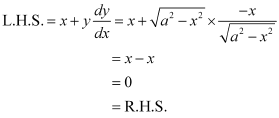Exercise 9.1
Q1: Determine order and degree(if defined) of differential equation 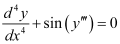
Ans:
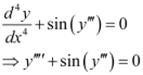
The highest order derivative present in the differential equation is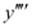 . Therefore, its order is four.
. Therefore, its order is four.
The given differential equation is not a polynomial equation in its derivatives. Hence, its degree is not defined.
Q2: Determine order and degree(if defined) of differential equation 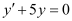
Ans: The given differential equation is:
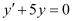
The highest order derivative present in the differential equation is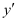 . Therefore, its order is one.
. Therefore, its order is one.
It is a polynomial equation in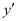 . The highest power raised to
. The highest power raised to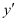 is 1. Hence, its degree is one.
is 1. Hence, its degree is one.
Q3: Determine order and degree(if defined) of differential equation 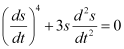
Ans:
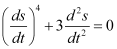
The highest order derivative present in the given differential equation is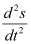 . Therefore, its order is two.
. Therefore, its order is two.
It is a polynomial equation in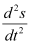 and
and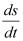 . The power raised to
. The power raised to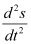 is 1.
is 1.
Hence, its degree is one.
Q4: Determine order and degree(if defined) of differential equation 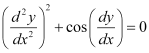
Ans:
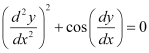
The highest order derivative present in the given differential equation is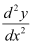 . Therefore, its order is 2.
. Therefore, its order is 2.
The given differential equation is not a polynomial equation in its derivatives. Hence, its degree is not defined.
Q5: Determine order and degree(if defined) of differential equation 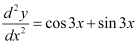
Ans:
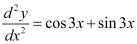
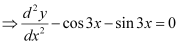
The highest order derivative present in the differential equation is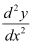 . Therefore, its order is two.
. Therefore, its order is two.
It is a polynomial equation in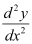 and the power raised to
and the power raised to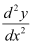 is 1.
is 1.
Hence, its degree is one.
Q6: Determine order and degree(if defined) of differential equation 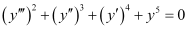
Ans: 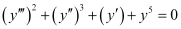
The highest order derivative present in the differential equation is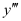 . Therefore, its order is three.
. Therefore, its order is three.
The given differential equation is a polynomial equation in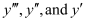 .
.
The highest power raised to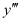 is 2. Hence, its degree is 2.
is 2. Hence, its degree is 2.
Q7: Determine order and degree(if defined) of differential equation 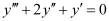
Ans: 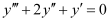
The highest order derivative present in the differential equation is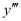 . Therefore, its order is three.
. Therefore, its order is three.
It is a polynomial equation in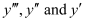 . The highest power raised to
. The highest power raised to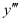 is 1. Hence, its degree is 1.
is 1. Hence, its degree is 1.
Q8: Determine order and degree(if defined) of differential equation 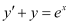
Ans:
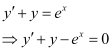
The highest order derivative present in the differential equation is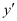 . Therefore, its order is one.
. Therefore, its order is one.
The given differential equation is a polynomial equation in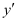 and the highest power raised to
and the highest power raised to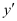 is one. Hence, its degree is one.
is one. Hence, its degree is one.
Q9: Determine order and degree(if defined) of differential equation 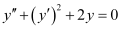
Ans: 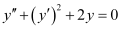
The highest order derivative present in the differential equation is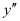 . Therefore, its order is two.
. Therefore, its order is two.
The given differential equation is a polynomial equation in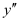 and
and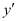 and the highest power raised to
and the highest power raised to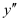 is one.
is one.
Hence, its degree is one.
Q10: Determine order and degree(if defined) of differential equation 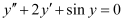
Ans: 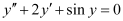
The highest order derivative present in the differential equation is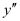 . Therefore, its order is two.
. Therefore, its order is two.
This is a polynomial equation in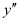 and
and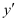 and the highest power raised to
and the highest power raised to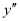 is one. Hence, its degree is one.
is one. Hence, its degree is one.
Q11: The degree of the differential equation 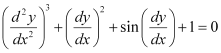 is
is
(A) 3
(B) 2
(C) 1
(D) not defined
Ans:
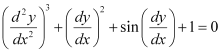
The given differential equation is not a polynomial equation in its derivatives. Therefore, its degree is not defined.
Hence, the correct answer is D.
Q12: The order of the differential equation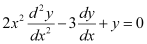 is
is
(A) 2
(B) 1
(C) 0
(D) not defined
Ans:
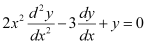
The highest order derivative present in the given differential equation is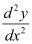 . Therefore, its order is two.
. Therefore, its order is two.
Hence, the correct answer is A.
Exercise 9.2
Q1: 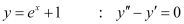
Ans:
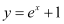
Differentiating both sides of this equation with respect to x, we get:

Now, differentiating equation (1) with respect to x, we get:
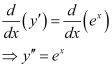
Substituting the values of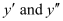 in the given differential equation, we get the L.H.S. as:
in the given differential equation, we get the L.H.S. as:
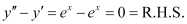
Thus, the given function is the solution of the corresponding differential equation.
Q2: 
Ans: 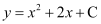
Differentiating both sides of this equation with respect to x, we get:
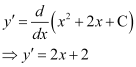
Substituting the value of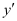 in the given differential equation, we get:
in the given differential equation, we get:
L.H.S. =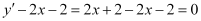 = R.H.S.
= R.H.S.
Hence, the given function is the solution of the corresponding differential equation.
Q3: 
Ans: 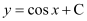
Differentiating both sides of this equation with respect to x, we get:
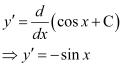
Substituting the value of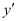 in the given differential equation, we get:
in the given differential equation, we get:
L.H.S. =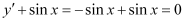 = R.H.S.
= R.H.S.
Hence, the given function is the solution of the corresponding differential equation.
Q4: 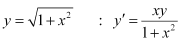
Ans:
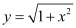
Differentiating both sides of the equation with respect to x, we get:
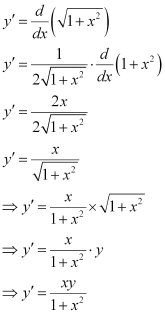
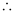 L.H.S. = R.H.S.
L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Hence, the given function is the solution of the corresponding differential equation.
Q5: 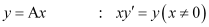
Ans: 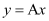
Differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get:
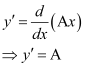
Substituting the value of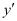 in the given differential equation, we get:
in the given differential equation, we get:
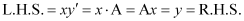
Hence, the given function is the solution of the corresponding differential equation.
Q6: 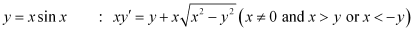
Ans: 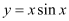
Differentiating both sides of this equation with respect to x, we get:
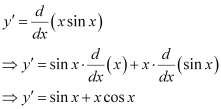
Substituting the value of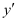 in the given differential equation, we get:
in the given differential equation, we get:
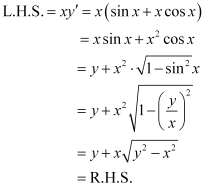
Hence, the given function is the solution of the corresponding differential equation.
Q7: 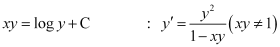
Ans: 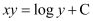
Differentiating both sides of this equation with respect to x, we get:
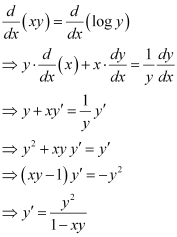
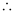 L.H.S. = R.H.S.
L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Hence, the given function is the solution of the corresponding differential equation.
Q8: 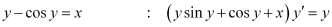
Ans: 
Differentiating both sides of the equation with respect to x, we get:
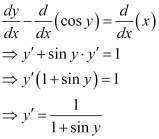
Substituting the value of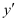 in equation (1), we get:
in equation (1), we get:
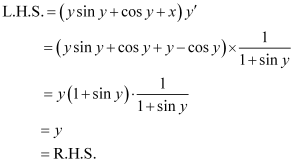
Hence, the given function is the solution of the corresponding differential equation.
Q9: 
Ans: 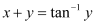
Differentiating both sides of this equation with respect to x, we get:
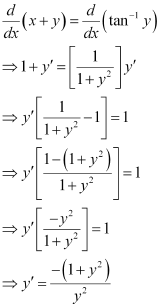
Substituting the value of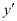 in the given differential equation, we get:
in the given differential equation, we get:
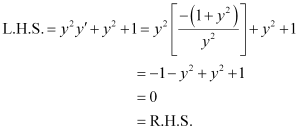
Hence, the given function is the solution of the corresponding differential equation.
Q10: 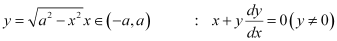
Ans: 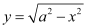
Differentiating both sides of this equation with respect to x, we get:
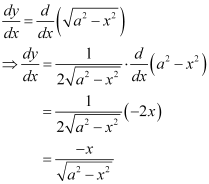
Substituting the value of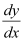 in the given differential equation, we get:
in the given differential equation, we get:
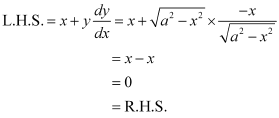
Hence, the given function is the solution of the corresponding differential equation.
Q11: The numbers of arbitrary constants in the general solution of a differential equation of fourth order are:
(A) 0
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
Ans: We know that the number of constants in the general solution of a differential equation of order n is equal to its order.
Therefore, the number of constants in the general equation of fourth order differential equation is four.
Hence, the correct answer is D.
Q12: The numbers of arbitrary constants in the particular solution of a differential equation of third order are:
(A) 3
(B) 2
(C) 1
(D) 0
Ans: In a particular solution of a differential equation, there are no arbitrary constants.
Hence, the correct answer is D.
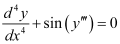
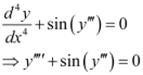
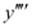 . Therefore, its order is four.
. Therefore, its order is four.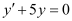
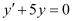
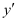 . Therefore, its order is one.
. Therefore, its order is one.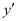 . The highest power raised to
. The highest power raised to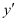 is 1. Hence, its degree is one.
is 1. Hence, its degree is one.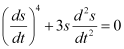
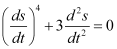
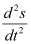 . Therefore, its order is two.
. Therefore, its order is two.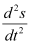 and
and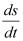 . The power raised to
. The power raised to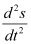 is 1.
is 1.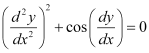
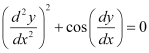
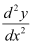 . Therefore, its order is 2.
. Therefore, its order is 2.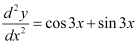
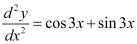
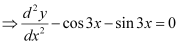
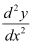 . Therefore, its order is two.
. Therefore, its order is two.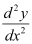 and the power raised to
and the power raised to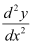 is 1.
is 1.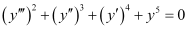
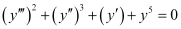
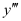 . Therefore, its order is three.
. Therefore, its order is three.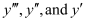 .
.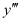 is 2. Hence, its degree is 2.
is 2. Hence, its degree is 2.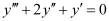
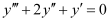
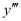 . Therefore, its order is three.
. Therefore, its order is three.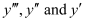 . The highest power raised to
. The highest power raised to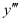 is 1. Hence, its degree is 1.
is 1. Hence, its degree is 1.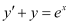
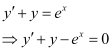
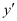 . Therefore, its order is one.
. Therefore, its order is one.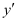 and the highest power raised to
and the highest power raised to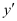 is one. Hence, its degree is one.
is one. Hence, its degree is one.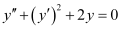
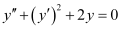
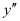 . Therefore, its order is two.
. Therefore, its order is two.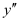 and
and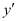 and the highest power raised to
and the highest power raised to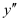 is one.
is one.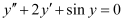
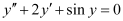
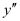 . Therefore, its order is two.
. Therefore, its order is two.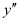 and
and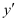 and the highest power raised to
and the highest power raised to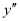 is one. Hence, its degree is one.
is one. Hence, its degree is one.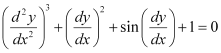 is
is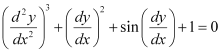
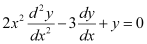 is
is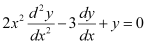
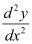 . Therefore, its order is two.
. Therefore, its order is two.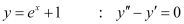
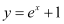

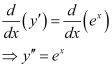
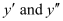 in the given differential equation, we get the L.H.S. as:
in the given differential equation, we get the L.H.S. as: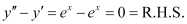

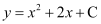
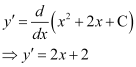
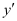 in the given differential equation, we get:
in the given differential equation, we get: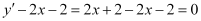 = R.H.S.
= R.H.S.
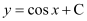
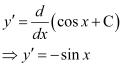
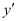 in the given differential equation, we get:
in the given differential equation, we get: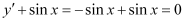 = R.H.S.
= R.H.S.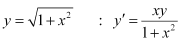
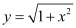
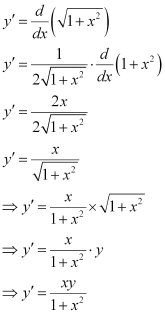
 L.H.S. = R.H.S.
L.H.S. = R.H.S.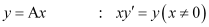
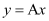
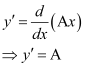
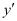 in the given differential equation, we get:
in the given differential equation, we get: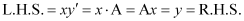
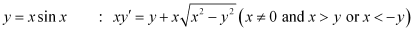
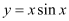
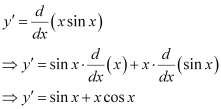
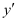 in the given differential equation, we get:
in the given differential equation, we get: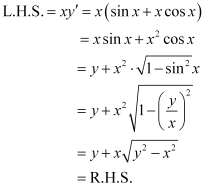
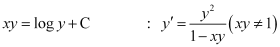
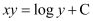
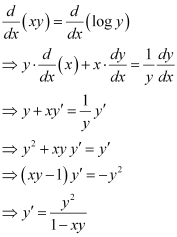
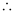 L.H.S. = R.H.S.
L.H.S. = R.H.S.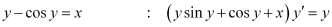

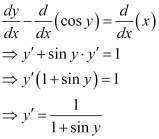
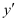 in equation (1), we get:
in equation (1), we get: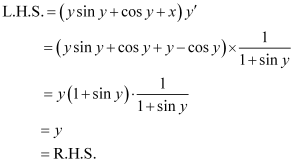

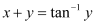
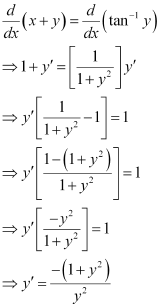
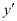 in the given differential equation, we get:
in the given differential equation, we get: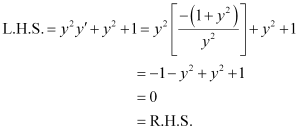
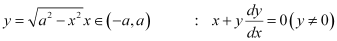
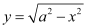
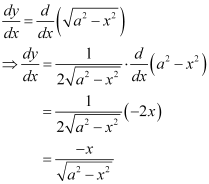
 in the given differential equation, we get:
in the given differential equation, we get: