Nervous Coordination In Animals - Class 10 PDF Download
Different organs work together in an organism to carry out different functions, this is known as coordination. Proper control and coordination are necessary to carry out essential functions of life.
Coordination is mainly of two types:
1. Nervous coordination
2. Chemical coordination
Animals - Nervous system
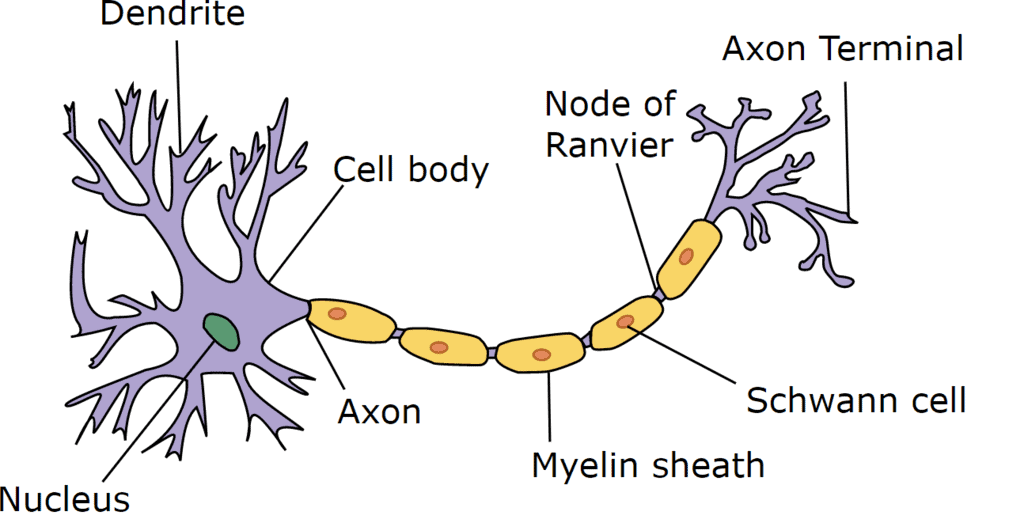
Neuron
The structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
Neuron (nerve cell) is the longest cell of the human body (up to 100 cm)
Neuron is made up of -
(i) Cell body
(ii) Cell processes (axon and dendron)
(i) Cell body: or Cyton or Soma or Perikaryon
- It contains granular cytoplasm which is called neuroplasm.
- Many small fibrils are present in the neuroplasm called neurofibrils for the conduction of nerve impulses.
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum coils around the ribosome form a granule like structure called Nissl's granule or Tigroid body.
- Nissl's granule is the centre of protein synthesis.
- Energy for the conduction of nerve impulses is provided by numerous mitochondria.
- Except for centriole, all other cell organelles are found in neuroplasm.
(ii) Cell process:
(a) Axon:
- It is the longest cell process of cyton, its diameter is uniform and contains axoplasm.
- Axoplasm of axon contains only neurofibrils and mitochondria.
- Nissl's granules are absent.
- Axon is covered by axolemma.
- Axolemma may be covered by a layer of phospholipids which is called medulla or myelin sheath.
- Myelin sheath acts as insulator and prevents leakage of ions.
- Myelin sheath is discontinuous around the axon. These interruptions where the axon is uncovered by myelin sheath are called nodes of Ranvier.
- Axon produces centrifugal conduction i.e. nerve impulse travels away from the cell body.
- The terminal ends of axon are branched which are called telodendria.
- Each telodendron ends in a swollen knob called synaptic knob.
- Nerve fibres in which myelin sheath is present, are called medullated or myelinated nerve fibres and nerve fibres without myelin sheath, are called non-medullated or non-myelinated nerve fibres.
Axon is the functional part of nerve cell, therefore the term "nerve fibre" usually refers to the axon.
 Neuron
Neuron
(b) Dendron:
- It is small cell process.
- Its fine branches are called 'dendrites'
- Dendron receive the stimuli and produce centripetal conduction i.e. nerve impulse travels towards the cell body.
- It is not covered by myelin sheath.
Differences between Axon and Dendron
| S.No. | Features | Axon | Dendron |
| 1 | Size | Long | Small |
| 2 | Number | Either absent or one | Either absent or one, mostly many |
| 3 | Diameter | Uniform | Non - Uniform |
| 4 | Branching | Generally unbranched | Branched |
| 5 | Terminal knobs (Telodendrin) | Present | Absent |
| 6 | Nissl's granule | Absent | Present |
| 7 | Myelin sheath | Present | Absent |
| 8 | The direction of nerve impulse | Away from cyton | Towards cyton |
Differences between medullated and non-medullated nerve fibre
| S.No. | Features | Medullated nerve fibre | Non-medullated nerve fibre |
| 1 | Occurrence | White Matter | Grey Matter |
| 2 | Sheath | Two: inner medullary, outer neurilemma | Only neurilemma |
| 3 | Node of Ranvier | Present | Absent |
| 4 | Speed of nerve impulse | Faster | Slower |
Type of Neurons
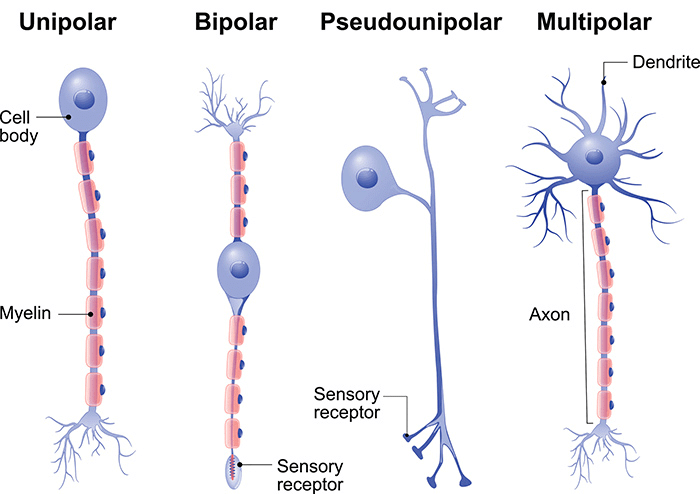
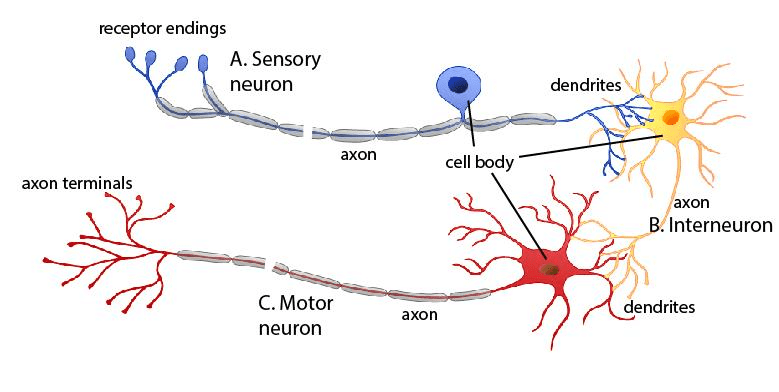 Three Types of Neurons
Three Types of Neurons
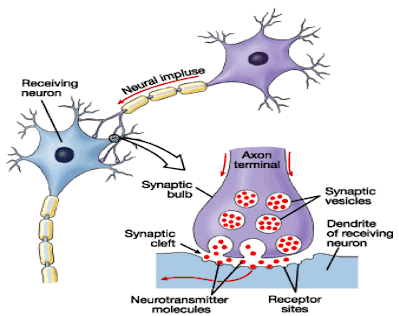
Synapse
The junction between two adjacent neurons i.e. between the axon ending of one neuron and dendrites of the next.
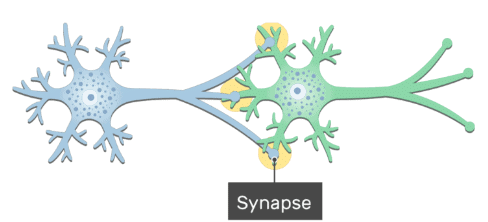 Synapse between two Neurons
Synapse between two Neurons
Nerve impulse
It is an electro-chemical information (signal) passing through neuron.
Neurotransmitters or Neurohormones
Chemical substances which either transmit or inhibit the message from one neuron to another.
| Stimulatory Neurotransmitters | Inhibitory Neurotransmitters |
| Stimulate impulse at synapse | Inhibit impulse at synapse |
| Example: Acetyl choline (ACh) | Example: GABA (Gamma Amino Butyric Acid) |
 Neuro-muscular Junction
Neuro-muscular Junction
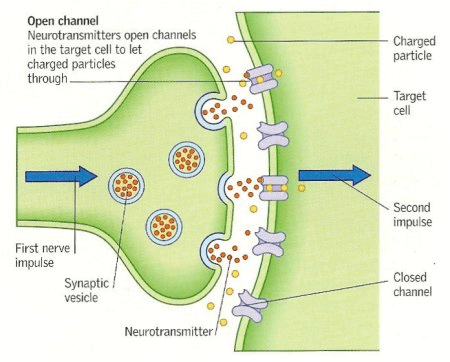 Transmission of Nerve Impulse across Synapse
Transmission of Nerve Impulse across Synapse
Working of Neuron or Transmission of Nerve Impulse
- Stimuli are detected by dendrites of receptor nerve cells located at our sense organs i.e. ear, eyes, nose, tongue and skin.
- A chemical reaction occurs and creates electric impulse.
- Impulse travels from dendrites and finally reaches axon endings (synaptic knobs)
- Impulse releases some chemicals like Acetylcholine from synaptic knob.
- By these chemicals, impulse transmits across synapse.
- This initiates a similar electric impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron and thus impulse is transferred from one nerve cell to another.
- Message is sent to CNS (brain & spinal cord) via sensory nerves.
- CNS sends message to muscles via motor nerves.
- Muscles of effector organ show response.
| Receptors | Stimuli | Location |
| Photoreceptors | light | eyes |
| Phonoreceptors | sound | internal ear |
| Olfactroreceptors | smell | nasal chamber |
| Gustatoreceptors | taste | taste buds on tongue |
| Tangoreceptors | touch | skin |
| Thermoreceptos | temperature | skin |
| Algesireceptors | pain | skin |
Physiology of Nerve Impulse
- At resting stage: in this stage, anions (negative ions) are present on the inner surface of the neuron membrane and cations (positive ions) are present on the outer surface of a neuron.
- This neuron membrane is said to be polarised.
- At exciting stage: As the neuron receive external stimuli, undergoes de-polarisation.
- The anions are now on the outer surface and cations on the inner surface.
- At this point, a nerve impulse is initiated.
- Repolarisation: As the impulse conducts forward, repolarisation occurs at the previous point.
- As the impulse reaches the nerve synapses, Acetylcholine is secreted by the terminal end. Through this, impulse is transmitted to the dendrites of the next nerve. Thus, the impulses are transmitted.
FAQs on Nervous Coordination In Animals - Class 10
| 1. What is the nervous system in animals? |  |
| 2. How does the nervous system coordinate in animals? |  |
| 3. What is nervous coordination in animals? |  |
| 4. How do animals use nervous coordination to survive? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of nervous coordination in animals? |  |















