NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 - Human Reproduction
Q1: Fill in the blanks:
(a) Humans reproduce __________. (asexually/sexually)
(b) Humans are__________. (oviparous/viviparous/ovoviviparous)
(c) Fertilization is __________ in humans. (external/internal)
(d) Male and female gametes are __________. (diploid/haploid)
(e) Zygote is __________. (diploid/haploid)
(f) The process of release of the ovum from a mature follicle is called__________.
(g) Ovulation is induced by a hormone called the __________.
(h) The fusion of the male and the female gametes is called __________.
(i) Fertilization takes place in the __________.
(j) The zygote divides to form __________, which is implanted in uterus.
(k) The structure which provides vascular connection between the fetus and uterus is called __________.
Ans: (a) Humans reproduce sexually. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes to produce offspring with genetic variation.
(b) Humans are viviparous. Viviparous animals give birth to live young after the development of embryos inside the body.
(c) Fertilization is internal in human. The fusion of egg and sperm occurs inside the female reproductive tract.
(d) Male and female gametes are haploid. Gametes have half the number of chromosomes compared to the normal diploid cells of the body.
(e) Zygote is diploid. The zygote is formed by the fusion of haploid gametes and contains the full complement of chromosomes.
(f) The process of release of the ovum from a mature follicle is called ovulation. It usually occurs once in each menstrual cycle in females.
(g) Ovulation is induced by a hormone called the luteinizing hormone. LH is secreted by the pituitary gland and triggers the release of the mature ovum from the follicle.
(h) The fusion of the male and the female gametes is called fertilization. It typically occurs in the fallopian tubes in humans.
(i) Fertilization takes place in the fallopian tube. The fallopian tubes are the site where sperm and egg meet and fertilization occurs.
(j) The zygote divides to form blastocyst, which is fertilization implanted in uterus. The embryo undergoes several rounds of cell division to develop into a multicellular structure.
(k) The structure which provides vascular connection between the fetus and uterus is called placenta. The placenta is an organ that forms during pregnancy and allows exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products between the mother and the developing fetus.
Q2: Draw a labeled diagram of male reproductive system.
Ans:
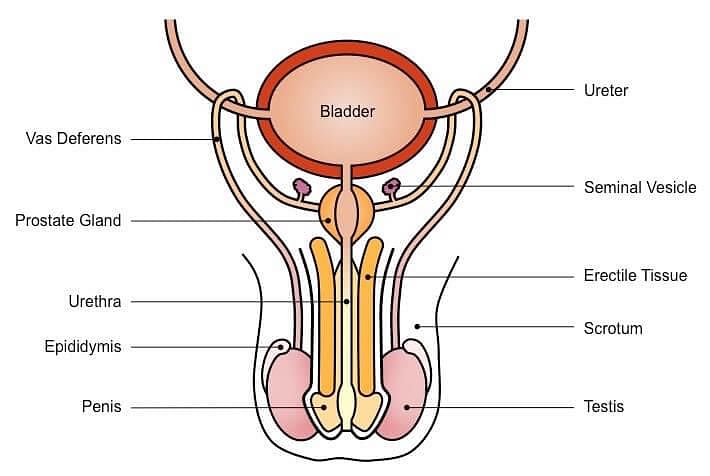 Male Reproductive System
Male Reproductive System
- Testes: Produce sperm and hormones (e.g., testosterone).
- Epididymis: Stores and matures sperm.
- Vas Deferens: Transports sperm from the epididymis to the urethra during ejaculation.
- Urethra: Carries sperm and urine out of the body.
- Prostate Gland: Produces seminal fluid, which nourishes and protects sperm.
- Seminal Vesicles: Produce seminal fluid, which provides energy for sperm.
- Bulbourethral Glands: Produce pre-ejaculatory fluid, which lubricates the urethra.
- Penis: Delivers sperm into the female reproductive tract during sexual intercourse.
Q3: Draw a labeled diagram of female reproductive system
Ans:
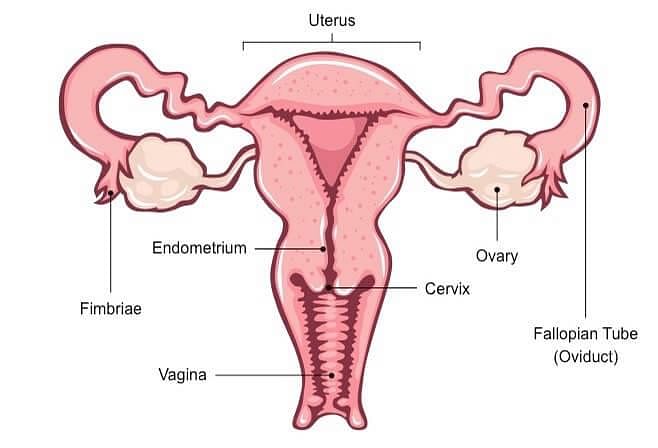 Fig: Female Reproductive system
Fig: Female Reproductive system
- Ovaries: Produce eggs (ova) and female sex hormones (e.g., estrogen and progesterone).
- Fallopian Tubes: Capture eggs released from the ovaries and provide the site for fertilization of eggs by sperm. They then transport fertilized eggs (embryos) to the uterus.
- Uterus: Also known as the womb, the uterus is where a fertilized egg implants and grows into a fetus during pregnancy.
- Cervix: The lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It produces cervical mucus that changes in consistency during the menstrual cycle to facilitate sperm transport or prevent sperm from entering the uterus.
- Vagina: A muscular tube that connects the cervix to the outside of the body. It serves as a birth canal during childbirth and also allows for sexual intercourse.
- Vulva: The external female genitalia, including the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and vaginal opening. The vulva protects the internal reproductive organs and is involved in sexual arousal.
Q4: Write two major functions each of testis and ovary.
Ans: Functions of the Testis:
- They produce male gametes called spermatozoa by the process of spermatogenesis.
- The leydig cells of the seminiferous tubules secrete the male sex hormone called testosterone. Testosterone aids the development of secondary sex characteristics in males.
Functions of the ovary:
- They produce female gametes called ova by the process of oogenesis.
- The growing Graffian follicles secrete the female sex hormone called estrogen. Estrogen aids the development of secondary sex characteristics in females.
Q5: Describe the structure of a seminiferous tubule.
Ans:
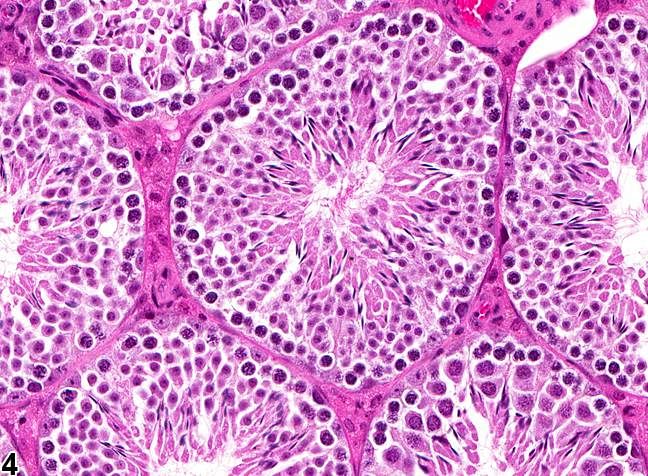 Seminiferous tubule
Seminiferous tubule
- Wall Structure: A seminiferous tubule is composed of a stratified epithelium, which is a multi-layered lining of cells. The cells are supported by a basement membrane, a thin layer of connective tissue that surrounds the tubule.
- Cell Types: The stratified epithelium of the seminiferous tubules contains different types of cells, including:
(i) Spermatogonia: These are the stem cells that give rise to sperm cells through a process called spermatogenesis. They are located near the basement membrane and undergo mitosis to produce more spermatogonia or differentiate into sperm cells.
(ii) Sertoli Cells: Also known as sustentacular cells, these are specialized cells that support and nourish the developing sperm cells. They are located within the stratified epithelium and extend from the basement membrane to the lumen of the tubule. Sertoli cells provide nutrients, remove waste products, and help in the process of sperm maturation.
(iii) Sperm Cells: As spermatogonia undergo successive rounds of cell division and differentiation, they develop into sperm cells. These mature sperm cells are released into the lumen of the tubule and are eventually carried out of the testes through the epididymis and vas deferens during ejaculation.
Spermatogenesis: Spermatogenesis is the process by which sperm cells are formed in the seminiferous tubules. It involves multiple stages of cell division and maturation, starting from spermatogonia, followed by spermatocytes, spermatids, and finally, mature sperm cells.
Overall, the structure of the seminiferous tubules is specifically adapted for the process of sperm production, providing a supportive environment for spermatogenesis and the maturation of sperm cells.
Q6: What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis.
Ans:
 Fig: Spermatogenisis
Fig: Spermatogenisis
Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm cell production that occurs in the seminiferous tubules of the testes in males. It involves several stages of cell division and differentiation, resulting in the production of mature sperm cells.
Here's a brief overview of the process of spermatogenesis:
- Spermatogonia: Spermatogonia are the diploid stem cells located near the basement membrane of the seminiferous tubules. They undergo mitosis to produce more spermatogonia or differentiate into primary spermatocytes.
- Primary Spermatocytes: Primary spermatocytes are diploid cells that undergo the first round of meiosis, resulting in the formation of two haploid secondary spermatocytes.
- Secondary Spermatocytes: Secondary spermatocytes are haploid cells that undergo the second round of meiosis, resulting in the formation of four haploid spermatids.
- Spermatids: Spermatids are haploid cells that undergo a process called spermiogenesis, which involves extensive structural and morphological changes. During spermiogenesis, spermatids develop a head, midpiece, and tail, eventually forming mature sperm cells.
- Sperm Cells: Mature sperm cells, also known as spermatozoa, are the final product of spermatogenesis. They have a compact head containing genetic material, a midpiece with mitochondria for energy production, and a tail (flagellum) for locomotion.
- Release of Sperm: Once mature, sperm cells are released into the lumen of the seminiferous tubules and are carried out of the testes through the epididymis and vas deferens during ejaculation.
It's important to note that spermatogenesis is a continuous process that occurs throughout the reproductive lifespan of males, and it is essential for the production of functional sperm cells necessary for fertilization and reproduction.
Q7: Name the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
Ans: Follicle-stimulating hormones (FSH) and luteinizing hormones (LH) are secreted by gonadotropin releasing hormones from the hypothalamus. These hormones are involved in the regulation of the process of spermatogenesis. FSH acts on sertoli cells, whereas LH acts on leydig cells of the testis and stimulates the process of spermatogenesis.
Q8: Define spermiogenesis and spermiation.
Ans: Spermiogenesis and spermiation are two closely related processes that occur during spermatogenesis, which is the process of sperm cell production in the testes of males.
- Spermiogenesis: It is the process of transforming spermatids into matured spermatozoa or sperms. Spermiogenesis is the process of maturation and structural transformation of haploid spermatids into mature sperm cells, also known as spermatozoa. During spermiogenesis, spermatids undergo several morphological changes to acquire the distinct structure of a mature sperm cell.
- Spermiation: It is the process when mature spermatozoa are released from the sertoli cells into the lumen of seminiferous tubules. Spermiation is the process by which mature sperm cells are released from Sertoli cells, which are the supporting cells in the seminiferous tubules. Once the spermatids have completed spermiogenesis and acquired their mature structure, they are released into the lumen of the seminiferous tubules.
Q9: Draw a labelled diagram of sperm.
Ans: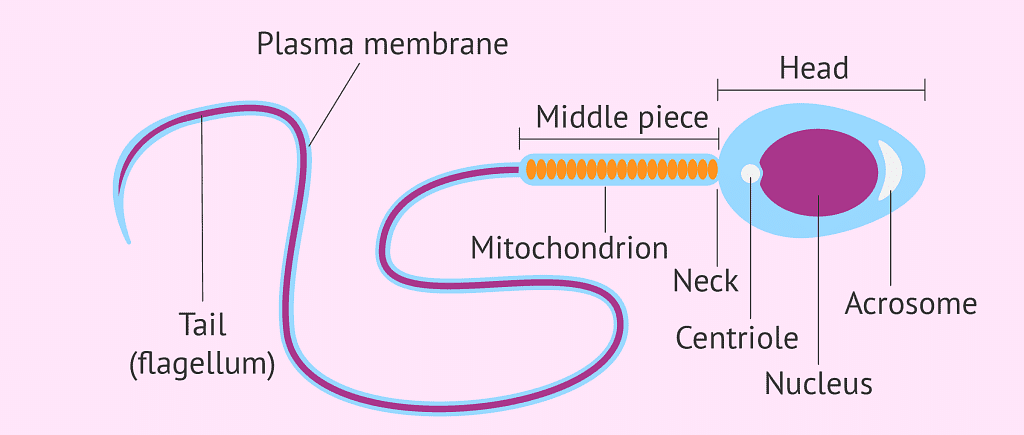 Fig: Structure of Sperm
Fig: Structure of Sperm
Q10: What are the major components of seminal plasma?
Ans: Semen (produced in males) is composed of sperms and seminal plasma. The major components of the seminal plasma in the male reproductive system are mucus, spermatozoa, and various secretions of accessory glands. The seminal plasma is rich in fructose, calcium, ascorbic acid, and certain enzymes. It provides nourishment and protection to sperms.
Q11: What are the major functions of male accessory ducts and glands?
Ans:
The male accessory ducts are vasa efferentia, epididymis, vas deferens, and rete testis.
- They play an important role in the transport and temporary storage of sperms.
On the contrary, male accessory glands are seminal vesicles, prostate glands, and bulbourethral glands.
- These glands secrete fluids that lubricate the reproductive system and sperms. The sperms get dispersed in the fluid which makes their transportation into the female body easier. The fluid is rich in fructose, ascorbic acid, and certain enzymes. They also provide nutrients and activate the sperm.
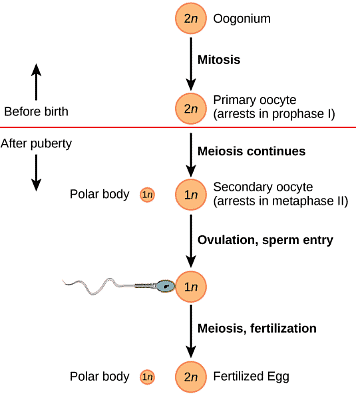
Q12: What is oogenesis? Give a brief account of oogenesis.
Ans:
- Oogenesis is the process of the formation of a mature ovum from the oogonia in females. It takes place in the ovaries.
- During oogenesis, a diploid oogonium or egg mother cell increases in size and gets transformed into a diploid primary oocyte.
- This diploid primary oocyte undergoes first meiotic division i.e., meiosis I or reductional division to form two unequal haploid cells.
- The smaller cell is known as the first polar body, while the larger cell is known as the secondary oocyte.
- This secondary oocyte undergoes second meiotic division i.e., meiosis II or equational division and gives rise to a second polar body and an ovum.
Hence, in the process of oogenesis, a diploid oogonium produces a single haploid ovum while two or three polar bodies are produced.
Q13: Draw a labeled diagram of a section through ovary.
Ans:
 Transverse section of Ovary
Transverse section of Ovary
Q14: Draw a labelled diagram of a Graafian Follicle?
Ans:
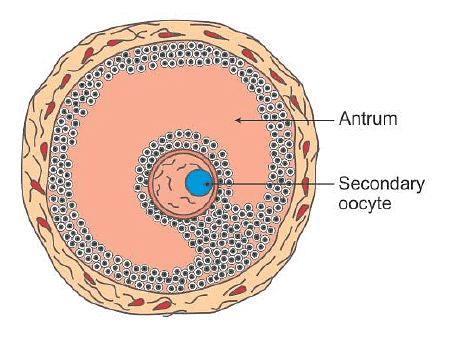 Graafian Follicle
Graafian Follicle
Q15: Name the functions of the following.
(a) Corpus luteum
(b) Endometrium
(c) Acrosome
(d) Sperm tail
(e) Fimbriae
Ans:
(a) Corpus luteum: Corpus luteum is formed from the ruptured Grafiaan follicle. It secretes progesterone hormone during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. A high level of progesterone inhibits the secretions of FSH and LH, thereby preventing ovulation. It also allows the endometrium of the uterus to proliferate and to prepare itself for implantation.
(b) Endometrium: It is the innermost lining of the uterus. It is rich in glands and undergoes cyclic changes during various phases of the menstrual cycle to prepare itself for the implantation of the embryo.
(c) Acrosome: It is a cap-like structure present in the anterior part of the head of the sperm. It contains hyaluronidase enzyme, which hydrolyses the outer membrane of the egg, thereby helping the sperm to penetrate the egg at the time of fertilization.
(d) Sperm tail: It is the longest region of the sperm that facilitates the movement of the sperm inside the female reproductive tract.
(e) Fimbriae: They are finger-like projections at the ovarian end of the fallopian tube. They help in the collection of the ovum (after ovulation), which is facilitated by the beating of the cilia.
Q16: Identify True/False statements. Correct each false statement to make it true.
(a) Androgens are produced by Sertoli cells. (True/False)
(b) Spermatozoa get nutrition from Sertoli cells. (True/False)
(c) Leydig cells are found in ovary. (True/False)
(d) Leydig cells synthesise androgens. (True/False)
(e) Oogenesis takes place in corpus luteum. (True/False)
(f) Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy. (True/False)
(g) Presence or absence of hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity or
sexual experience. (True/False)
Ans:
(a) Androgens are produced by Sertoli cells. (False) Androgens are produced by Leydig cells found in seminiferous tubules of the testis.
(b) Spermatozoa get nutrition from Sertoli cells. (True)
(c) Leydig cells are found in ovary. (False) Leydig cells are found in the seminiferous tubules of the testis.
(d) Leydig cells synthesise androgens. (True)
(e) Oogenesis takes place in corpus luteum. (False) Oogenesis takes place in the ovary.
(f) Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy. (True)
(g) Presence or absence of the hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity or sexual experience. (True)
Q17: What is menstrual cycle? Which hormones regulate menstrual cycle?
Ans:
- The menstrual cycle is a series of cyclic physiologic changes that take place inside the female reproductive tract in primates. The whole cycle takes around 28 days to complete. The end of the cycle is accompanied by the breakdown of uterine endothelium, which gets released in the form of blood and mucous through the vagina. This is known as menses.
- The follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estrogen, and progesterone are the various hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle. The level of FSH and LH secreted from the anterior pituitary gland increases during the follicular phase.
- FSH secreted under the influence of RH (releasing hormone) from the hypothalamus stimulates the conversion of a primary follicle into a graafian follicle.
- The level of LH increases gradually leading to the growth of follicle and secretion of estrogen. Estrogen inhibits the secretion of FSH and stimulates the secretion of luteinizing hormone. It also causes the thickening of the uterine endometrium.
- The increased level of LH causes the rupturing of the graafian follicle and release the ovum into the fallopian tube.
- The ruptured graafian follicle changes to corpus luteum and starts secreting progesterone hormone during the luteal phase. Progesterone hormone helps in the maintenance and preparation of endometrium for the implantation of the embryo.
- High levels of progesterone hormone in the blood decrease the secretion of LH and FSH, therefore inhibiting further ovulation.
Q18: What is parturition? Which hormones are involved in induction of parturition?
Ans: Parturition is the process of giving birth to a baby as the development of the foetus gets completed in the mother’s womb. The hormones involved in this process are oxytocin and relaxin.

Oxytocin leads to the contraction of smooth muscles of myometrium of the uterus, which directs the full term foetus towards the birth canal.
On the other hand, relaxin hormone causes relaxation of the pelvic ligaments and prepares the uterus for child birth.
Q19: In our society the women are often blamed for giving birth to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct?
Ans:
- All human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes. Human males have 22 pairs of autosomes and contain one or two types of sex chromosome. They are either X or Y.
- On the contrary, human females have 22 pairs of autosomes and contain only the X sex chromosome.
- The sex of an individual is determined by the type of the male gamete (X or Y), which fuses with the X chromosome of the female.
- If the fertilizing sperm is X, then the baby will be a girl and if it is Y, then the baby will be a boy. Hence, it is incorrect to blame a woman for the gender of the child.
Q20: How many eggs are released by a human ovary in a month? How many eggs do you think would have been released if the mother gave birth to identical twins? Would your answer change if the twins born were fraternal?
Ans:
- An ovary releases an egg every month. When two babies are produced in succession, they are called twins. Generally, twins are produced from a single egg by the separation of early blastomeres resulting from the first zygotic cleavage. As a result, the young ones formed will have the same genetic make- up and are thus, called identical twins.
- If the twins born are fraternal, then they would have developed from two separate eggs. This happens when two eggs (one from each ovary) are released at the same time and get fertilized by two separate sperms. Hence, the young ones developed will have separate genes and are therefore, called non-identical or fraternal twins.
Q21: How many eggs do you think were released by the ovary of a female dog which gave birth to 6 puppies?
Ans: Dogs and rodents are polyovulatory species. In these species, more than one ovum is released from the ovary at the time of ovulation. Hence, six eggs were released by the ovary of a female dog to produce six puppies.
|
78 videos|276 docs|174 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 - Human Reproduction
| 1. What is the process of fertilization in human reproduction? |  |
| 2. What are the major hormones involved in human reproduction? |  |
| 3. How does the menstrual cycle play a role in human reproduction? |  |
| 4. What are the different methods of contraception available for human reproduction? |  |
| 5. What are the common reproductive disorders that can affect human fertility? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















