Ascaris - Class 11 PDF Download
Introduction
(i) Ascaris is called round worm or thread worm.
(ii) Besides human they are also found in pig, sheep, cow, monkey etc.
(iii) Ascaris was described and discovered by Guddy.
(iv) In Korea 50-70% people are infected with Ascaris.
(v) Maximum cases is reported from Korea and Phillipines.
Classification
- Phylum - Aschelmintheis Body thread-like, head indistinct, body with thick cuticle. Alimentary canal complete
- Class - Nematoda Cosmopoliton in distribution, Dioecious. Mouth has 3 lips, pharynx with no bulb.
- Genus - Ascaris Monogenetic intestinal parasite of mammals unisexual body.
Species:
(a) lumbricoides (Intestinal parasite of man)
(b) suum (Intestinal parasite of Pig and Gorilla)
(c) megalocephala (Intestinal parasite of Horse).
Habit & Habitat
(i) Ascaris is an endoparasite living in the. lumen of small intestine of man.
(ii) The worms remain free in the intestine of the host and ingest the chyme of the host.
(iii) Since Ascaris lives in the lumen of small intestine so it is called coelozoic parasite.
(iv) It completes its life cycle in a single host so Monogenetic parasite.
(v) It is Unisexual or Dioecious animals.
(vi) Sexual dimorphism is present because sexes are seperate.
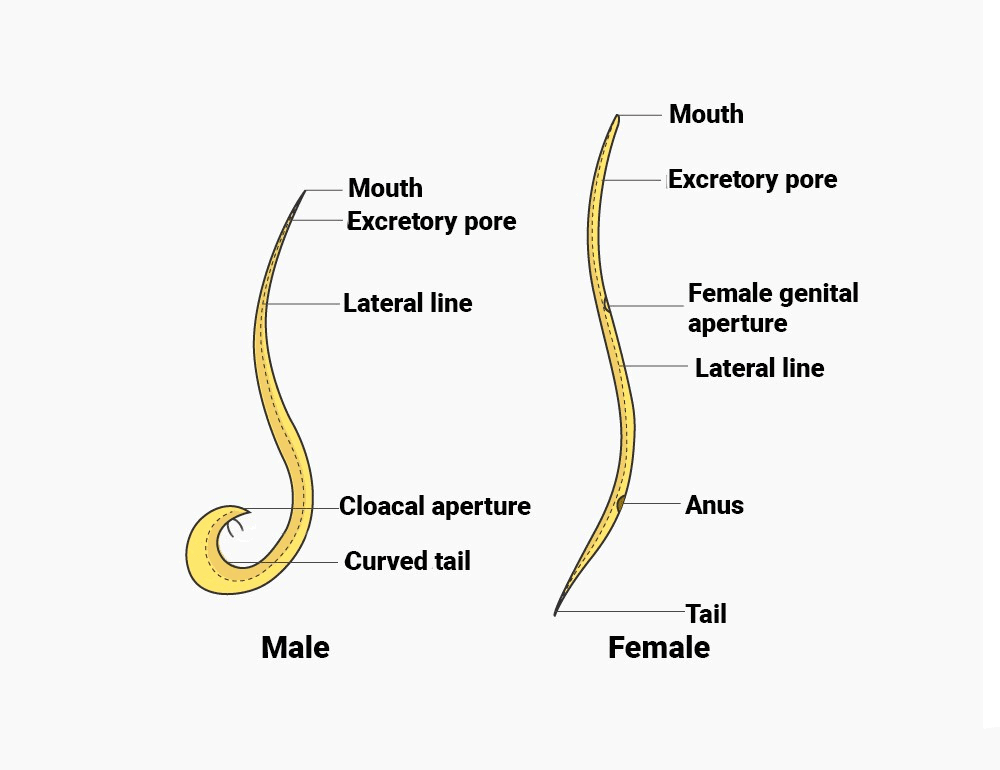
External Structure
Shape
(i) The body is elongated and cylindrical tapering at both ends.
(ii) The anterior end more cylindrical than the posterior end.
Colour
(i) Ascaris are light yellow to light pink in colour.
(ii) The body wall is semitransparent.
Size
(i) The female is larger than male.
(ii) Male Ascaris is 15 to 30 cm in length, 2-4 mm. in diameter.
(iii) Female Ascaris is 20 to 40 cm in length 4 - 6 mm. in diameter.
The posterior end of the male, is curved while it is straight in female.
Morphology
(i) The body is covered by a shiny semitransparent and elastic cuticle.
(ii) Four longitudinal streaks or line are present from anterior to posterior end on the body.
External Apertures
Male Ascaris has three aperture but Female has four aperture. The aperture are as follows-
(A) Mouth
(B) Excretory pore
(C) Cloaca
(D) Genital pore or Gonopore (absent in male)
(A) Mouth
(i) Mouth is present at the anterior end, triradiate in shape and surrounded by 3 lips or labia.
(ii) Inner margin of lips bear teeth like structure called denticles. It is made up of keratin.
Functions
Help in attachment to intestinal wall.
Lips
(i) Out of 3 lips one lip is mid dorsal and two lips are ventrolateral.
(ii) The dorsal lips bears two double sensory papilla upon its lateral sides.
(iii) Ventrolateral lips bears a double papilla, a single papilla and a amphid.
(iv) Amphid is chemoreceptor while the other sensory papillae are tangoreceptors and gustoreceptor.
(B) Excretory pore
It is present on mid ventral side about 2mm behind the mouth.
(C) Anus or Cloaca
(i) It is present on ventral side about 2mm before the posterior end of the body but in male Ascaris seperate anus is absent cloaca perform the function of anus.
(ii) Two small needle like and cuticular penial spicules or copulatory setae protrude out from the cloacal aperature.
(iii) Anus is transverse pore guarded by two thick lips.
(iv) Depressor ani muscle are found in anus.
(v) It is found only in female situated on mid ventral side.
Anal papilla
(i) Anal papilla is found in male Ascaris.
(ii) Above the cloaca 50 pairs of precloacal papillae are found, while below the cloca 5 pair of post cloacal papillae are found.
Phasmids
Phasmids are unicellular gland, found in a pair in both male and female Ascaris.
Difference between Male and Female Ascaris
S.No. | Male Ascaris | Female Ascaris |
1. | Body smaller 15 to 30 cm long and 2 to 4 mm thick. | Body larger 20-40 cm long and 4 to 6 mm thick. |
2. | Tail end is curved ventrally. | Tail end is straight. |
3. | Anus and Genital pore are common. Cloaca performs the function of anus as well as genital pore. cloacal located mid ventrally about 2mm in front of posterior end. | Anus and genital pore separate genital pore mid ventral at about 1/3rd body length behind anterior end anus mid ventral about 2mm in front of hind end. |
4 | A pair of needle like and protrusible penial setae is found in cloaca. | No penial setae is found |
5. | Pre cloacal and post cloacal papilla present upon ventral body surface. | No such papilla is found. |
Body Wall
The body wall of Ascaris is made up of 3 layers.
- Cuticle
- Epidermis or subcuticle or hypodermis
- Muscular layer
Cuticle
(i) It is secreted by epidermis.
(ii) It is nonliving and acellular.
(iii) It act as a selective permeable membrane. It is soluble in KOH.
(iv) It consist of numerous layers.
The layers of cuticle are as follows-
S.No. Male Ascaris Female Ascaris
1. Body smaller 15 to 30 cm long and Body larger 20-40 cm long and 4 to 6 mm thick. 2 to 4 mm thick.
2. Tail end is curved ventrally. Tail end is straight.
3. Anus and Genital pore are common. Anus and genital pore separate genital pore Cloaca performs the function of anus mid ventral at about 1/3rd body length behind as well as genital pore. anterior end anus mid ventral about 2mm in cloacal located mid ventrally about front of hind end. 2mm in front of posterior end.
4. A pair of needle-like and protrusible No penial setae is found. penial setae is found in cloaca.
5. Pre cloacal and post cloacal papilla No such papilla is found.
Lipid layer
(i) This layer is composed of lipid and is 1000 Å thick.
(ii) It is osmophilic layer.
Corticle and cortex layer
Its cortical layer contains polyphenols and guinone which make it resistant against digestive juices of the host.
Matrix layer Fibre layer
It consists of collagen fibres that cross each other obliquely.
Basement layer
(i) It is inner most layer of cuticle and surrounding the epidermis to allow growth after embryonic development.
(ii) The cuticle moults four times and cuticle is resecreted after each moult by the epidermis.
Epidermis
(i) It forms a syncytial layer below the cuticle.
(ii) It is found along the entire length of the body.
(iii) Fat and glycogen reserve food are present in epidermis.
Muscular layer
(i) Circular muscles are absent in the body wall of Ascaris.
(ii) Only longitudinal muscles are present.
(iii) Longitudinal muscles are present in form of four group. One dorsal, one ventral, and two ventrolateral.
(iv) Each group has 150 muscles.
(v) The arrangement of muscle known as polymyorion and coelomyorion.
Body Cavity & Pseudocoelomic Fluid
(i) Adult Ascaris posses a body cavity the pseudocoel between body wall and internal organ.
(ii) This cavity is not true coelom because-
(a) It is not lined by coelomic epithelium.
(b) It has no relation with the reproductive and excretory organ.(Mesothelium)
(c) It develops from the blastocoel.
(iii) The pseudocoel of Ascaris contain five giant mesenchymal cell known as pseudo-coelocyte occupying the fixed positions.
(iv) Out of these, the largest cell lies on the dorsal side of the pharynx, and from it extend numerous thin cytoplasmic strands in the form of fenestrated membrane.
(v) The pseudocoelom filled with pseudocoelomic fluid.
(vi) Pseudocoelomic fluid is pinkish proteinous fluid. It possess 90-95% water. Besides protein, fatty acid, nitrogen phosphate, sodium chloride are also found in pseudocoelomic fluid.
Functions
(i) Pseudocoelomic fluid acts as hydrostatic skeleton.
(ii) Keeps body wall stretched.
(iii) Pseudocoelomic fluid helps in distribution of nutrients
(iv) Protects the internal organs.
Note : Pseudocoelemic fluid is foul smelling fluid due to the presence of fatty acid.
Excretory System
(i) Ascaris has H-shaped excretory system composed of giant cell called Renette cell.
(ii) Excretory structure of Ascaris mainly include 2 longitudinal excretory canal passing through lateral cord.
(iii) Left longitudinal excretory canal is more developed than right longitudinal excretory canal.
(iv) Both excretory canal remain connected by transverse connection.
(v) A terminal duct emerges out from transverse connection and open out through excretory pore.
(vi) Urea is the chief excretory product of Ascaris, so Ascaris is Uriotelic. Some ammonia also get excreted. Hence it is ammonotelic also.
Respiratory System
(i) In Ascaris respiration is anaerobic.
(ii) In presence of oxygen may show aerobic respiration.
(iii) Anaerobic respiration results information of lactic acid CO2 and fatty acids.
Nervous System
(i) The nervous system of Ascaris was studied by Gold Schmith.
(ii) 162 nerve cell are present in nervous system.
(iii) Nervous system of Ascaris is hypodermis type.
(iv) A nerve ring surround the pharynx.
(v) Nerve ring has 7 ganglia in embryo and 8 ganglia in adult.
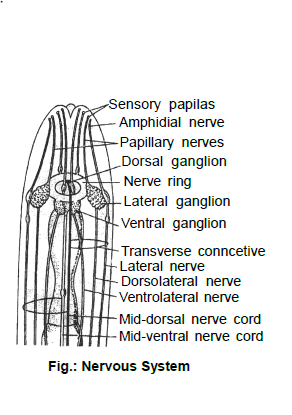
Sensory Organs
(i) Labial sensory papillae : These are the sensory papillae located upon lips of the mouth. These papillae consist of a fine fibre of a papillary nerve. These receptors are, probably, gustatory (taste organs) in function.
(ii) Amphids : These are two pits upon ventro-lateral lips of the mouth. Each pit contains a group of glandular and nerve cells innervated by amphidial nerve gustatory in function.
(iii) Phasmids : Pit-like chemoreceptors present upon lateral sides of body in the tail region. A small unicellular gland opens into each phasmid.
(iv) Cervical papillae : Tactile organs present upon the lateral sides of body 2mm behind anterior end.
(v) Anal papillae : These occur only in male Ascaris and comprise about 50 pairs of preanal and 5 pairs of postanal papillae. These too are tactile and help in copulation.
Digestive System
Alimentary canal
Ascaris has a straight alimentary canal from mouth to anus and is divided into four parts.
- Buccal capsule
- Pharynx
- Intestine
- Rectum
Buccal capsule
It is a small triangular chamber into which the terminal, triradiate mouth opens.
Pharynx
(i) It is a short and slender tube with a narrow, triradiate cavity is lined by cuticle.
(ii) Pharynx wall is composed of Radial fibres. Radial fibres regulates the lumen of pharynx.
(iii) Within pharynx 3 unicellular pharyngeal glands are found which secrets digestive juice.
(iv) The pharynx acts as a sucking and pumping organ.
(v) It sucks the chyme in the host and pumps it into the intestine The three pharyngeal gland cells produce a digestive juice and pour it into the pharyngeal cavity
Intestine
(i) The pharynx is followed by a long and thick intestine representing the midgut
(ii) The passage between pharynx and intestine is guarded by valve. This valve is known as pharyngointestinal valve.
(iii) It has a thin non-muscular and non glandular wall and a wide cavity.
(iv) The wall consists of a single layer of columnar cells.
(v) A thin cuticle secreted by the epithelial cell themselves envelops the intestine.
(vi) The free inner margin of each cell is produced into several finger like structure- This structure known as microvilli forming a short of brush border to increase the surfac area.
(vii) Muscle fibres are absent in the intestine.
Rectum
(i) The intestine is followed by a short rectum, which too is dorsoventrally flattened.
(ii) In male the rectum opens into the cloaca which is also the ejaculatory duct.
(iii) The anus is a transverse slit guarded by anterior and posterior lips and is provided with a special muscle the depressor ani.
Food Feeding and Digestion
(i) The food of Ascaris lumbricoides consists of blood and fully or incompletely digested food occurring in fluid form in the host`s gut.
(ii) The food is sucked by the rhythmic pumping action of the pharynx.
(iii) Digestion is completely extracellular in the intestine is aided by the enzymes proteases, amylase and lipase.
(iv) The digested food is absorbed by the intestinal cells and distributed by the pseudocoelomic fluid.
(v) Excess of food is stored mainly as glycogen and fat in the epidermis.
Reproductive System
(i) Ascaris is unisexual organism.
(ii) They have Telogonic and Tubular gonad.
(iii) At the centre of testes and ovary semisolid Rachis is found.
Male Reproductive system
Male reproductive system consists of following parts-
Single Testis
Single Vas deferens
Single Seminal vesicle
Single Ejaculatory duct
Single Penial setae
Testis
(i) Male Ascaris possess single testis this condition known as monorchic or monodelphic.
(ii) Testis is a long, thin and coiled tube like structure occupying most of the pseudocoel in posterior two thirds of body
(iii) Sperm formation is telogonic - sperms are formed at the apex of testis. Sperm has acrosome, nucleus mitochondria but tail is absent. Sperm of Ascaris is non flagellated. Vas deferens Testis open into coiled short and non–muscular tube like structure, known as vas deferens.
Seminal vesicle
(i) Vas deferens opens in seminal vesicle.
(ii) This is a long, straight and muscular tube.
(iii) Mature sperms are stored in seminal vesicle.
Ejaculatory duct
(i) Posterior part of seminal vesicle is narrow and muscular and glandular this tube like part is known as ejaculatory duct.
(ii) Ejaculatory duct combining with rectum forms cloaca.
Pineal sac and pineal setae
(i) Two small contractile penial sacs open dorsally into cloaca.
(ii) Each sac contains a needle like penial structure, composed of chitin, called pineal setae.
(iii) During copulation penial setae opens the female genital pore.
Female Reproductive System
Female reproduction system consists of following parts-
Two ovaries
Two oviducts
Two uteri
One vagina
Ovaries
(i) These are two in number, so female ovary is didelphic. Each ovary of Ascaris is a long thread like much twisted and blind tube.
(ii) They are found in 2/3rd part of the body.
Oviduct
From the distal end of each ovary a thick, twisted tube arises known as oviduct.
Uteri or uterus
(i) Each oviduct open into a much wider, thicker almost untwisted tube the uterus.
(ii) The uteri serve to store the eggs after fertilization.
Vagina
(i) In the anterior 1/3rd of the body the two uteri fuse to form a median short and highly muscular tube,
the vagina having an inner lining of cuticle.
(ii) The vagina opens to the exterior through the female gonopore or vulva.
Life Cycle
Ascaris is monogenetic parasite. They complete their life cycle in man.
Copulation
(i) Copulation takes place in the small intestine of man.
(ii) During copulation sperms are discharged by male in the vagina of female.
Fertilization
(i) Fertilization is always internal in Ascaris.
(ii) Fertilization takes place at the proximal ends of the uteri.
(iii) After fertilization the ova undergo second maturation division and get converted into ovum.
Mammilated egg
(i) Soon after fertilization, fertilization membrane develops around the eggs which becomes hard and forms chitinous capsule.
(ii) Zygote secretes fat layer just below the chitinous layer.
(iii) Uterus secrets albuminous layer just outside of the chitinous layer. Albuminous layer is rough and
warty, now the zygote is called mammilated egg.
Life Cycle of Ascaris
The Path of Migration of Juvenile Ascaris in Host Body
Egg laying
(i) Mammilated eggs are delivered in the human small intestine. A female Ascaris deliver 15 thousand to 2.5 lakhs egg per day.
(ii) Further development of mammilated egg is not possible in human intestine, due to deficiency of O2.
From intestine, mammilated, egg comes out to the world along with stool.
(i) 85º F is the ideal tempreture for embryonic development.
(ii) At the end of gastrula 0.2 mm long first juvenile or Rhabditiform larva is formed.
(iii) Within chitinous capsule first moulting takes place as a result 2nd juvenile get formed. Chitin coated capsule along with 2nd juvenile is called embryonated egg.
Infection
(i) Embryonic egg is the infective stage of the Ascaris.
(ii) Healthy person get infected through food and water contaminated by embryonated egg. Embryonated eggs remain alive in soil up to 5-6 years.
(iii) Within duodenum embryonated eggs get dissolved by digestive juice as a result 2nd stage juvenile get formed.
Migration
(A) Primary migration
(i) 2nd stage juvenile larva within intestine penetrates intestinal wall and enters within hepatic portal system, from hapatic larva reaches within liver.
(ii) From liver 2nd stage juvenile larva reaches within heart.
(iii) From heart through pulmonary artery larvea reaches with lungs alveoli.
(iv) Primary migration get completed in 12-15 days.
(v) Within alveoli 2nd and 3rd moulting takes place as a result 3rd and 4th stage larva get formed.
(vi) 4th stage larva is 2-3 mm long.
(B) Secondary migration
(i) 4th stage larva reaches to trachea from lungs alveoli.
(ii) From trachea it reaches to pharynx from pharynx the fourth stage larva reaches to small intestine.
(iii) In small intestine 4th moulting takes place, fourth stage larva turns into adult.
(iv) Secondary migration get completed in 10 days.
(v) After last moulting, adult Ascaris accquire sexual maturity after 8 to 10 weeks (60-70 days).
(vi) Life span of Ascaris is 9-12 months only.
Aberrant migration
Sometime larva, Migrates from lungs to brain, spinal cord, eyes and forms cyst, such type of migration is called aberrant migration.
Pathogenicity
(i) Disease caused by Ascaris is called Ascariasis.
(ii) Fever, anemia leucocytosis, eosinophilla abdominal fever, vomiting are the symptoms of Ascariasis.
Treatment
Ascaris is trated by oil of Chenopodium, piperazine, mebendazole, alcopar, diethyl carbamazine.
Special Points
(i) Cuticle of Ascaris is soluble in KOH.
(ii) Per minute female Ascaris deliver 162 eggs.
(iii) Salivary gland remains absent in Ascaris.
(iv) Albendazole is the most effective drug for treatment of Ascarisis.
FAQs on Ascaris - Class 11
| 1. What is the classification of Ascaris? |  |
| 2. Where does Ascaris live and what is its habitat? |  |
| 3. What are the external structures of Ascaris? |  |
| 4. What are the external apertures of Ascaris? |  |
| 5. What is the nervous system of Ascaris like? |  |
















