Locomotion & Movement NCERT Solutions | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Q1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions.
Ans: The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows:
 Sarcomere of skeletal muscle
Sarcomere of skeletal muscle
- Z line: The boundary that defines the edges of a sarcomere.
- A band: The dark band in the middle, containing thick myosin filaments.
- I band: The light band on either side of the A band, containing thin actin filaments.
- H zone: The central part of the A band where there are no thin filaments overlapping.
- M line: A thin fibrous membrane that holds the thick filaments together in the A band.
A sarcomere is the functional unit of muscle contraction, located between two Z lines. In a relaxed state, the thin filaments partially overlap the thick filaments, creating the H zone.
Q2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle contraction.
Ans: The sliding filament theory describes how muscles contract. This process involves the thin filaments sliding over the thick filaments, leading to the shortening of the myofibril. Here are the key points:
- Muscle fibres have alternating light and dark bands, known as the I-band (light, containing actin) and the A-band (dark, containing myosin).
- The Z-line bisects each I-band and anchors the thin filaments.
- The central area of the A-band that is not overlapped by thin filaments is called the H-zone.
- During contraction, the myosin heads, or cross bridges, attach to the thin filaments.
- This action pulls the thin filaments towards the centre of the sarcomere, causing the Z-lines to move closer together.
- As a result, the I-band shortens, and the H-zone disappears, while the overall length of the A-band remains constant.
Muscle contraction is initiated when a signal from the nervous system triggers the release of calcium ions. These ions bind to proteins on the actin filaments, exposing binding sites for myosin. The myosin heads then attach to these sites, forming cross bridges. The energy from ATP hydrolysis allows the myosin heads to pull the actin filaments, resulting in contraction. Once the contraction is complete, calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, leading to muscle relaxation as the Z-lines return to their original position.
 Sliding filament theory of muscle contractionQ3: Describe the important steps in muscle contraction.
Sliding filament theory of muscle contractionQ3: Describe the important steps in muscle contraction.
Ans: During skeletal muscle contraction, the thick filament slides over the thin filament by a repeated binding and releases myosin along the filament. This whole process occurs in a sequential manner.
 Steps in muscle contraction
Steps in muscle contraction
- Step 1: Muscle contraction is initiated by signals that travel along the axon and reach the neuromuscular junction or motor end plate. Neuromuscular junction is a junction between a neuron and the sarcolemma of the muscle fibre. As a result, Acetylcholine (a neurotransmitter) is released into the synaptic cleft by generating an action potential in sarcolemma.
- Step 2: The generation of this action potential releases calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in the sarcoplasm.
- Step 3: The increased calcium ions in the sarcoplasm leads to the activation of actin sites. Calcium ions bind to the troponin on actin filaments and remove the tropomyosin, wrapped around actin filaments. Hence, active actin sites are exposed and this allows myosin heads to attach to this site.
- Step 4: In this stage, the myosin head attaches to the exposed site of actin and forms cross bridges by utilizing energy from ATP hydrolysis. The actin filaments are pulled. As a result, the H-zone reduces. It is at this stage that the contraction of the muscle occurs.
- Step 5: After muscle contraction, the myosin head pulls the actin filament and releases ADP along with inorganic phosphate. ATP molecules bind and detach myosin and the cross bridges are broken.
- Stage 6: This process of formation and breaking down of cross bridges continues until there is a drop in the stimulus, which causes an increase in calcium. As a result, the concentration of calcium ions decreases, thereby masking the actin filaments and leading to muscle relaxation.
Q4: Write true or false. If false change the statement so that it is true.
(a) Actin is present in thin filament
(b) H-zone of striated muscle fibre represents both thick and thin filaments.
(c) Human skeleton has 206 bones.
(d) There are 11 pairs of ribs in man.
(e) Sternum is present on the ventral side of the body.
Ans:
(a) True
(b) False
The H-zone contains only thick filaments (myosin), not both thick and thin. The H-zone of striated muscle fibre represents only thick filaments.
(c) True
(d) False
Humans have 12 pairs of ribs, not 11. There are 12 pairs of ribs in man.
(e) True
Q5: Write the difference between:
(a) Actin and Myosin
(b) Red and White muscles
(c) Pectoral and Pelvic girdle
Ans:
(a) Actin and Myosin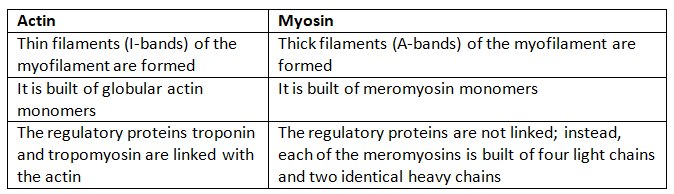
(b) Red and White muscles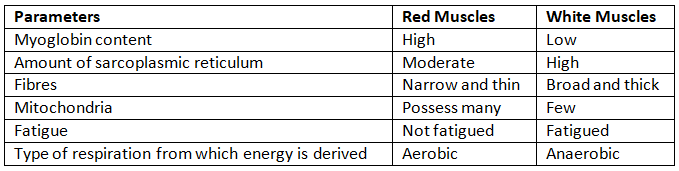
(c) Pectoral and Pelvic girdle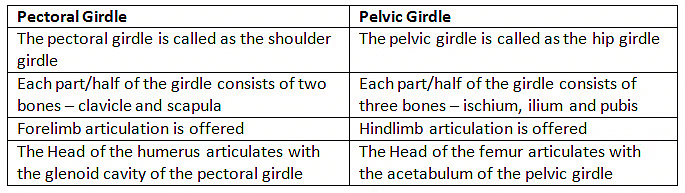
Q6: Match Column I with Column II: 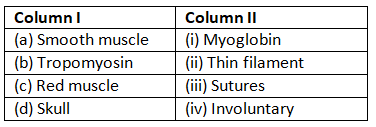
Ans: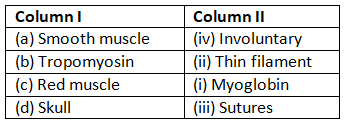
Q7: What are the different types of movements exhibited by the cells of human body?
Ans: Movement is a characteristic feature of living organisms. The different types of movement exhibited by cells of the human body are:
- Amoeboid movement: Leukocytes present in the blood show amoeboid movement. During tissue damage, these blood cells move from the circulatory system towards the injury site to initiate an immune response.
- Ciliary movement: Reproductive cells such as sperms and ova show ciliary movement. The passage of ova through the fallopian tube towards the uterus is facilitated by this movement.
- Muscular movement: Muscle cells show muscular movement.
Q8: How do you distinguish between a skeletal muscle and a cardiac muscle?
Ans: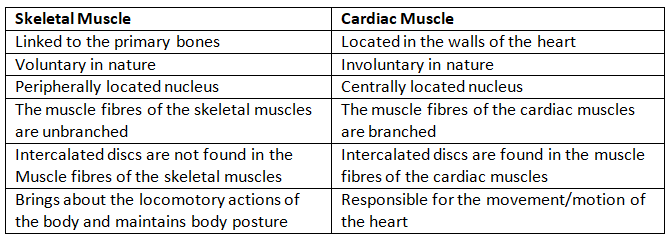
Q9: Name the type of joint between the following:
(a) atlas/axis
(b) carpal/metacarpal of thumb
(c) between phalanges
(d) femur/acetabulum
(e) between cranial bones
(f) between pubic bones in the pelvic girdle
Ans: (a) atlas/axis: Pivotal joint
(b) carpal/metacarpal of thumb: Saddle joint
(c) between phalanges: Hinge joint
(d) femur/acetabulum: Ball and socket joint
(e) between cranial bones: Fibrous joint
(f) between pubic bones in the pelvic girdle: cartilaginous joint (also called symphysis pubis)
Q10: Fill in the blank spaces:
(a) All mammals (except a few) have __________ cervical vertebra.
(b) The number of phalanges in each limb of human is __________
(c) Thin filament of myofibril contains 2 ‘F’ actins and two other proteins namely __________ and __________.
(d) In a muscle fibre Ca++ is stored in __________
(e) __________ and __________ pairs of ribs are called floating ribs.
(f) The human cranium is made of __________ bones.
Ans: (a) All mammals (except a few) have Seven cervical vertebra.
(b) The number of phalanges in each limb of a human is 14.
(c) Thin filament of myofibril contains 2 ‘F’ actins and two other proteins, namely troponin and tropomyosin.
(d) In a muscle fibre, Ca is stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
(e) 11th and 12th pairs of ribs are called floating ribs.
(f) The human cranium is made up of eight bones.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Locomotion & Movement NCERT Solutions - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. How do muscles work in the process of locomotion? |  |
| 2. What role do joints play in the movement of the body? |  |
| 3. How does the nervous system control movement and coordination? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of locomotion seen in animals? |  |
| 5. How do skeletal and muscular systems work together to facilitate movement? |  |

















