Chapter : Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis, PPT, Semester, Engineering - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis
Sorting
- a set (container) of n elements
- E.g. array, set of words, etc.
- there is an order relation that can be set across the elements
- Arrange the elements in ascending order
- Start à 1 23 2 56 9 8 10 100
- à 1 2 8 9 10 23 56 100
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Bubble Sort
Simplest sorting algorithm
- :
- 1. Set flag = false
- 2. Traverse the array and compare pairs of two elements
- 1.1 If E1 £ E2 - OK
- 1.2 If E1 > E2 then Switch(E1, E2) and set flag = true
- 3. If flag = true goto 1.
What happens?
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Bubble Sort
- 1 23 2 56 9 8 10 100
- 1 2 23 56 9 8 10 100
- 1 2 23 9 56 8 10 100
- 1 2 23 9 8 56 10 100
- 1 2 23 9 8 10 56 100
---- finish the first traversal ----
---- start again ----
- 1 2 23 9 8 10 56 100
- 1 2 9 23 8 10 56 100
- 1 2 9 8 23 10 56 100
- 1 2 9 8 10 23 56 100
---- finish the second traversal ----
---- start again ----
………………….
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Implement Bubble Sort with an Array
void bubbleSort (Array S, length n) {
boolean isSorted = false;
while(!isSorted) {
isSorted = true;
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
if(S[i] > S[i+1]) {
int aux = S[i];
S[i] = S[i+1]; S[i+1] = aux; isSorted = false;
}
}
}
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Running Time for Bubble Sort
- One traversal = move the maximum element at the end
- Traversal #i : n – i + 1operations
- Running time:
(n – 1) + (n – 2) + … + 1 = (n – 1) n / 2 = O(n 2)
- When does the worst case occur ?
- Best case ?
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Sorting Algorithms Using Priority Queues
- Remember Priority Queues = queue where the dequeue operation always removes the element with the smallest key à removeMin
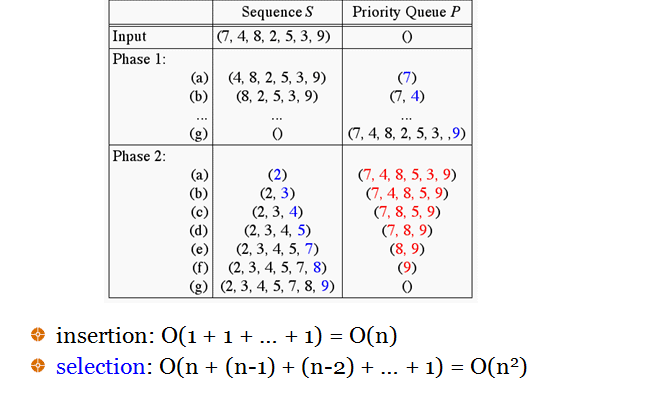
- Selection Sort
- insert elements in a priority queue implemented with an unsorted sequence
- remove them one by one to create the sorted sequence
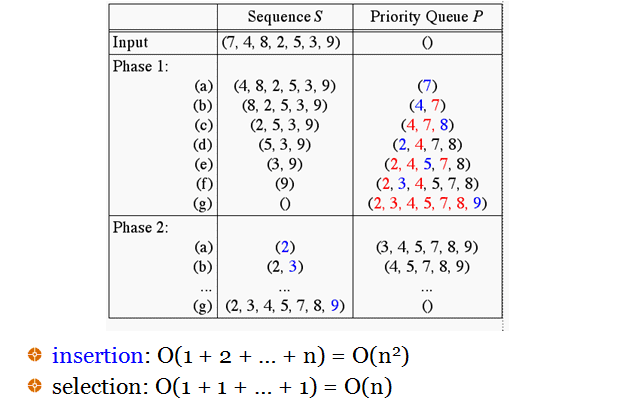
- Insertion Sort
- insert elements in a priority queue implemented with a sorted sequence
- remove them one by one to create the sorted sequence
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Selection Sort
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Insertion Sort
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Sorting with Binary Trees
- Using heaps (see lecture on heaps)
- How to sort using a minHeap ?
- Using binary search trees (see lecture on BST)
- How to sort using BST?
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Heap Sorting
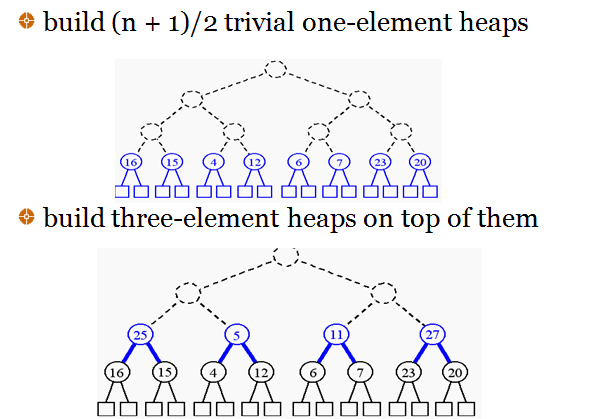
- Step 1: Build a heap
- Step 2: removeMin( )
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Recall: Building a Heap
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
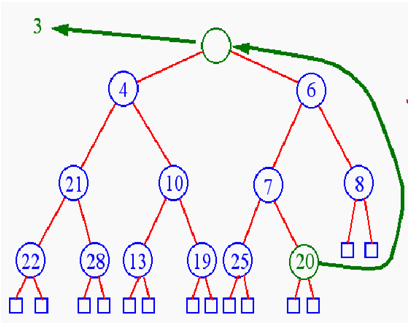
Recall: Heap Removal
- Remove element from priority queues? removeMin( )
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Recall: Heap Removal
- Begin downheap
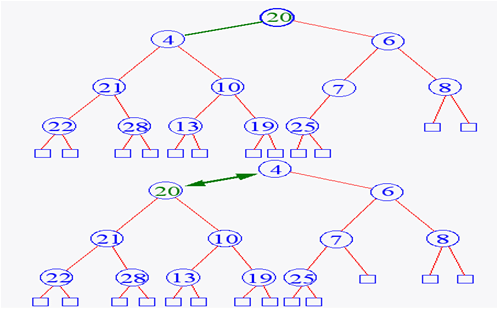
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Sorting with BST
- Use binary search trees for sorting
- Start with unsorted sequence
- Insert all elements in a BST
- Traverse the tree…. how ?
- Running time?
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Next
- Sorting algorithms that rely on the “DIVIDE AND CONQUER” paradigm
- One of the most widely used paradigms
- Divide a problem into smaller sub problems, solve the sub problems, and combine the solutions
- Learned from real life ways of solving problems
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Divide-and-Conquer
Divide and Conquer is a method of algorithm design that has created such efficient algorithms as Merge Sort.
- In terms or algorithms, this method has three distinct steps:
- : If the input size is too large to deal with in a straightforward manner, divide the data into two or more disjoint subsets.
- : Use divide and conquer to solve the subproblems associated with the data subsets.
- : Take the solutions to the subproblems and “merge” these solutions into a solution for the original problem.
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Merge-Sort
- : If S has at leas two elements (nothing needs to be done if S has zero or one elements), remove all the elements from S and put them into two sequences, S1 and S2, each containing about half of the elements of S. (i.e. S1 contains the first én/2ù elements and S2 contains the remaining ën/2û elements.
- : Recursive sort sequences S1 and S2.
- : Put back the elements into S by merging the sorted sequences S1 and S2 into a unique sorted sequence.
Merge Sort Tree:
- Take a binary tree T
- Each node of T represents a recursive call of the merge sort algorithm.
- We associate with each node v of T a the set of input passed to the invocation v represents.
- The external nodes are associated with individual elements of S, upon which no recursion is called.
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Merge-Sort
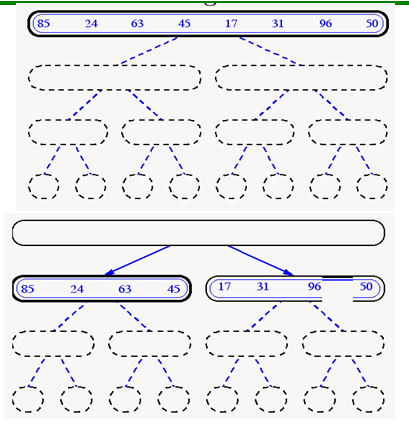
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Merge-Sort(cont.)
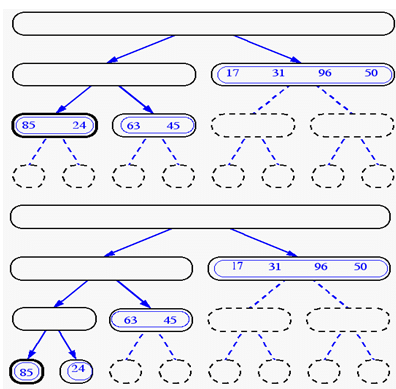
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Merge-Sort (cont’d)
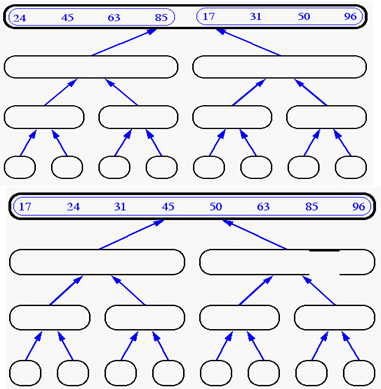
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Merging Two Sequences
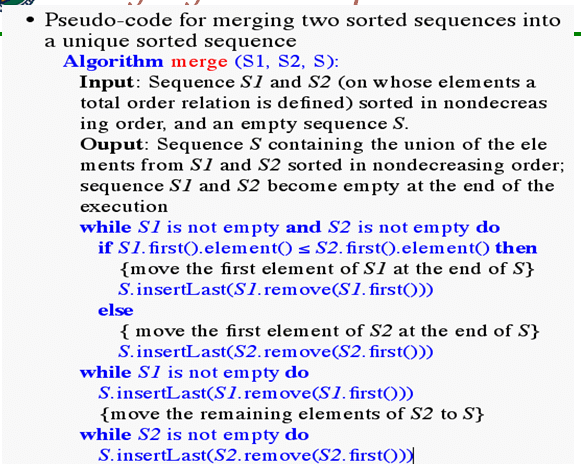
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Quick-Sort
- Another divide-and-conquer sorting algorihm
- To understand quick-sort, let’s look at a high-level description of the algorithm
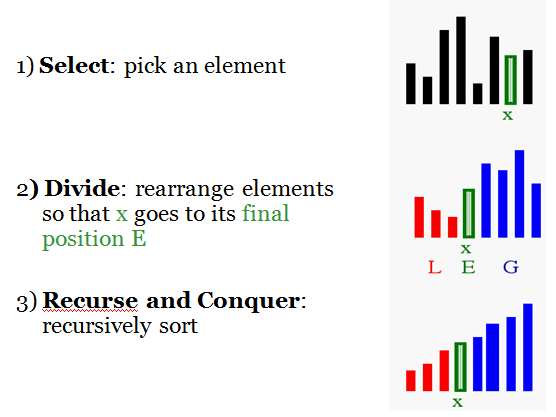
1) Divide : If the sequence S has 2 or more elements, select an element x from S to be your pivot. Any arbitrary element, like the last, will do. Remove all the elements of S and divide them into 3 sequences:
L, holds S’s elements less than x
E, holds S’s elements equal to x
G, holds S’s elements greater than x
2) Recurse: Recursively sort L and G
3) Conquer: Finally, to put elements back into S in order, first inserts the elements of L, then those of E, and those of G.
Here are some diagrams....
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Idea of Quick Sort
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
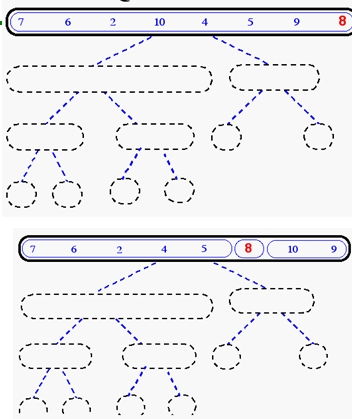
Quick-Sort Tree
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
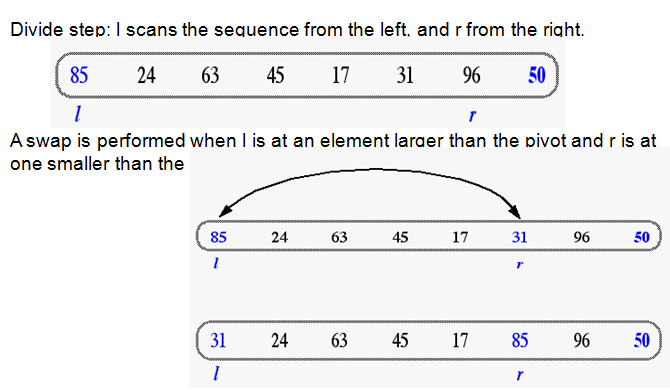
In-Place Quick-Sort
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
In Place Quick Sort (cont’d)
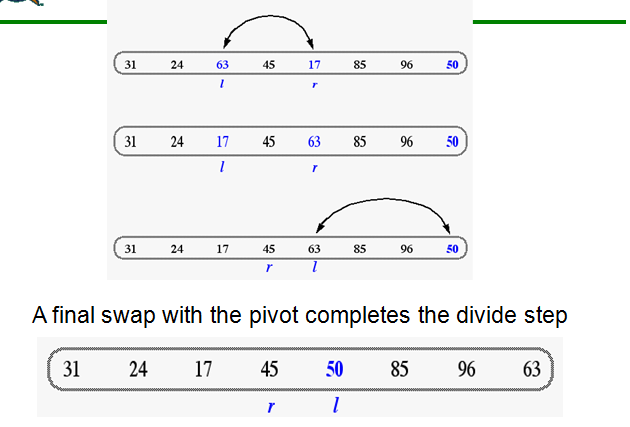
Data structures & Algorithm Analysis…………………………NextSlide……………………………………………………….
Running time analysis
- Average case analysis
- Worst case analysis
- What is the worst case for quick-sort?
- Running time?
FAQs on Chapter : Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis, PPT, Semester, Engineering - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is the importance of data structures and algorithm analysis in computer science engineering? |  |
| 2. Can you explain the difference between data structures and algorithms? |  |
| 3. How do data structures and algorithm analysis impact software development? |  |
| 4. What are some commonly used data structures in computer science engineering? |  |
| 5. How can algorithm analysis be performed in computer science engineering? |  |



















