Hydrogen atom of terminal Alkynes.
General Reaction
Sodium ethynide and other sodium alkynides can be prepared by treating terminal alkynes with sodium amide in liquid ammonia.
(R or R' or both may be hydrogen)
The following example illustrates this synthesis of higher alkyne homologues.
(R'-X must be an unhindered primary halide or tosylate)
The unshared electron pair of the alkynide ion attacks the back side of the carbon atom that bears the halogen atom and forms a bond to it. The halogen atom departs as a halide ion.
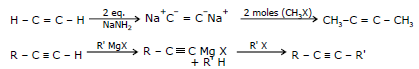
e.g.
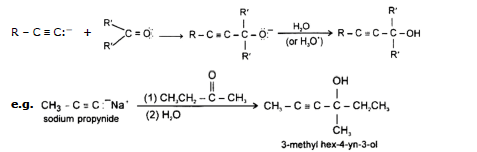
Addition of acetylide ions to carbonyl groups
e.g.
Sodium Propanal 1-Pentyn-3-ol
acetylide
e.g.
3-Methyl-1-butyne 4-Methyl-1-Phenyl pent-2-yne-1-ol
e.g.
Cyclohexanone 1-Ethynylcyclohexanol(3º)
Ex.7 Show how to synthesize 3-decyne from acetylene along with necessary alkyl halides.
Sol. H - C º C - H H3C - (CH2)5 - C º C - H
1-Octyne
H3C - (CH2)5 - C º C - H CH3 - (CH2)5 - C º C - CH2CH3
1-Octyne 3-Decyne
Q.5 Show how you would synthesize the following compound, beginning with acetylene and any necessary additional reagents.
(IV) By Kolble's Electrolytic synthesis.
(V) By Hydrolysis of carbides
CaC2 2HOH → C2H2 Ca(OH)2
MgC2 2HOH → C2H2 Mg(OH)2
Mg2C3 4HOH→ CH3 - C º CH 2Mg(OH)2
10. Chemical reactions of Alkyne
(I) Reduction to alkenes
(a) By Lindlar's reagent
General Reaction
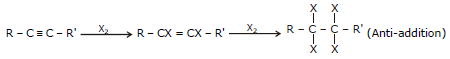
(b) By Brich reduction
General Reaction R - C º C - R' (anti addition)
e.g.
(c) By hydroboration reduction
General Reaction R - C º C - R'
Ex.8 Identify (X) and (Y) in the following reaction
CH3-CH2 - C º CH
Ans. (X) : (Y) :
(II) Addition of Halogen (X2=Cl2, Br2)
General Reaction R - C º C - R' R - CX = CX - R'
(Anti-addition)
Ex.9 Explain why alkynes are less reactive than alkenes toward addition of Br2.
Sol. The three memebered ring bromonium ion fromed from the alkyne (A) has a full double bond causing it to be more strained and less stable than the one from the alkene (B).
(A) (B)
(A) less stable than (B)
Also, the C's of A that are part of the bormonium ion have more s-character than those of B, further making A less stable than B.
(III) Addition of Hydrogen halides (Were HX = HCl, HBr, HI)
General Reaction R - C º C - R'
e.g.
e.g. CH3-C º C - CH2CH3 HBr →
e.g. H - C º C - CH2CH2CH3
Ex.10 Identify the product when one equivalent of HBr reacts with 1-pentene-4-yne
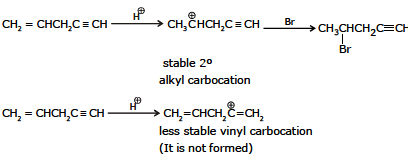
Ex.11 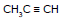
(X) + (Y)
Idntify (X) and (Y) in the above reaction.
Ans. After first HBr molecule is added, product is 2 : Second addition
3 and
. Since 2º carbocation ion is more stable than 1º, hence final product is
Y is CH3CH2CHBr2
(IV) Addition of water
(a) Mercuric ion catalyzed hydration:
General Reaction 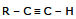 + H2O
+ H2O
(Martkovnikov rule) Vinyl alcohol Ketone
(unstable) (stable)
Electrophilic addition of mercuric ion gives a vinyl cation, which reacts with water and loses a proton to give an organomercurical alcohol. Under the acidic reaction condition, Hg is replaced by hydrogen to give a vinyl alcohol, callled an enol.
Mech.
e.g. 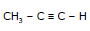 + H2O
+ H2O
Ex.12 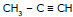 + H2O
+ H2O X
Identify the (X) in the above reaction
Sol. (X) = Acetone (a ketone) stable
Ex.13 When 2-heptyne was treated with aq. H2SO4 containing some HgSO4, two products, each having the moleuclar formual C7H14O, were obtained approximately in equal amounts. What are these two compounds?
Ans. 
Q.9 From which alkyne could each of the following compound be prepared by acid-catalysed hydration?
(a) (b)
(c)
(b) Hydroboration-oxidation
In alkyne, except that a hindered dialkylborane must be used to prevent addition of two molecules of borane across the triple bond.
General Reaction

Ex.14 Compare the results of hydroboration oxidation and mercuric ion-catalysed hydration for
(a) 2-butyne (b) Cyclohexyl-actylene
Ans.
(V) Formation of Alkylide anions (Alkynides)
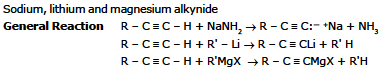
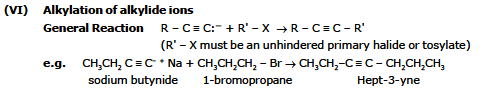
(VII) Reactions with Carbonyl Groups
General Reaction
Ex.15 Give the products of the following reactions.
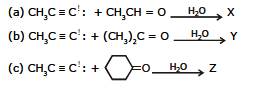
Sol. (a)
(b)
(c)
Q.10 What are the products of the following reactions:
(a) (b)
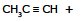
(c)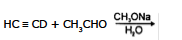
Q.11 Identify 'X' in the following reaction
(VIII) Oxidation of a-Dlketones
If an alkyne is treated with aqueous KMnO4 under nearly neutral conditions, an a-diketone results.
General Reaction
e.g.
Ex.16 Give the product of the following reactions.
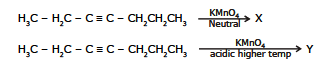
Sol. X = CH3CH2C - CCH2CH2CH3 Y = CH3CH2COOH HOOCCH2CH2CH3 || ||
O O
(α diketone)
(IX) Oxidative Cleavage
If the reaction mixture becomes warm or too basic the diketone undergoes oxidative cleavage. The products are the salts of carboxylic acids, which can be converted to the free acids by adding dilute acid.
General Reaction
e.g.
e.g.
Ex.17 Give the products of the following reactions
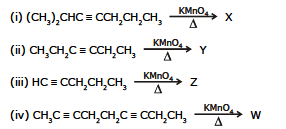
Sol. X: (CH3)2CHCOOH HOOCCH2CH2CH3
Y: 2CH3CH2COOH, symmetrical internal alkynes give one acid
Z: CH3COOH HOOCCH2CH2COOH HOOCCH2CH3
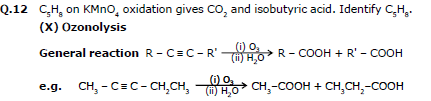
Ex.18 C8H10 (A) Acid (B) Identify (A) and (B) in the above reaction
Sol. (A) (B)
COOH
Ex.19 A certain hydrocarbon has the formula C16H26. Ozonation followed by hydrolysis gave CH3(CH2)4CO2 H and succinic acid as the only product. What is hydrocarbon
Sol. DU = 4
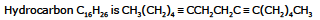
Solution Unsolved problems
1. It means there is chiral carbon, hence structure is
2. Alkyne  has unsaturation hence C5H8 has also one ring of three or four carbon atoms.
has unsaturation hence C5H8 has also one ring of three or four carbon atoms.
(a) (b)
(a) Exists as cis-and trans-isomer
(cis) (trans)
3 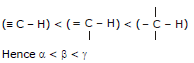
4. As the S-character of the orbital that binds carbon to another atom increases, the pair of electrons in that orbital is more strongly held and it requires more energy for homolytic cleavage of both the C - H and C - C bonds.
5. Mech.
6. We need to add two groups to acetylene and ethyl group and a six-carbon aldehyde (to form the secondary alcohol). If we formed the alcohol group first, the weakly acidic - OH group would interfere with the alkylation by the ethyl group. Therefore, we should add the less reactive ethyl group first, and add the alcohol group later in the synthesis.
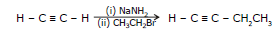
The ethyl group is not acidic and it does not interefere with the addition of the second group

Reason : Electron donating groups such as R's make the p-bond more electron - rich and more reactive. Conversely, electron - withdrawing groups such as halogens make the p-bond more electron-poor and less reactive.
7.
FAQs on Hydrocarbons, Class 11, Chemistry Detailed Chapter Notes
| 1. What are hydrocarbons? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes? |  |
| 3. What is the general formula for alkanes? |  |
| 4. How are hydrocarbons classified? |  |
| 5. What are the uses of hydrocarbons? |  |















