Key Notes - Accounting for partnership firms: Fundamentals | Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Learning Objectives
After studying this chapter, the student will be confident to:
- Define partnership and list its key features.
- Identify the relevant sections of the Indian Partnership Act 1932 for accounting purposes.
- Explain how profits or losses are shared among partners and prepare the Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
- Calculate interest on capital and drawings in different scenarios.
- Explain how a guarantee of a minimum profit impacts the sharing of profits among partners.
- Make necessary adjustments to correct past mistakes in partners' capital accounts.
- Prepare the final accounts of a partnership firm.
- “Partnership is the relation between two or more persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any one of them acting for all.”

Features Of Partnership
- Two or more persons:. valid partnership requires at least two individuals. As per the Companies Act, 2013, the maximum number of partners is limited to 100.
- Agreement: Partnership is formed through an agreement, which can be either written or spoken. The written agreement is referred to as the Partnership Deed, serving as the foundation of the partners' relationship.
- Existence of business and profit motive: Partnerships are established to conduct legal business with the aim of making profits. Simply owning a property together does not qualify as a partnership.
- Sharing of Profits: Partners must agree to share the profits, and sharing losses is implied in this context. If individuals collaborate on a charity, it is not considered a partnership.
- Business carried on by all or any of them acting for all: This means that each partner can be involved in managing the business and is accountable for the actions of other partners regarding the firm's business.
- Relationship of Principal and Agent: Each partner acts as both an agent and a partner. They can bind one another through their actions, making each a principal in their obligations.
Partnership Deed
Partnership arises from an agreement, so it’s crucial for all partners to agree on specific terms and conditions. These terms can be either written or spoken. The Partnership Act does not mandate a written agreement, but having one helps prevent misunderstandings and disputes. The document that outlines these terms is known as a Partnership Deed. This deed typically includes details about various aspects of the partnership, such as the business goals, each partner’s capital contribution, how profits and losses will be shared, and the partners' rights to interest on capital and loans. The clauses within the deed can be modified if all partners agree. It should be carefully drafted according to the Stamp Act and ideally registered with the Registrar of Firms.
The partnership deed is a written agreement among the partners which contains the terms of agreement. It is also called ‘ Articles of Partnership’.
A partnership deed should contain the following points:
- Name and address of the firm as well as partners.
- Name and addresses of the partners.
- Nature and place of the business.
- Duration, if any of partnership.
- Capital contribution by each partner.
- Interest on capital.
- Drawings and interest on drawings.
- Profit sharing ratio.
- Interest on loan.
- Partner’s Salary/commission etc.
- Method for valuation of goodwill and assets.
- Accounting period of the firm and duration of partnership
- Rights and duties of partners how disputes will be settled.
- Decisions taken if some partner becomes insolvent.
- Opening of Bank Account – whereas it will be in the name of firm or partners.
- Rules to be followed in case of admission & Settlement of accounts or retirement or death of partner.
- Revaluation of assets & liabilities, if any to be done.
- Method of recording of firm’s accounts Auditing
- Date of commencement of partnership
Benefits of Partnership Deed
- It regulates the rights, duties, and liabilities of each partner.
- It helps to avoid any misunderstanding amongst the partners because all the terms and conditions of partnership have been laid down beforehand in the deed.
- Any dispute amongst the partners may be settled easily as the partnership deed may be ready referred to.
Hence, it is always best course to have a written partnership deed duly signed by all the partners and registered under the Act.
Rules applicable in the absence of partnership deed
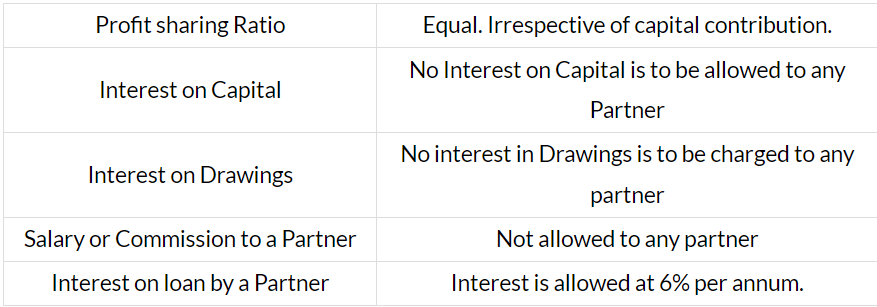
Distribution of Profits among Partners
- The transactions of a partnership firm are recorded using the principles of double-entry bookkeeping.
- A Profit and Loss Appropriation Account is prepared to display how profits are shared among partners, following the rules of the Partnership Deed or, in its absence, the Indian Partnership Act, 1932.
- This account is an extension of the Profit and Loss Account and details how profits are distributed among partners.
- It includes entries for:
- Interest on capital
- Interest on drawings
- Salary to partners
- Division of profits
- All adjustments related to a partner's salary, commission, interest on capital, and interest on drawings are handled through this account.
Partner’s Capital Accounts
It is an account which represents the partners' interest in the business.
In case of partnership business, a separate capital account is maintained for each partner. The capital accounts of partners may be maintained by any of the following two methods.
1. Fixed Capital Accounts
2. Fluctuating Capital Accounts
1. Fixed Capital Accounts: In this method, the initial amounts put in by the partners stay the same unless more capital is added through an agreement. Each partner's capital account will consistently show a credit balance, remaining unchanged yearly unless there are additions or withdrawals of capital. All transactions related to drawings, interest on capitals, interest on drawings, partner salaries, and profit or loss shares are recorded in a different account called a Current Account. Therefore, under this method, each partner has two accounts: a capital account and a current account.
2. Fluctuating Capital Accounts: This approach involves only one account per partner, which is the capital account. Adjustments such as interest on capital and interest on drawings are noted in this account, causing the balance to change over time. This is why it is termed the fluctuating capital method. The partners' capitals remain fixed unless extra capital is added or a part of the capital is withdrawn as agreed by the partners. Unless stated otherwise, the capital account should typically be set up using this method.
|
42 videos|199 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Key Notes - Accounting for partnership firms: Fundamentals - Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is a partnership deed? |  |
| 2. What are the benefits of having a partnership deed? |  |
| 3. How is the profit-sharing ratio decided in a partnership firm? |  |
| 4. Can a partner be removed from a partnership firm? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between a partnership firm and a limited liability partnership (LLP)? |  |






















