NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 - Ecosystem
Q1: Fill in the blanks.
(a) Plants are called as_________ because they fix carbon dioxide.
(b) In an ecosystem dominated by trees, the pyramid (of numbers) is _________ type.
(c) In aquatic ecosystems, the limiting factor for the productivity is _________.
(d) Common detritivores in our ecosystem are_________.
(e) The major reservoir of carbon on earth is_________.
Ans:
(a) Plants are called as autotrophs because they fix carbon dioxide.
(b) In an ecosystem dominated by trees, the pyramid (of numbers) is of inverted type.
(c) In aquatic ecosystems, the limiting factor for productivity is light.
(d)Common detritivores in our ecosystem are earthworms.
(e) A major reservoir of carbon on Earth is oceans.
Q2: Which one of the following has the largest population in a food chain?
(a) Producers
(b) Primary consumers
(c) Secondary consumers
(d) Decomposers
Ans: (d) Decomposers
Decomposers include micro-organisms such as bacteria and fungi. They form the largest population in a food chain and obtain nutrients by breaking down the remains of dead plants and animals.
 Food Chain Decomposers
Food Chain Decomposers
Q3: The second tropic level in a lake is
(a) Phytoplankton
(b) Zooplankton
(c) Benthos
(d) Fishes
Ans: (b) Zooplankton
Zooplankton are primary consumers in aquatic food chains that feed upon phytoplankton. Therefore, they are present at the second tropic level in a lake.
 Zooplankton
Zooplankton
Q4: Secondary producers are
(a) Herbivores
(b) Producers
(c) Carnivores
(d) None of the above
Ans: (d) None of the above
Plants are the only producers. Thus, they are called primary producers. There are no other producers in a food chain.
Q5: What is the percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), in the incident solar radiation.
(a) 100%
(b) 50 %
(c) 1-5%
(d) 2-10%
Ans: (b) 50%
Out of total incident solar radiation, about fifty percent of it forms photosynthetically active radiation or PAR.
Q6: Distinguish between
(a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain
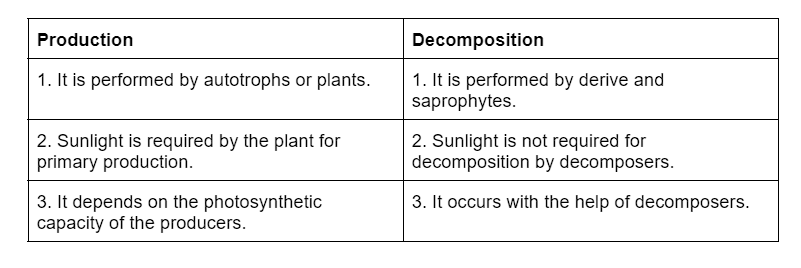
(b) Production and decomposition
(c) Upright and inverted pyramid
(d) Food chain and Food web
(e) Litter and detritus
(f) Primary and secondary productivity
Ans: (a) 
(b)
(c)

(d)

(e)

(f)

Q7: Describe the components of an ecosystem.
Ans: An ecosystem is defined as an interacting unit that includes both the biological community as well as the non-living components of an area. The living and the non-living components of an ecosystem interact among themselves and function as a unit, which gets evident during the processes of nutrient cycling, energy flow, decomposition, and productivity. There are many ecosystems such as ponds, forests, grasslands, etc.
 Components of an EcosystemThe two components of an ecosystem are:
Components of an EcosystemThe two components of an ecosystem are:
- Biotic component: It is the living component of an ecosystem that includes biotic factors such as producers, consumers, decomposers, etc. Producers include plants and algae. They contain chlorophyll pigment, which helps them carry out the process of photosynthesis in the presence of light.
Thus, they are also called converters or transducers. Consumers or heterotrophs are organisms that are directly (primary consumers) or indirectly (secondary and tertiary consumers) dependent on producers for their food.
Decomposers include micro-organisms such as bacteria and fungi. They form the largest population in a food chain and obtain nutrients by breaking down the remains of dead plants and animals. - Abiotic component: They are the non-living component of an ecosystem such as light, temperature, water, soil, air, inorganic nutrients, etc.
Q8: Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
Ans: An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation of various ecological parameters such as the number of individuals present at each trophic level, the amount of energy, or the biomass present at each trophic level.
Ecological pyramids represent producers at the base, while the apex represents the top level consumers present in the ecosystem.
There are three types of pyramids:
- Pyramid of numbers
- Pyramid of energy
- Pyramid of biomass
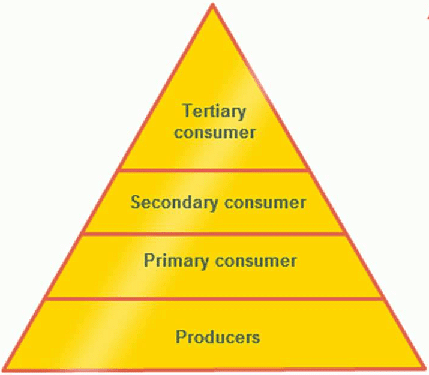
Pyramid of numbers: It is a graphical representation of the number of individuals present at each tropic level in a food chain of an ecosystem. The pyramid of numbers can be upright or inverted depending on the number of producers.
For example, in a grassland ecosystem, the pyramid of numbers is upright. In this type of a food chain, the number of producers (plants) is followed by the number of herbivores (mice), which in turn is followed by the number of secondary consumers (snakes) and tertiary carnivores (eagles).
Hence, the number of individuals at the producer level will be the maximum, while the number of individuals present at top carnivores will be least.
 Pyramid of numbers
Pyramid of numbers
On the other hand, in a parasitic food chain, the pyramid of numbers is inverted. In this type of a food chain, a single tree (producer) provides food to several fruit eating birds, which in turn support several insect species.
Pyramid of biomass: A pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation of the total amount of living matter present at each trophic level of an ecosystem. It can be upright or inverted. It is upright in grasslands and forest ecosystems as the amount of biomass present at the producer level is higher than at the top carnivore level. The pyramid of biomass is inverted in a pond ecosystem as the biomass of fishes far exceeds the biomass of zooplankton (upon which they feed). 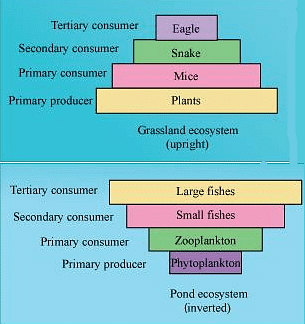 Pyramid of biomass
Pyramid of biomass
Q9: What is primary productivity? Give brief description of factors that affect primary productivity.
Ans: It is defined as the amount of organic matter or biomass produced by producers per unit area over a period of time.
Primary productivity of an ecosystem depends on the variety of environmental factors such as light, temperature, water, precipitation, etc. It also depends on the availability of nutrients and the availability of plants to carry out photosynthesis.
 Primary Productivity
Primary Productivity
Q10: Define decomposition and describe the processes and products of decomposition.
Ans: Decomposition is the process that involves the breakdown of complex organic matter or biomass from the body of dead plants and animals with the help of decomposers into inorganic raw materials such as carbon dioxide, water, and other nutrients.
 Decomposition Process
Decomposition Process
The various processes involved in decomposition are as follows:
- Fragmentation: It is the first step in the process of decomposition. It involves the breakdown of detritus into smaller pieces by the action of detritivores such as earthworms.
- Leaching: It is a process where the water soluble nutrients go down into the soil layers and get locked as unavailable salts.
- Catabolism: It is a process in which bacteria and fungi degrade detritus through various enzymes into smaller pieces.
- Humification: The next step is humification which leads to the formation of a darkcoloured colloidal substance called humus, which acts as reservoir of nutrients for plants.
- Mineralization: The humus is further degraded by the action of microbes, which finally leads to the release of inorganic nutrients into the soil. This process of releasing inorganic nutrients from the humus is known as mineralization. Decomposition produces a dark coloured, nutrient-rich substance called humus. Humus finally degrades and releases inorganic raw materials such as CO2 , water, and other nutrient in the soil.
Q11: Give an account of energy flow in an ecosystem.
Ans: Energy enters an ecosystem from the Sun. Solar radiations pass through the atmosphere and are absorbed by the Earth’s surface. These radiations help plants in carrying out the process of photosynthesis. Also, they help maintain the Earth’s temperature for the survival of living organisms. Some solar radiations are reflected by the Earth’s surface. Only 2-10 percent of solar energy is captured by green plants (producers) during photosynthesis to be converted into food. The rate at which the biomass is produced by plants during photosynthesis is termed as ‘gross primary productivity’. When herbivores consume these green plants, only 10% of the stored energy from producers is transferred to herbivores. Plants use the remaining 90 % of this energy for various processes such as respiration, growth, and reproduction. Similarly, only 10% of the energy of herbivores is transferred to carnivores. This is known as ten percent law of energy flow.
 Flow of energy
Flow of energy
Old NCERT Solution
Q1: Write important features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem.
Ans:
- Sedimentary cycles have their reservoirs in the Earth’s crust or rocks. Nutrient elements are found in the sediments of the Earth. Elements such as sulphur, phosphorus, potassium, and calcium have sedimentary cycles.
- Sedimentary cycles are very slow. They take a long time to complete their circulation and are considered as less perfect cycles. This is because during recycling, nutrient elements may get locked in the reservoir pool, thereby taking a very long time to come out and continue circulation. Thus, it usually goes out of circulation for a long time.
Q2: Outline salient features of carbon cycling in an ecosystem.
Ans:
- The carbon cycle is an important gaseous cycle which has its reservoir pool in the atmosphere. All living organisms contain carbon as a major body constituent. Carbon is a fundamental element found in all living forms. All biomolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins required for life processes are made of carbon. Carbon is incorporated into living forms through a fundamental process called ‘photosynthesis’.
- Photosynthesis uses sunlight and atmospheric carbon dioxide to produce a carbon compound called ‘glucose’. This glucose molecule is utilized by other living organisms. Thus, atmospheric carbon is incorporated in living forms.
- Now, it is necessary to recycle this absorbed carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere to complete the cycle. There are various processes by which carbon is recycled back into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide gas.
- The process of respiration breaks down glucose molecules to produce carbon dioxide gas. The process of decomposition also releases carbon dioxide from dead bodies of plants and animals into the atmosphere. Combustion of fuels, industrialization, deforestation, volcanic eruptions, and forest fires act as other major sources of carbon dioxide.
 Carbon cycle
Carbon cycle
|
78 videos|276 docs|174 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 - Ecosystem
| 1. What are the different components of an ecosystem? |  |
| 2. How do energy and nutrients flow through an ecosystem? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of biodiversity in an ecosystem? |  |
| 4. How does human activity impact ecosystems? |  |
| 5. How can we protect and conserve ecosystems? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















