NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 - Application of Derivative
Exercise 6.1
Q1: Find the rate of change of the area of a circle with respect to its radius r when
(a) r = 3 cm
(b) r = 4 cm
Ans: - The area of a circle (A)with radius (r) is given by,
Now. the rate of change of the area with respect to its radius is given by.
When r = 3 cm,
dA/dr = 2π(3) = 6π
Hence, the area of the circle is changing at the rate of 6n cm when its radius is 3 cm.
When r = 4 cm.
dA/dr = 2π(4) = 8π
Hence, the area of the circle is changing at the rate of 8π cm when its radius is 4 cm.
Q2: The volume of a cube is increasing at the rate of 8 cm3/s. How fast is the surface area increasing when the length of an edge is 12 cm?
Ans: Let x be the length of a side, V be the volume, and s be the surface area of the cube.
Then. V = x3 and S = 6x, where x is a function of time t.
It is given that (dV/dt) -8 cm3/s
Then, by using the chain rule, we have:
Hence, if the length of the edge of the cube is 12 cm, then the surface area is increasing at the rate of 8/3 cm2/s.
Q3: The radius of a circle is increasing uniformly at the rate of 3 cm/s. Find the rate at which the area of the circle is increasing when the radius is 10 cm.
Ans: The area of a circle (A) with radius (r) is given by,
A = πr2
Now, the rate of change of area (A) with respect to time (t) is given by, [By chain rule]
It is given that,
dr/dt = 3cm/s
∴ dA/dt = 2πr(3) = 6πr
Thus, when r = 10 cm,
dA/dt = 6π(10) = 60π cm2/s
Q4: An edge of a variable cube is increasing at the rate of 3 cm/s. How fast is the volume of the cube increasing when the edge is 10 cm long?
Ans: Let x be the length of a side and V be the volume of the cube. Then,
It is given that,
dx/dt = 3cm/s
∴ dV/dt = 3x2 (3) = 9x2
Thus, when x = 10 cm,
dV/dt = 9(10)2 = 900cm3/s
Hence, the volume of the cube is increasing at the rate of 900 cm3/s when the edge is 10 cm long.
Q5: A stone is dropped into a quiet lake and waves move in circles at the speed of 5 cm/s. At the instant when the radius of the circular wave is 8 cm, how fast is the enclosed area increasing?
Ans: The area of a circle (A) with radius (r) is given by
Therefore, the rate of change of area (A) with respect to time (t) is given by, [By chain rule]
It is given that, dr/dt = 5 cm/s
Thus, when r = 8 cm,
dA/dt = 2π (8) (5) = 80π
Hence, when the radius of the circular wave is 8 cm, the enclosed area is increasing at the rate of 80π cm2/s.
Q6: The radius of a circle is increasing at the rate of 0.7 cm/s. What is the rate of increase of its circumference?
Ans: The circumference of a circle (C) with radius (r) is given by
C= = 2πr.
Therefore, the rate of change of circumference (C) with respect to time (t) is given by.
It is given that dr/dt = 0.7 cm/s
Hence, the rate of increase of the circumference is 2π (0.7) = 1.4π cm/s.
Q7: The length x of a rectangle is decreasing at the rate of 5 cm/minute and the width y is increasing at the rate of 4 cm/minute. When x = 8 cm and y = 6 cm, find the rates of change of (a) the perimeter, and (b) the area of the rectangle.
Ans: Since the length (x) is decreasing at the rate of 5 cm/minute and the width (y) is increasing at the rate of 4 cm/minute, we have:
dx/dt = -5 cm/min and dy/dt = 4 cm/min
(a) The perimeter (Pi of a rectangle is given by.
P = 2(x+y)
(b) The area (A) of a rectangle is given by,
A = x.y
When x = 8 cm andy = 6 cm.
dA/dt = (-5 x 6 +4 x 8) cm2/ min = 2 cm2 / min
Q8: A balloon, which always remains spherical on inflation, is being inflated by pumping in 900 cubic centimetres of gas per second. Find the rate at which the radius of the balloon increases when the radius is 15 cm.
Ans: The volume of a sphere (V) with radius (r) is given by,
V = 4/3πr3
∴ The rate of change of volume (F) with respect to time (t) is given by.
Therefore, when radius =15 cm.
Hence, the rate at which the radius of the balloon increases when the radius is 15 cm is 1/π cm/s.
Q9: A balloon, which always remains spherical, has a variable radius. Find the rate at which its volume is increasing with the radius when the latter is 10 cm.
Ans: The volume of a sphere (V) with radius (r) is given by V = 4/3 πr2
The rate of change of volume (V) with respect to its radius (r) is given by
Therefore, when radius =10 cm.
dV/dr = 4π(10)2 = 400π
Hence, the volume of the balloon is increasing at the rate of 400π cm3/s.
Q10: A ladder 5 m long is leaning against a wall. The bottom of the ladder is pulled along the ground, away from the wall, at the rate of 2 cm/s. How fast is its height on the wall decreasing when the foot of the ladder is 4 m away from the wall?
Ans: Let y m be the height of the wall at which the ladder touches. Also, let the foot of the ladder be x m away from the wall.
Then, by Pythagoras' theorem, we have:
x2 + y2 = 25 [Length of the ladder = 5 m]
Then, the rate of change of height (y) with respect to time (t) is given by.
Now., when x = 4 m. we have: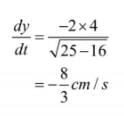 Hence, the height of the ladder on the wall is decreasing at the rate of 8/3 cm/s.
Hence, the height of the ladder on the wall is decreasing at the rate of 8/3 cm/s.
Q11: A particle moves along the curve . Find the points on the curve at which the y-coordinate is changing 8 times as fast as the x-coordinate.
Ans: The equation of the curve is given as:
The rate of change of the position of the particle with respect to time (t) is given by.
When the y-coordinate of the particle changes 8 times as fast as the
x-coordinate i.e., , we have:
When
When
Hence, the points required on the curve are (4,11) and
Q12: The radius of an air bubble is increasing at the rate of ½ cm/s. At which rate is the volume of the bubble increasing when the radius is 1 cm?
Ans: The air bubble is in the shape of a sphere.
Now, the volume of an air bubble (V) with radius (r) is given by,
V = 4/3πr3
The rate of change of volume (V) with respect to time (t) is given by..[By chain rule]
It is given that dr/dt = 1/2 cm/s
Therefore , when r = 1 cm,
Hence, the rate at which the volume of the bubble increases is 2π cm3/s.
Q13: A balloon, which always remains spherical, has a variable diameter 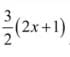 . Find the rate of change of its volume with respect to x.
. Find the rate of change of its volume with respect to x.
Ans: The volume of a sphere (V) with radius (r) is given by,
V = 4/3πr3
It is given that:
Diameter
Hence, the rate of change of volume with respect to x is as
Q14: Sand is pouring from a pipe at the rate of 12 cm3/s. The falling sand forms a cone on the ground in such a way that the height of the cone is always one-sixth of the radius of the base. How fast is the height of the sand cone increasing when the height is 4 cm?
Ans: The volume of a cone (V) with radius (r) and height (h) is given by,
V = 1/3πr2h
It is riven that.
h= 1/6r = r=6h
∴ V = 1/3π(6h)2h = 12πh3
The rate of change of volume with respect to time (t) is given by.
It is also given that
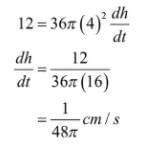
Q15: The total cost C (x) in Rupees associated with the production of x units of an item is given by C (x) = 0.007x3 - 0.003x2 +15x + 4000
Find the marginal cost when 17 units are produced.
Ans: Marginal cost is the rate of change of total cost with respect to output.
∴ Marginal cost (MC)
= 0.021x2 - 0.006x + 15
When x = 17, MC = 0.021 (172)- 0.006 (17) + 15
= 0.021(289)-0.006(17)+ 15
= 6.069- 0.102+ 15
= 20.967
Hence, when 17 units are produced, the marginal cost is Rs. 20.967.
Q16: The total revenue in Rupees received from the sale of x units of a product is given by R(x) = 13x2 26x 15
Find the marginal revenue when x = 7.
Ans: Marginal revenue is the rate of change of total revenue with respect to the number of units sold.
∴ Marginal Revenue (MR) = dR/dx = 13(2x) +26 = 26x+26
When x = 73
MR = 26(7) + 26 = 182 + 26 = 208
Hence, the required marginal revenue is Rs 208.
Q17: The rate of change of the area of a circle with respect to its radius r at r = 6 cm is
(A) 10π (B) 12π (C) 8π (D) 11π
Ans: The area of a circle (A) with radius (r) is given by,
A = πr2
Therefore, the rate of change of the area with respect to its radius r is
Hence, the required rate of change of the area of a circle is 12π cm;. s.
The correct answer is B.
Q18: The total revenue in Rupees received from the sale of x units of a product is given by
R(x) = 3x2 + 36x + 5. The marginal revenue, when x=15 is
(A) 116 (B) 96 (C) 90 (D) 126
Ans: Marginal revenue is the rate of change of total revenue with respect to the number of units sold.
∴ Marginal Revenue (MR)= dR/dx= 3(2x) + 36 = 6x + 36
∴ When x = 15,
MR = 6(15) + 36 = 90 + 36 = 126
Hence, the required marginal revenue is Rs 126.
The correct answer is D.
Exercise 6.2
Q1: Show that the function given by f(x) = 3x 17 is strictly increasing on R.
Ans: Let be any two numbers in R.
Then, we have:
Let x1 and x2 be any two numbers in R.
Then, we have: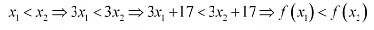 Hence, f is strictly increasing on R.
Hence, f is strictly increasing on R.
Q2: Show that the function given by/(x) = e2x is strictly increasing on R.
Ans: Let x1 and x2 be any two numbers in R.
Then, we have: 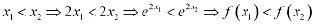 Hence, f is strictly increasing on R.
Hence, f is strictly increasing on R.
Q3: Show that the function given by f(x) = sin x is
(a) strictly increasing in  (b) strictly decreasing in
(b) strictly decreasing in 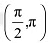 (c) neither increasing nor decreasing in (0, π)
(c) neither increasing nor decreasing in (0, π)
Ans: The given function is f(x) = sinx.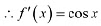 (a) Since for each
(a) Since for each 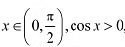 we have
we have 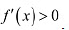 Hence, f is strictly increasing in
Hence, f is strictly increasing in 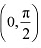
(b) Since for each 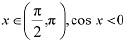 , we have
, we have 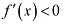
Hence, f is strictly decreasing in 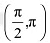
(c) From the results obtained in (a) & (b), it is clear that f is neither increasing nor decreasing in (0, π)
Q4: Find the intervals in which the function f given by f(x) = 2x2 − 3x is
(a) strictly increasing
(b) strictly decreasing
Ans: The given function is f(x) = 2x2 - 3x.
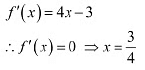 Now, the point 3/4 divides the real line into two disjoint intervals, i.e.,
Now, the point 3/4 divides the real line into two disjoint intervals, i.e.,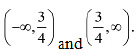
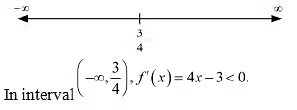 Hence, the given function (f) is strictly decreasing in the interval
Hence, the given function (f) is strictly decreasing in the interval 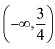 In interval
In interval 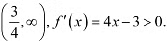 Hence, the given function (J) is strictly increasing in the interval
Hence, the given function (J) is strictly increasing in the interval 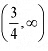 Q5: Find the intervals in which the function/given by/x) = 2x3 - 3x2 - 36x+ 7 is
Q5: Find the intervals in which the function/given by/x) = 2x3 - 3x2 - 36x+ 7 is
(a) strictly increasing
(b) strictly decreasing
Ans: The given function is 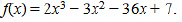
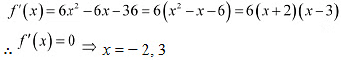 The points x = -2 and x = 3 divide the real line into three disjoint intervals, i.e.,
The points x = -2 and x = 3 divide the real line into three disjoint intervals, i.e.,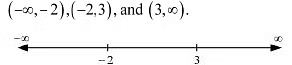 In intervals (-∞, -2) and (3, ∞) , f'(x) is positive while in interval (-2,3), f'(x) is negative.Hence, the given function (f) is strictly increasing in intervals (-∞, -2) and (3, ∞), while fthe unction if) is strictly decreasing in the interval (-2,3).
In intervals (-∞, -2) and (3, ∞) , f'(x) is positive while in interval (-2,3), f'(x) is negative.Hence, the given function (f) is strictly increasing in intervals (-∞, -2) and (3, ∞), while fthe unction if) is strictly decreasing in the interval (-2,3).
Q6: Find the intervals in which the following functions are strictly increasing or decreasing:
(a) x2 + 2x- 5
(b) 10 - 6x— 2x2
(c) -2x3 - 9x2 - 12x+ 1
(d) 6 - 9x -x2
(e) (x + 1)3 (x — 3)3
Ans: (a) We have,
f(x) = x2 +2x-5
∴ f'(x) = 2x+2
Now,
f'(x) = 0 ⇒ x = -1
Point x = -1 divides the real line into two disjoint. intervals i.e.. (-∞, -1) and (-1, ∞)
In interval 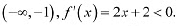
∴ f is strictly decreasing in interval (-∞, -1).Thus, f is strictly decreasing for x < -1.
In interval 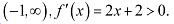
∴ f is strictly increasing in interval (-1, ∞). Thus, f is strictly decreasing for x < - 1.
(b) We have,
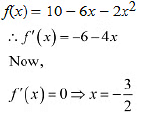 The point x = -3/2 divides the real line into two disjoint intervals i.e., (-∞, -3/2) and (-3/2, ∞). In interval (-∞, -3/2) i.e., when x < -3/2, f'(x) = - 6 - 4x < 0
The point x = -3/2 divides the real line into two disjoint intervals i.e., (-∞, -3/2) and (-3/2, ∞). In interval (-∞, -3/2) i.e., when x < -3/2, f'(x) = - 6 - 4x < 0
∴ f is strictly increasing for x< -3/2
In interval (-3/2, ∞) i.e , when x > -3/2, f'(x) = -6-4x<0
∴ f is strictly decreasing for x> -3/2
(c) We have
f(x) = -2x3 - 9x2 - 12x +1
∴ f'(x) = -6x2 - 18x - 12 = -6(x2+3x+2) = -6(x+1)(x+2)
Now,
f'(x) = 0 ⇒ x = -1 and x = -2
Points x = - 1 and x = -2 divide the real line into three disjoint intervals i.e...
(-∞, -2),(-2, -1) and (-1, ∞)
In intervals (-∞, -2) and (-1, ∞) he., when x < - 2 and x > - 1,
f'(x) = -6(x+1)(x+2) < 0
∴ f is strictly de ere as ing for x < - 2 and x > -1.
Now, in interval (-2, -1) i.e.. when - 2 < x < - 1.
f'(x) = -6(x+1)(x+2) > 0
∴ f is strictly increasing for 2 < x < 1
(d) We have.
f(x) = 6-9x = x2
∴ f'(x) = -9 -2x
Now, f'
(x) = 0 gives x = -9/2
The point x = -9/2 divides the real line into two disjoint intervals i.e., (-∞, -9/2) and (-9/2,∞ )
In interval (-∞, -9/2) i.e., for 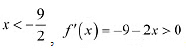 ∴ f is strictly increasing for x < -9/2In interval (-9/2,∞ ) i.e. for
∴ f is strictly increasing for x < -9/2In interval (-9/2,∞ ) i.e. for 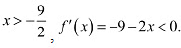 ∴ f is strictly decreasing for
∴ f is strictly decreasing for 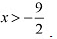 (e) We have.f(x) = (x+1)3 (x-3)3
(e) We have.f(x) = (x+1)3 (x-3)3
f'(x) = 3(x+1)2(x-3)3 +3(x-3)2 (x+1)3
= 3(x+1)2(x-3)2 [x-3+x+1]
=3(x+1)2(x-3)2(2x-2)
=6 (x+1)2(x-3)2 (x-1)
The points x = -1,x = 1. and x = 3 divide the real line into four disjoint intervals i.e., (-∞, -1) (-1,1), (1,3), and (3, ∞)
In intervals (-∞, -1) and (-1,1), f'(x) = 6(x+1)2(x-3)2(x-1) <0
∴ f is strictly decreasing in intervals (-∞, -1) and (-1,1)
In intervals 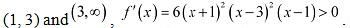 ∴ f is strictly increasing in intervals (1,3), and (3, ∞)
∴ f is strictly increasing in intervals (1,3), and (3, ∞)
Q7: Show that 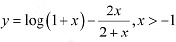 , is an increasing function of x throughout its domain.Ans: We have.
, is an increasing function of x throughout its domain.Ans: We have.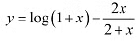
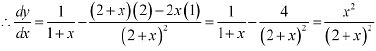
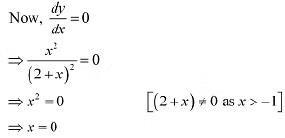 Since x > - 1. point x =0 divides the domain (-1 ∞) in two disjoint intervals i.e.. -1 < x < 0 & x > 0.When -1 < x < 0. we have:
Since x > - 1. point x =0 divides the domain (-1 ∞) in two disjoint intervals i.e.. -1 < x < 0 & x > 0.When -1 < x < 0. we have: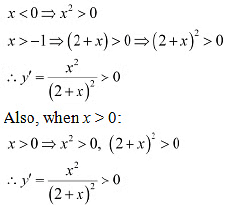 Hence, function f is increasing throughout this domain.
Hence, function f is increasing throughout this domain.
Q8: Find the values of x for which y = [x(x-2)]2 is an increasing function.
Ans: We have.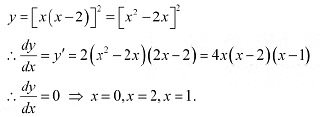 The points x = 0.x = 1. andx = 2 divide the real line into four disjoint intervals
The points x = 0.x = 1. andx = 2 divide the real line into four disjoint intervals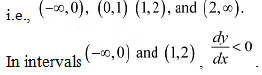 ∴ y is strictly decreasing in intervals (-∞ , 0) and (1,2). However, in intervals (0, 1) and (2, ∞), dy/dx > 0
∴ y is strictly decreasing in intervals (-∞ , 0) and (1,2). However, in intervals (0, 1) and (2, ∞), dy/dx > 0
∴ y is strictly increasing in intervals (0,1) and (2, ∞).
∴ y is strictly increasing for 0 < x < 1 and x > 2.
Q9: Prove that 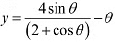 is an increasing function of θ in [0, π/2]
is an increasing function of θ in [0, π/2]
Ans: We have.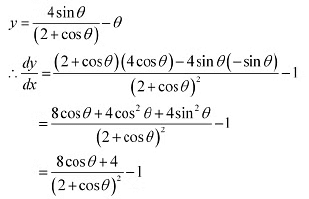
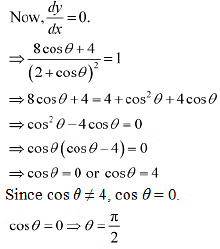
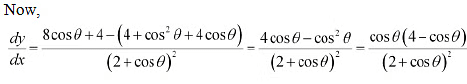 In interval
In interval 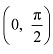 We have cos
We have cos 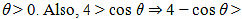
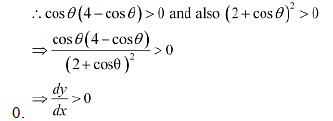 Tli ere fore.}' is strictly increasing in interval (0, π/2)Also, the given function is continuous at x=0 and x = π/2
Tli ere fore.}' is strictly increasing in interval (0, π/2)Also, the given function is continuous at x=0 and x = π/2
Hence, it is increasing in interval [0, π/2].
Q10: Prove that the logarithmic function is strictly increasing on (0, ∞).
Ans: The given function is f (x) = log x.
∴ f'(x) = 1/x
It is clear that for x > 0, f'(x) = 1/x >0 .
Hence, f(x) = log x is strictly increasing in interval (0;∞).
Q11: Prove that the function/given by f(x) = x2 - x + 1 is neither strictly increasing nor strictly decreasing on (-1, 1).
Ans: The given function is f(x) = x2 - x + 1.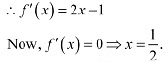 The point 1/2 divides the interval (-1, 1) into two disjoint intervals, i.e..
The point 1/2 divides the interval (-1, 1) into two disjoint intervals, i.e.. 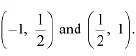 Now, in interval
Now, in interval 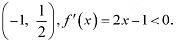 Therefore, f is strictly decreasing in interval (-1, 1/2). However, in interval
Therefore, f is strictly decreasing in interval (-1, 1/2). However, in interval 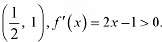 Therefore, f is strictly increasing in interval (1/2,1). Hence. f is neither strictly increasing nor decreasing in interval (-1.1).
Therefore, f is strictly increasing in interval (1/2,1). Hence. f is neither strictly increasing nor decreasing in interval (-1.1).
Q12: Which of the following functions are strictly decreasing on (0,π/2) ?
(A) cos x
(B) cos2x
(C) cos 3x
(D) tan x
Ans: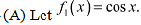
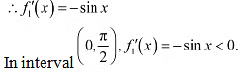 Thus, cosx is strictly decreasing in the interval
Thus, cosx is strictly decreasing in the interval 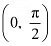
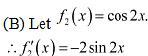
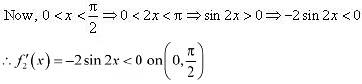
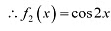 is strictly decreasing in interval
is strictly decreasing in interval 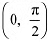
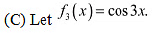
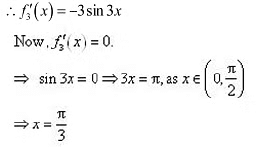 The point
The point 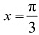 divides the interval
divides the interval 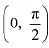 into two disjoint intervals i.e.,
into two disjoint intervals i.e., 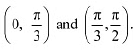
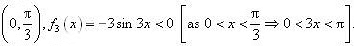 f3 is strictly decreasing in interval
f3 is strictly decreasing in interval 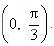 However, in interval
However, in interval 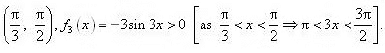 ∴ f3 is strictly increasing in the interval
∴ f3 is strictly increasing in the interval 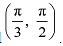 Hence, f3 is neither increasing nor decreasing in the interval
Hence, f3 is neither increasing nor decreasing in the interval 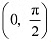 .
. 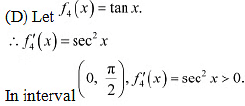 ∴ f4 is strictly increasing in the interval
∴ f4 is strictly increasing in the interval 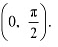 Therefore, functions cos x and cos 2x are strictly decreasing in
Therefore, functions cos x and cos 2x are strictly decreasing in 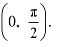 Hence, the correct answers are A and B.
Hence, the correct answers are A and B.Question 13: On which of the following intervals is the function f given by
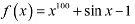 strictly decreasing?
strictly decreasing?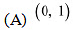
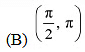
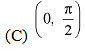 (D) ) None of theseAns: We have,
(D) ) None of theseAns: We have,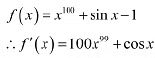 In interval
In interval 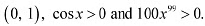
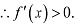 Thus, function fis strictly increasing in interval (0,1).In interval
Thus, function fis strictly increasing in interval (0,1).In interval 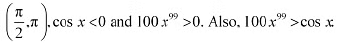
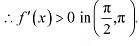 Thus, function f is strictly increasing in interval
Thus, function f is strictly increasing in interval 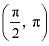
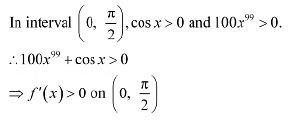 ∴ f is strictly increasing in interval
∴ f is strictly increasing in interval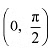 .Hence, function f is strictly decreasing in none of the intervals.
.Hence, function f is strictly decreasing in none of the intervals.The correct answer is D.
Q14: Find the least value of a such that the function f given f(x) = x2 + ax+ 1 is strictly increasing on (1, 2).
Ans: We have
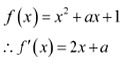 Now, function f will be increasing in
Now, function f will be increasing in 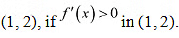
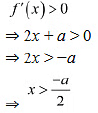 Therefore, we have to find the least value of a such that
Therefore, we have to find the least value of a such that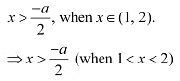 Thus, the least value of a for/to be increasing on (1? 2) is given by.-a/2 =1
Thus, the least value of a for/to be increasing on (1? 2) is given by.-a/2 =1-a/2 =1 ⇒ a = -2
Hence, the required value of a is -2.
Q15: Let I be any interval disjoint from (−1, 1). Prove that the function f given by f(x) = x 1/x. is strictly increasing on I.
Ans: We have,
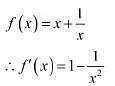
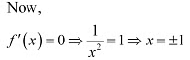 The points x = 1 andx = -1 divide the real line in three disjoint intervals i.e.,
The points x = 1 andx = -1 divide the real line in three disjoint intervals i.e., 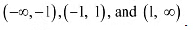 In interval (-1,1). it is observed that:
In interval (-1,1). it is observed that: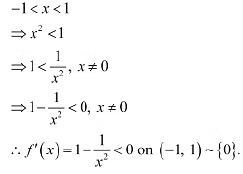 In intervals
In intervals 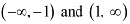 , it is observed that:
, it is observed that: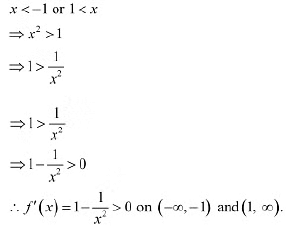 ∴ f is strictly increasing on (-∞, 1) and (1, ∞)
∴ f is strictly increasing on (-∞, 1) and (1, ∞)Q16: Prove that the function f given by f(x) = log sin x is strictly increasing on (0,π/2) and strictly decreasing on (π/2, π)
Ans:-
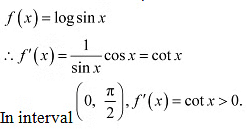 In interval
In interval 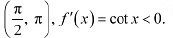 ∴ f is strictly decreasing in
∴ f is strictly decreasing in 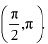 Q17: Prove that the function f given by f (x) = log cos x is strictly decreasing on
Q17: Prove that the function f given by f (x) = log cos x is strictly decreasing on 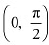 and strictly increasing on
and strictly increasing on 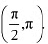
Ans: We have,
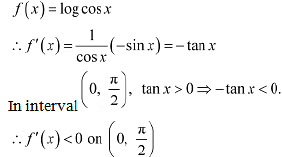 ∴ f is strictly decreasing on
∴ f is strictly decreasing on 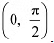 In interval
In interval 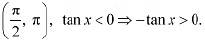
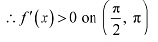 ∴ f is strictly increasing on
∴ f is strictly increasing on 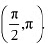
Q18: Prove that the function given by
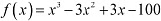 is increasing in R.ANS: We have,
is increasing in R.ANS: We have,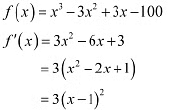
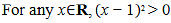 Thus, f'(x) is always positive in R.Hence, the given function (f) is increasing in R.
Thus, f'(x) is always positive in R.Hence, the given function (f) is increasing in R.Q19: The interval in which y= x2 e-x is increasing is
(A) (-∞,∞)
(B) (-2,0)
(C) (2,∞)
(D) (0,2)
Ans: We have.
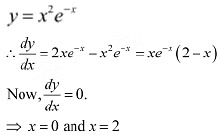 The points x = 0 and x = 2 divide the real line into three disjoint intervals i.e.;
The points x = 0 and x = 2 divide the real line into three disjoint intervals i.e.;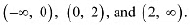 In intervals
In intervals 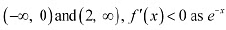 is always positive.∴ f is decreasing on (-∞,0) and (2, ∞)In interval (0,2),
is always positive.∴ f is decreasing on (-∞,0) and (2, ∞)In interval (0,2), 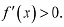 ∴ f is strictly increasing on (0.2).Hence f is strictly increasing in interval (0,2).
∴ f is strictly increasing on (0.2).Hence f is strictly increasing in interval (0,2).The correct answer is D.
Exercise 6.3
Q1: Find the maximum and minimum values,, if any, of the following functions given by
(i) f(x) =(2x- 1)2+ 3
(ii) f(x) = 9x2 + 12x+2
(iii) f(x) = -(x - 1)2+ 10
(iv) g(x) = x3 + 1
Ans: (i) The given function is f(x) = (2x- 1)2 + 3.
It can be observed that (2x- 1)2 > 0 for every x ∈ R.
There fore ,f(x)= (2x - 1)2 + 3 > 3 for every x ∈ R.
The minimum value of/is attained when 2x - 1 = 0.
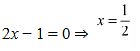
∴ Minimum value of 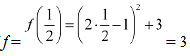
Hence, function f does not have a maximum value.
(ii) The given function is f(x) = 9x2 + 12x + 2 = (3x+2)2- 2.
It can be observed that (3x+2)2 > 0 for every x ∈ R.
There fore f = (2x - 1)2 + 3 > 3 for every x ∈ R.
The minimum value of fis attained when 2x - 1 = 0.
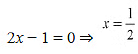
∴ Minimum value of 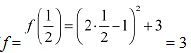
Hence, function f does not have a maximum value.
(ii) The given function is f(x) = 9x2 + 12x + 2 = (3x + 2)2 - 2
It can be observed that (3x + 2)2 > 0 for every x ∈ R.
Therefore, f(x) = (3x + 2)2 − 2 ≥ −2 for every x ∈ R.
The minimum value of f is attained when 3x + 2 = 0.
Hence, function f does not have a maximum value.
(iii) The given function is f(x) = − (x − 1)2 10.
It can be observed that (x − 1)2 ≥ 0 for every x ∈ R.
Therefore, f(x) = − (x − 1)2 10 ≤ 10 for every x ∈ R.
The maximum value of f is attained when (x − 1) = 0.
(x − 1) = 0 ⇒ x = 0
∴ Maximum value of f = f(1) = − (1 − 1)2 10 = 10
Hence, function f does not have a minimum value.
(iv) The given function is g(x) = x3 1.
Hence, function g neither has a maximum value nor a minimum value.
Q2: Find the maximum and minimum values, if any, of the following functions given by
(i) f(x) = |x + 2| − 1
(ii) g(x) = − |x + 1| + 3
(iii) h(x) = sin(2x) 5
(iv) f(x) = |sin 4x + 3|
(v) h(x) = x +1, x ∈ (−1, 1)
Ans : 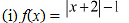
We know that 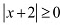 for every x ∈ R.Therefore,
for every x ∈ R.Therefore, 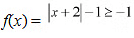 for every x ∈ R.
for every x ∈ R.
The minimum value of/is attained when 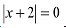
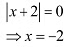
∴ Minimum value of 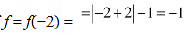
Hence: function f does not have a maximum value.
(ii) 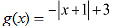 We know that
We know that 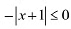 for every x ∈ R.Therefore,
for every x ∈ R.Therefore, 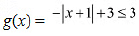 for every x ∈ R.
for every x ∈ R.
The maximum value of g is attained when 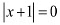
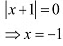
∴ Maximum value of g = g(-1) 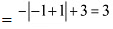
Hence, function g does not have a minimum value.
(iii)h(x) = sin2x+ 5
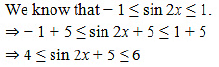
Hence, the maximum and minimum values of h are 6 and 4 respectively.
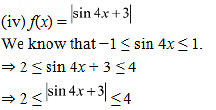
Hence, the maximum and minimum values of f are 4 and 2 respectively.
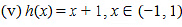
Here, if a point x0 is closest to 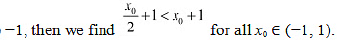
Also, if x1 is closest to 1. then 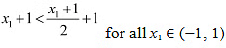
Hence, function h(x) has neither maximum nor minimum value in (-1. 1).
Q3: Find the local maxima and local minima,, if any, of the following functions. Find also the local maximum and the local minimum values, as the case may be: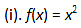
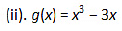
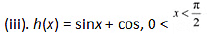
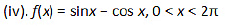
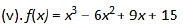
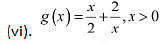
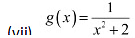
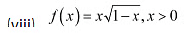
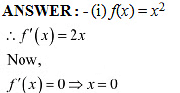
Thus.x = 0 is the only critical point which could possibly be the point of local maxima or local minima of f.
We have f''(0) = 2 which is positive.
Therefore, by second derivative test.x = 0 is a point of local minima and local minimum value of f at x = 0 is f (0) = 0.
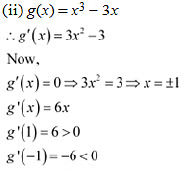
By second derivative test. x= 1 is a point of local minima and local minimum value ofg atr = 1 is g(l) = l3 - 3 = 1 - 3 = -2.
However. x = -1 is a point of local maxima and local maximum value of g at
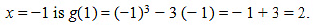
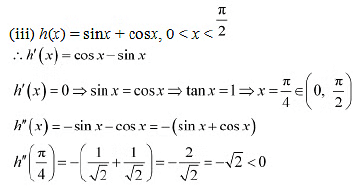
Therefore, by second derivative test. 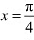 is a point: of local maxima and the local maximum value
is a point: of local maxima and the local maximum value
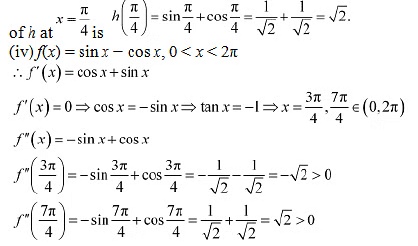
Therefore, by second derivative test, 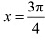 is a point of local maxima and the local maximum value of
is a point of local maxima and the local maximum value of 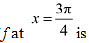
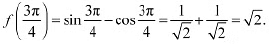 However,
However, 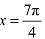 is a point of local minima and the local minimum value of f at
is a point of local minima and the local minimum value of f at 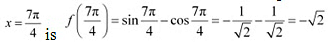
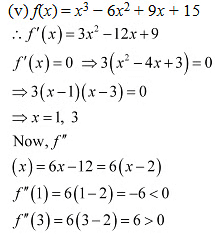
Therefore, by second derivative test.x = 1 is a point of local maxima and the local maximum value of f at x = 1 is f(1) = 1-6-9-15=19. However, x = 3 is a point of local minima and the local minimum value of f at x = 3 is f (3) = 27- 54+ 27+ 15 = 15.
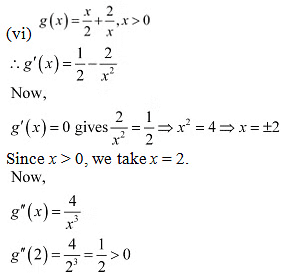
Therefore, by second derivative test. x = 2 is a point of local minima and the local minimum value of g at 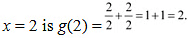
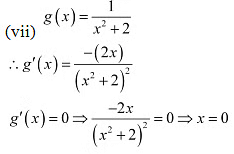
Now, for values close to x = 0 and to the left of 0, g (x) > 0. Also, for values close to x = 0 and to thi right of 0, g'(x) < 0
Therefore, by first derivative test, x = 0 is a point of local maxima and the local maximum value of 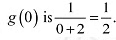
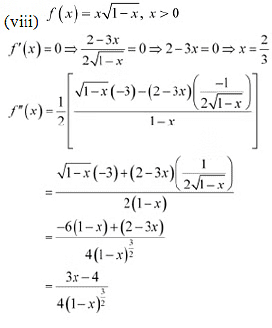
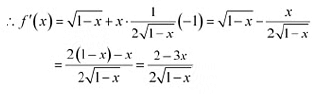
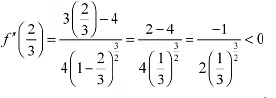
Therefore, by second derivative test. 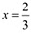 is a point of local maxima and the local maximum value off at
is a point of local maxima and the local maximum value off at 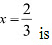
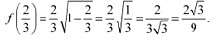
Q4: Prove that the following functions do not have maxima or minima:
(i) f(x) = ex
(ii) g(x) = logx
(iii) h(x) = x3 + x2 + x+ 1
Ans: 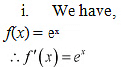
Now., if 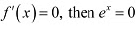 . But. the exponential function can never assume 0 for any value of x.
. But. the exponential function can never assume 0 for any value of x.
Therefore, there does not exist 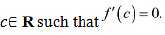
Hence, function f does not have maxima or minima.
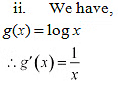
Therefore, there does not exist c ∈ R such that .
Hence, function g does not have maxima or minima.
iii. We have,
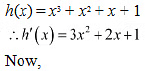
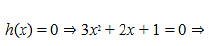
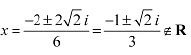
Therefore, there does not exist c∈ R such that h'(c)=0.
Hence, function h does not have maxima or minima.
Q5: Find the absolute maximum value and the absolute minimum value of the following functions in the given intervals: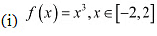
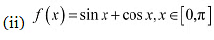
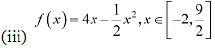
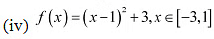
Ans: (i) The given function is f (x) = x3.
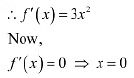
Then, we evaluate the value of/ at critical point x = 0 and at endpoints of the interval [—2,2].
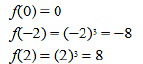
Hence, we can. conclude that the absolute maximum value off on [-2. 2] is 8 occurring at x = 2. Also, the absolute minimum value off on [-2,2] is -8 occurring at x = -2.
(ii) The given function is f(x) = sin x + cosx
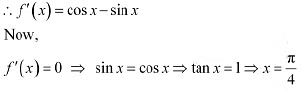
Then, we evaluate the value of/at critical point 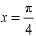 and at the end points of the interval [0, π] .
and at the end points of the interval [0, π] .
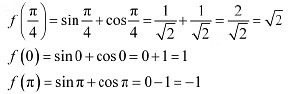
Hence, we can conclude that the absolute maximum value of 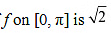 occurring at
occurring at 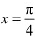 and the absolute minimum value of
and the absolute minimum value of 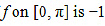 occurring at x = π
occurring at x = π
(iii) The given function is 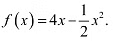
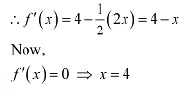
Then, we evaluate the value of/at critical point x = 4 and at the end points of the interval 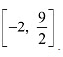
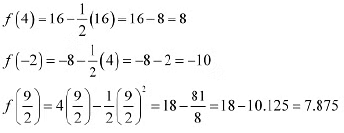
Hence, we can conclude that the absolute maximum value off on 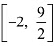 is 8 occurring at x = 4 and the absolute minimum value of f or
is 8 occurring at x = 4 and the absolute minimum value of f or 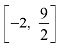 is -10 occurring at x = -2.
is -10 occurring at x = -2.
(iv) The riven function is
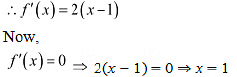
Then, we evaluate the value off at critical point x = 1 and at the endpoints of the interval [3,1].
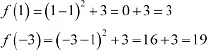
Hence, we can conclude that the absolute maximum value of/on [-3,1] is 19 occurring at x = -3 and the minimum value of f on [-3. 1] is 3 occurring at x = 1.
Q6: Find the maximum profit that a company can make, if the profit function is given by p(x) = 41 - 24x - 18x2
Ans: The profit function is riven as p(x) = 41 - 24x - 18x2
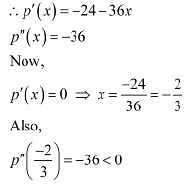
By second derivative test. 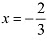 is the point of local maxima of p.
is the point of local maxima of p.
∴ Maximum profit 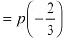
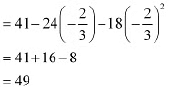
Hence, the maximum profit that the company can make is 49 units.
Q7: Find both the maximum value and the minimum value of on the interval [0, 3]
Ans:
Now, for which there are no real roots.
Therefore, we consider only x= 2 ∈[0,3].
Now, w:e evaluate the value off at critical pointx = 2 and at. the end points ofthe interval [0,3].
Hence, we can conclude that the absolute maximum value of f on [0, 3] is 25 occurring at x = 0 and the absolute minimum value of f at [0. 3] is - 39 occurring at x = 2.
Q8: At what points in the interval [0, 2π], does the function sin 2x attain its maximum value?
Ans: -Let f(x) = sin 2x.
Then, we evaluate the values of/at critical points and at the end points of the
Hence, we can conclude that the absolute maximum value of f on [0, 2π] is occurring at and
Q9: What is the maximum value of the function sinx + cos x?
Ans: Let f (x) = sin x- cos x.
We first consider the interval [1, 3].
Then, we evaluate the value of f at the critical point x = 2 ∈ [1, 3] and at the end points of the interval [1, 3].
f(2) = 2(8) − 24(2) 107 = 16 − 48 107 = 75
f(1) = 2(1) − 24(1) 107 = 2 − 24 107 = 85
f(3) = 2(27) − 24(3) 107 = 54 − 72 107 = 89
Hence, the absolute maximum value of f(x) in the interval [1, 3] is 89 occurring at x = 3.
Next, we consider the interval [−3, −1].
Evaluate the value of f at the critical point x = −2 ∈ [−3, −1] & at the end points of the interval [1, 3].
f(−3) = 2 (−27) − 24(−3) 107 = −54 72 107 = 125
f(−1) = 2(−1) − 24 (−1) 107 = −2 24 107 = 129
f(−2) = 2(−8) − 24 (−2) 107 = −16 48 107 = 139
Hence, the absolute maximum value of f(x) in the interval [−3, −1] is 139 occurring at x = −2.
Q10: It is given that at x = 1, the function x4− 62x2 ax 9 attains its maximum value, on the interval [0, 2]. Find the value of a.
Ans: Let f(x) = x4 − 62x2 ax 9.
It is given that function f attains its maximum value on the interval [0, 2] at x = 1.
Now, will be negative when (sin x + cos x) is positive i.e,, when sin x ana cos x are both positive. Also, we knowe that sin x and cos x both are positive in the first quadrant. Then,
will be negative when
∴ By second derivative test./will be the maximum at and the maximum value of f is
Q11: Find the maximum value of 2x3 - 24x + 107 in the interval [1, 3]. Find the maximum value of the same function in [-3, -1].
Ans: Let f(x) = 2x3 - 24x + 107.
Q12: Find the maximum and minimum values of x + sin 2x on [0, π].
Ans: Let f(x) = x + sin 2x.
Then, we evaluate the value of f at critical points and at the end points of the interval [0, 2π].
Hence, we can conclude that the absolute maximum value of f(x) in the interval [0, 2π] is 2π occurring at x =2π & the absolute minimum value of f(x) in the interval [0,2π] is 0 occurring at x = 0.
Q13: Find two numbers whose sum is 24 and whose product is as large as possible.
Ans: Let one number be x. Then, the other number is (24 − x).
Let P(x) denote the product of the two numbers. Thus, we have
By second derivative test, x = 12 is the point of local maxima of P. Hence, the product of the numbers is the maximum when the numbers are 12 and 24 − 12 = 12.
Q14: Find two positive numbers x and y such that x + y = 60 and xy3 is maximum
Ans: The two numbers are x and y such that x + y = 60.
By second derivative test, x = 15 is a point of local maxima of f. Thus, function xy3 is maximum when x = 15 and y = 60 − 15 = 45.
Hence, the required numbers are 15 and 45.
Q15: Find two positive numbers x and y such that their sum is 35 and the product x2y5 is a maximum
Ans: Let one number be x. Then, the other number is y = (35 − x).
When x = 35, and y= 35 - 35 = 0. This will make the product x2y5 equal to 0.
x = 0 and x =35 cannot be the possible values of x.
When x = 10, we have:
By second derivative test, P(x) will be the maximum when x = 10 and y = 35 − 10 = 25.
Hence, the required numbers are 10 and 25.
Q16: Find two positive numbers whose sum is 16 and the sum of whose cubes is minimum.
Ans: - Let one number be x. Then, the other number is (16 − x).
Let the sum of the cubes of these numbers be denoted by S(x). Then,
By second derivative test, x = 8 is the point of local minima of S.
Hence, the sum of the cubes of the numbers is the minimum when the numbers are 8 and 16 −8 =8.
Q17: A square piece of tin of side 18 cm is to made into a box without top, by cutting a square from each corner and folding up the flaps to form the box. What should be the side of the square to be cut off so that the volume of the box is the maximum possible?
Ans: Let the side of the square to be cut off be x cm. Then, the length and the breadth of the box will be (18 − 2x) cm each and the height of the box is x cm.
Therefore, the volume V(x) of the box is given by
If x = 9. then the length and the breadth will become 0
By second derivative test, x = 3 is the point of maxima of V.
Hence, if we remove a square of side 3 cm from each corner of the square tin and make a box from the remaining sheet, then the volume of the box obtained is the largest possible
Q18: A rectangular sheet of tin 45 cm by 24 cm is to be made into a box without top, by cutting off square from each corner and folding up the flaps. What should be the side of the square to be cut off so that the volume of the box is the maximum possible?
Ans: Let the side of the square to be cut off be x cm. Then, the height of the box is x, the length is 45 − 2x, and the breadth is 24 − 2x.
Therefore, the volume V(x) of the box is given by,
If x = 9. then the length and the breadth will become 0
By second derivative test, x = 5 is the point of maxima.
Hence, the side of the square to be cut off to make the volume of the box maximum possible is 5 cm.
Q19: Show that of all the rectangles inscribed in a given fixed circle, the square has the maximum area.
Ans: Let a rectangle of length l and breadth b be inscribed in the given circle of radius a.
Then, the diagonal passes through the centre and is of length 2a cm.
Now, by applying the Pythagoras theorem, we have:
∴ By the second derivative test, when, then the area of the rectangle is the maximum.
Since , the rectangle is a square.
Hence, it has been proved that of all the rectangles inscribed in the given fixed circle, the square has the maximum area.
Q20: Show that the right circular cylinder of given surface and maximum volume is such that is heights is equal to the diameter of the base.
Ans: Let r and h be the radius and height of the cylinder respectively.
Then, the surface area (S) of the cylinder is given by
Let V be the volume of the cylinder. Then.
Q21: Of all the closed cylindrical cans (right circular), of a given volume of 100 cubic centimetres, find the dimensions of the can which has the minimum surface area?
Ans: Let r and h be the radius and height of the cylinder respectively.
Then, volume (V) of the cylinder is given by,
Surface area (S) of the cylinder is given by.
Now, it is observed that when
∴ By second derivative test, the surface area is the minimum when the radius of the cylinder is
Q22: A wire of length 28 m is to be cut into two pieces. One of the pieces is to be made into a square and the other into a circle. What should be the length of the two pieces so that the combined area of the square and the circle is minimum?
Ans: Let a piece of length l be cut from the given wire to make a square.
Then, the other piece of wire to be made into a circle is of length (28 − l) m.
Now, side of square = l/4.
Let r be the radius of the circle. Then,
The combined areas of the square and the circle (A) is given by,
∴ By second derivative test, the area (A) is the minimum when
Hence, the combined area is the minimum when the length of the wire in making the square is cm while the length of the wire in making the circle is
Q23: Prove that the volume of the largest cone that can be inscribed in a sphere of radius R is 8/27 of the volume of the sphere.
Ans: Let r and h be the radius and height of the cone respectively inscribed in a sphere of radius R.
Let V be the volume of the cone.
Then,
Height of the cone is given by,
[ABC is a right triangle]
∴ By second derivative test the volume of the cone is die maximum when
Q24: Show that the right circular cone of least curved surface and given volume has an altitude equal to time the radius of the base.
Ans: Let r and h be the radius and the height (altitude) of the cone respectively.
Then, the volume (V) of the cone is given as:
The surface area (S) of the cone is given by.
S = πrI (where l is the slant height)
Thus, it. can be easily verified that when
Q25: Show that the semi-vertical angle of the cone of the maximum volume and of given slant height is
Ans: Let θ be the semi-vertical angle of the cone.
It is clear that
Let r, h. and 1 be the radius, height, and the slant height of the cone respectively.
The slant height of the cone is given as constant.
Now, r = l sin θ and h = 1 cos θ
The volume (V) of the cone is given by,
Q26: The point on the curve x2 = 2y which is nearest to the point (0, 5) is
(A)
(B)
(C) (0, 0)
(D) (2, 2)
Ans: The given curve is x2 = 2y.
For each value of x. the position of the point will be
The distance d(x) between the points and (0,5) is given by.
∴ By second derivative test. d(x) is the minimum at
When
Hence, the point on the curve x2 = 2y which is nearest to the point (0, 5) is
The correct answer is A.
|
177 videos|618 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 - Application of Derivative
| 1. What is the concept of the application of derivatives? |  |
| 2. How can derivatives be applied in business and economics? |  |
| 3. How are derivatives used in physics and engineering? |  |
| 4. What are some common applications of derivatives in daily life? |  |
| 5. How can derivatives be used to solve optimization problems? |  |






















