Business Services Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
The chapter Business Services gives you a brief introduction to the characteristics of business services, the difference between services and goods, the classification of types of business services, the concept of e-banking, the identification and classification of types of insurance policies, and the description of different types of warehouses.
Definition
Auxiliaries to trade are also known as business services. The service sector includes commercial firms engaged in banking, communication, transport, insurance, and warehousing. Business cannot even be imagined in the absence of these services. All these services collectively constitute the Service Sector.
Nature/Features/characteristics of Services:
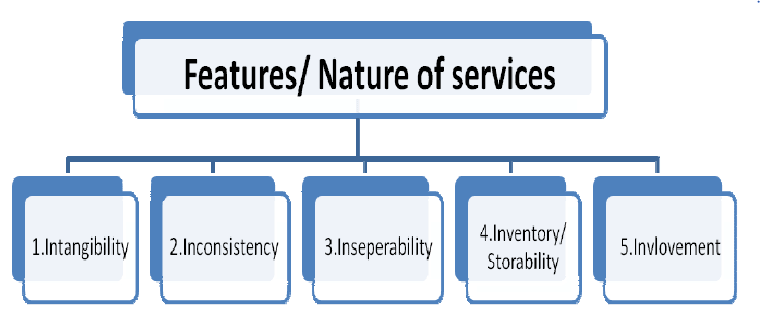
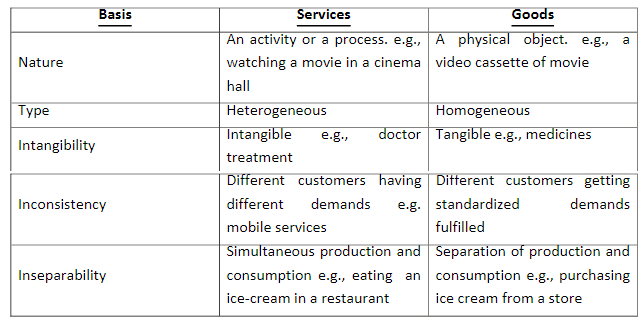
- Intangibility: A service is intangible and cannot be physically perceived or observed. It is something that is encountered or received by the buyer or recipient. Additionally, it is not possible to assess the quality of service prior to its utilisation.
- Inconsistency: Achieving perfect standardisation in services is not feasible. Even when the service provider remains constant, the quality of the service can vary over time.
- Inseparability: A distinguishing feature of services is the inseparability of the service itself from the service provider. In contrast to goods or products, services cannot be detached from their providers, and there is no storage phase between their creation and consumption.
- Storage: Services are distinct from goods or products in that the production and consumption of services are not inseparable. This is primarily due to the fact that services, being intangible in nature, cannot be stored or inventoried. As a result, there is no possibility of accumulating a stockpile of services.
- Involvement: Involvement is a key feature of services that refers to the active participation and engagement of both the service provider and the customer during the service delivery process. It encompasses the interactions, communication, and cooperation between the two parties involved.
Difference between Services and Goods:
Types of Services
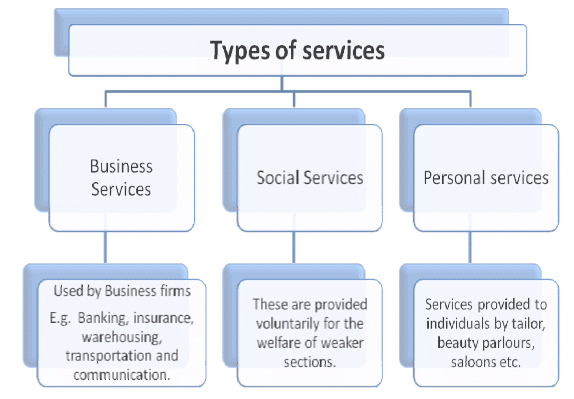
- Business Services: Services used by business enterprises in conducting the activities of the business. Examples: Banking, insurance, warehousing, communication services, etc.
- Social Services: These are provided voluntarily to fulfil social goals. Example: Providing education and health facilities to the employees and their family members.
- Personal Services: Services which are experienced differently by different customers. e.g. tourism, restaurants, etc.
Banking
A bank is an institution that accepts deposits and withdrawals by cheque and makes loans and advances for the purpose of earning profits.
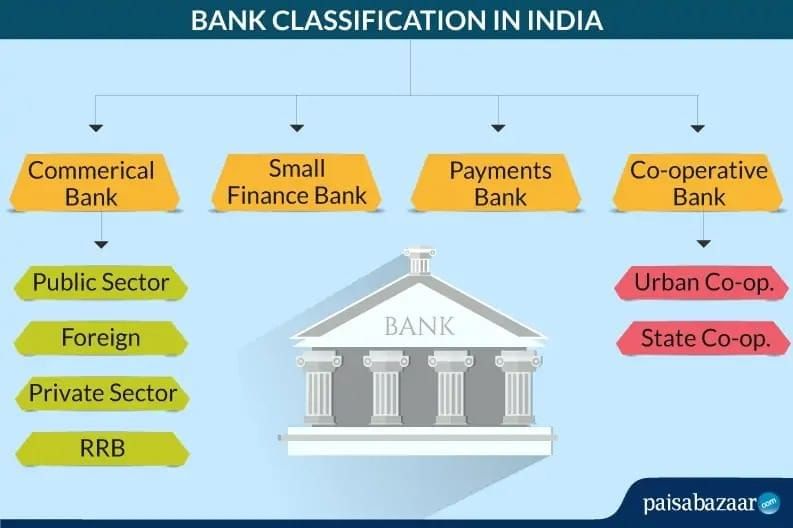
Types of Banks
Commercial Banks – Deal in money by accepting deposits and offering loans or investments, as per the Indian Banking Regulation Act, 1949. They include public sector banks (SBI, PNB, IOB) and private sector banks (HDFC, ICICI, Kotak Mahindra, J&K Bank).
Cooperative Banks – Governed by the State Cooperative Societies Acts, they provide affordable credit, mainly for rural and agricultural needs.
Specialised Banks – Serve specific sectors like foreign exchange, industry, exports, and development (e.g., industrial banks, EXIM Bank).
Central Bank – Regulates and oversees all banks, manages currency and credit policy, and serves as the government’s banker. In India, this is the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
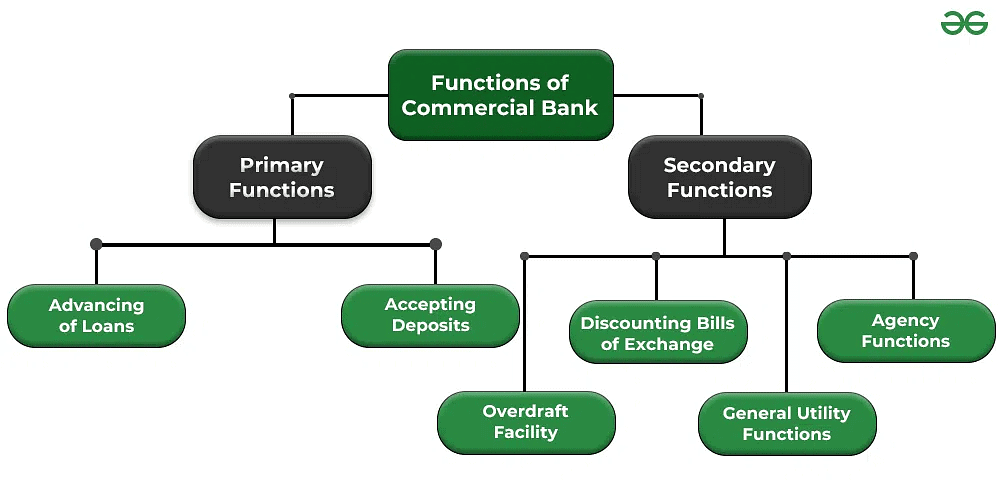
Functions of Commercial Banks
Banks perform both primary and additional services:
Accepting Deposits – Collect money through current, savings, and fixed deposits. Current accounts allow free withdrawals; savings accounts encourage saving with interest (as per RBI guidelines); fixed deposits offer higher interest but have withdrawal restrictions.
Lending Funds – Provide loans and advances such as overdrafts, cash credit, term loans, and bill discounting, supporting trade, industry, and other activities.
Cheque Facility – Enable withdrawal and transfer of funds via bearer cheques (cashable immediately) and crossed cheques (deposit only).
Remittance of Funds – Transfer money between places using drafts, pay orders, or mail transfers for a small fee.
Allied Services – Include bill payments, locker facilities, share transactions, insurance premium payments, and dividend collection.
Bank Draft
It is a financial instrument with the help of which money can be remitted from one place to another. Anyone can obtain a bank draft after depositing the amount in the bank. The bank issues a draft for the amount in its own branch at other places or other banks (only in case of a tie-up with those banks) in those places. The payee can present the draft to the drawee bank at their place and collect the money. The bank charges some commission for issuing a bank draft.
Banker’s cheque or Pay Order
It is almost like a bank draft. It refers to that bank draft which is payable within the town. In other words, banks issue a pay order for local purposes and issue a bank draft for outstation transactions.
E-BANKING
E-banking means banking transactions carried out with the help of computer systems (i.e., banking over the internet).

- Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT): Under this system, a bank transfers wages and salaries directly from the company’s account to the accounts of employees of the company.
- Automatic Teller Machine (ATM): It refers to an electronic terminal that allows people with a plastic card to perform simple banking transactions like withdrawal of cash 24x7 without any help from a human teller.
- Debit Card: It refers to a plastic card that allows the bank to take money from the customer’s account and transfer it to a seller’s account.
- Credit Card: It refers to a plastic card that allows the customer to buy now and pay back the loaned amount to the bank at a future date.
- Online Banking: Under this system, when the customer gives instructions to his computer, the bank computer transfers money from/ to customer’s account to the biller’s account.
Benefits of E-Banking
For Customers:
Enables digital payments and promotes transparency.
Offers 24×7×365 access from anywhere via computer or mobile.
Records every transaction, encouraging financial discipline.
Provides greater security by reducing the need to carry cash.
Enhances customer satisfaction through unlimited, branch-free access.
For Banks:
Gives a competitive edge and a wider network beyond physical branches.
Allows transactions through any internet-connected device.
Reduces branch workload via centralised databases and automation of accounting tasks.
Insurance
It is a contract whereby, in exchange for fixed consideration, one party promises to pay a fixed amount either upon the happening of an event or at the expiry of a certain period.
Functions of Insurance
The functions of insurance can be listed as follows:
- They provide certainty to the insured.
- They ensure the protection of the family.
- They are risk-sharing policies.
- They prevent the damage that can come from loss.
- It provides capital.
- It’s known for improving efficiency.
- It helps in boosting the economy.
Fundamental Principles of Insurance
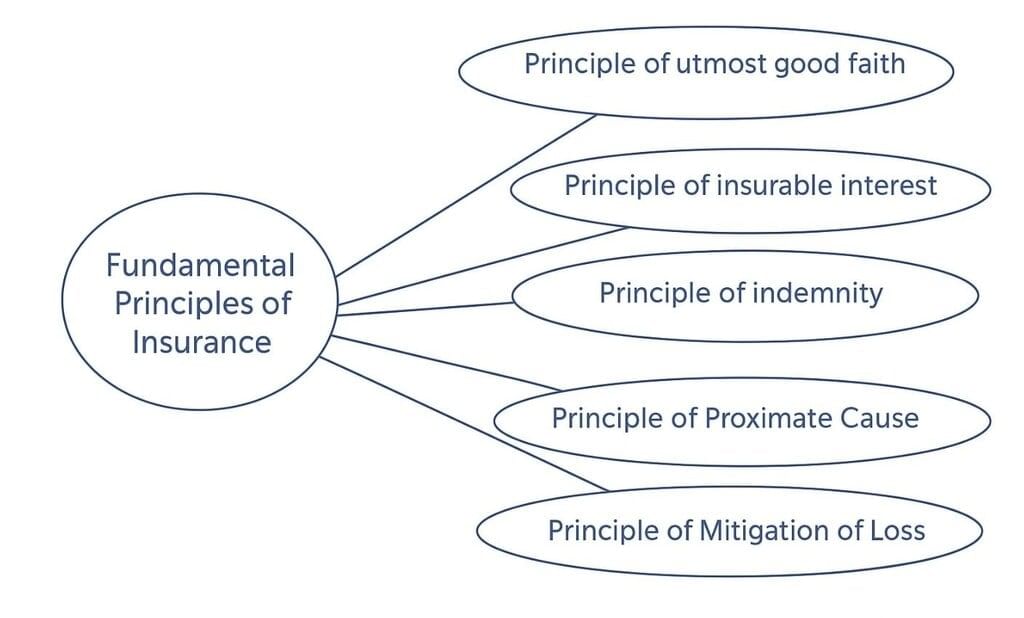
- Principle of utmost faith: It means that no material or important facts should be concealed by both parties of the insurance contract.
- Principle of Insurable Interest: There must be some pecuniary interest in the subject matter of the insurance contract.
- Principle of Indemnity: It means that the insured can get only the compensation against actual loss, and he cannot make a profit out of the insurance.
- Principle of proximate cause: It refers to the direct cause and not the remote cause.
- Principle of mitigation of loss: It states that it is the duty of the insured to take reasonable steps to minimise the loss/damage to the insured property.
Types of Insurance

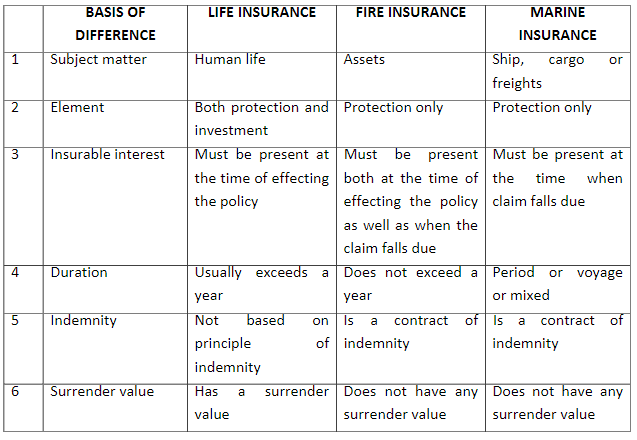
Life Insurance: It is a contract under which the insurer, in consideration of a premium, undertakes to pay a fixed sum of money on the death of the insured or on the expiry of a specified period of time, whichever is earlier.
Fire insurance: It is a contract whereby the insurer undertakes to make good any loss/damage caused by fire during a specified period.
Marine Insurance: Marine insurance is an agreement whereby the insurer undertakes to indemnify the insured against perils of the sea.
Difference between Life, Fire and Marine Insurance:
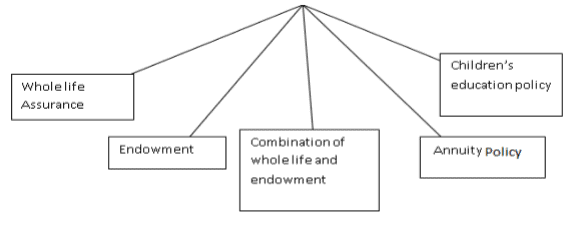
Types of Life Insurance Policies (Insurance Products)
Communication services:
These are helpful to businesses for establishing links with the outside world. The main services are postal and telecommunication.
Transportation:
It refers to the physical movement of goods from one place to another.
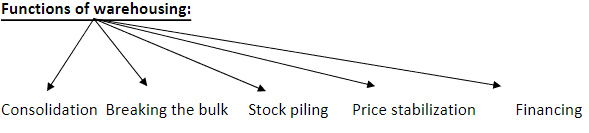
Warehousing: It refers to the activity under which goods are kept safely and systematically at a particular place.
Warehouse: It refers to a specially built building where the raw materials and finished goods are kept safely till their owner needs them.
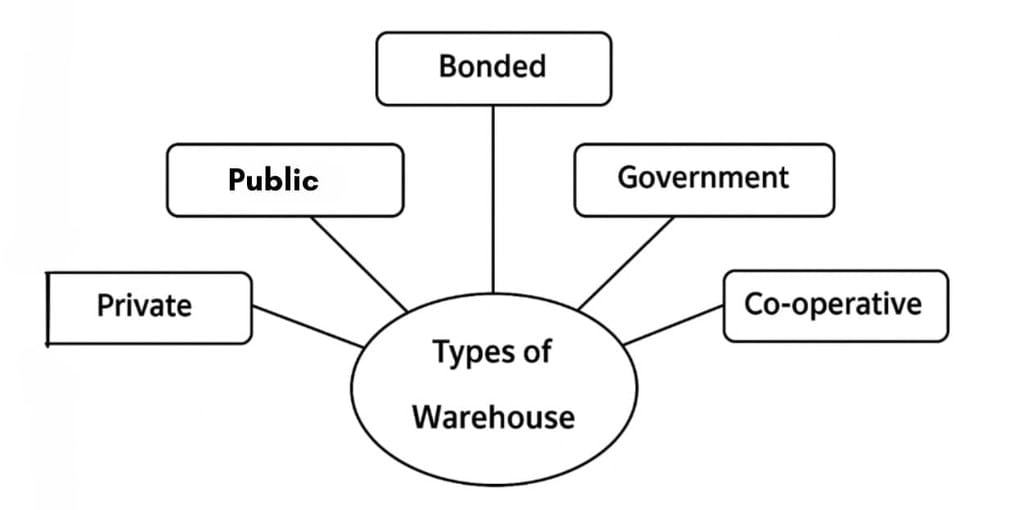
Types of Warehouses:
Postal Services
This service is required by every business to send and receive letters, market reports, parcels, money orders, etc., regularly. All these services are provided by the post and telegraph offices scattered throughout the country. The postal department performs the following services.
1. Financial Services: They provide postal banking facilities to the general public and mobilise their savings through the following savings schemes like public provident fund (PPF), KisanVikasPatra, National Saving Certificate, Recurring Deposit Scheme and Money Order facility.
2. Mail Services: The mail services offered by post offices include transmission of messages through postcards, Inland letters, envelopes, etc. The various mail services all:
- UPC (under postal certificate): When ordinary letters are posted, the post office does not issue any receipt. However, if the sender wants to have proof, then a certificate can be obtained from the post office on payment of the prescribed fee. This paper now serves as evidence of posting the letters.
- Registered Post: Sometimes we want to ensure that our mail is definitely delivered to the addressee; otherwise, it should come back to us. In such situations, the post office offers a registered post facility, which serves as proof that the mail has been posted.
- Parcel: Transmission of articles from one place to another in the form of parcels is known as parcel post. Postal charges vary according to the weight of the parcels.
Allied Postal Services
1. Greetings Post: Greetings can be sent through post offices to people at different places.
2. Media Post: Cooperatives can advertise their brands through postcards, envelopes, etc.
3. Speed Post: It allows the speedy transmission of articles (within 24 hours) to people in specified cities.
4. e-bill post: The post offices collect payments of bills on behalf of BSNL and other organisations.
5. Courier Services: Letters, documents, parcels, etc., can be sent through the courier service. As it is a private service, the employees work with more responsibility.
Telecom Services

In today’s global business world, the dream of doing business across the world will remain a dream only in the absence of telecom services. The various types of telecom services are
1. Cellular mobile services: cordless mobile communication device including voice and non-voice messages, data services and PCO services.
2. Radio Paging Services means of transmitting information to persons even when they are mobile.
3. Fixed Line Services include voice and non-voice messages and data services to establish a link for long-distance traffic.
4. Cable services, Linkages and switched services within a licensed area of operation to operate media services, which are essentially one-way entertainment-related services.
5. VSAT Service (Very Small Aperture Terminal) is a satellite-based communication service. It offers government and business agencies a highly flexible and reliable communication solution in both urban and rural areas.
6. DTH Services (Direct to Home) a satellite-based media services provided by cellular companies with the help of a small dish antenna and a setup box.
|
38 videos|180 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Business Services Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are the key features that differentiate services from goods? |  |
| 2. What are some common types of services provided by commercial banks? |  |
| 3. What are the primary functions of a commercial bank? |  |
| 4. What is a bank draft and how does it differ from a regular cheque? |  |
| 5. What is a banker’s cheque or pay order and when is it used? |  |

















