High Order Thinking Skills Questions - Introduction Micro Economics | Economics Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Q.1. Explain the properties of the Production Possibility Curve (PPC). (Delhi 2010c)
Ans. The Production Possibility Curve (PPC) has two main properties:
- Downward Sloping: The PPC slopes downwards, indicating that to produce more of one good, the production of another good must be reduced.
- Concave to the Origin: The PPC is shaped like a curve that bows outwards. This means that as production of one good increases, the opportunity cost of producing additional units of that good also increases. This reflects the law of increasing opportunity costs.
Q.2. Does massive unemployment shift the PPC to the left?Ans. Massive unemployment will shift the Production Possibility Curve (PPC) to the left due to the underutilisation of the labour force. This indicates that:
- The country's resources are idle and not being used effectively.
- Potential production in areas like farming and manufacturing is lost.
- Overall economic output is reduced, leading to a decrease in available goods and services.
Q.3. What does the slope of PPC show?
Ans. The slope of the PPC (Production Possibility Curve) shows:
- The marginal opportunity cost of producing one good over another.
- As you increase the production of one good, you must reduce the production of another.
- This reflects the trade-off between different goods in an economy.
Q.4. Unemployment is reduced due to the measures taken by the government. State its economic value in the context of the Production Possibilities Frontier. Ans. When the government takes measures to reduce unemployment, it helps the economy use its resources more effectively. This leads to:
Ans. When the government takes measures to reduce unemployment, it helps the economy use its resources more effectively. This leads to:
- Movement from inside the Production Possibilities Curve (PPC) to points on the PPC.
- Increased output and income.
Thus, the economic value is evident in the enhanced productivity of the economy.
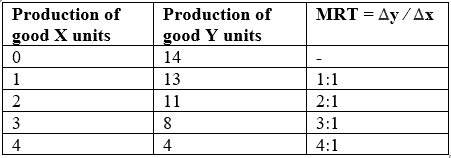
Q.5. From the following PP schedule calculate MRT of good x.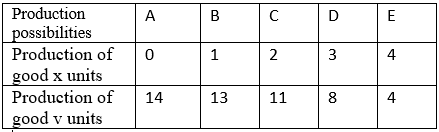
Ans. To calculate the Marginal Rate of Transformation (MRT) of good X, follow these steps:
- Identify the production possibilities of the economy for goods X and Y.
- Determine the change in the quantity of good Y that can be produced when one additional unit of good X is produced.
- Use the formula: MRT = ΔY / ΔX, where ΔY is the change in the quantity of good Y and ΔX is the change in the quantity of good X.
- The result will give you the MRT, indicating the rate at which good Y can be transformed into good X.
|
59 videos|220 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on High Order Thinking Skills Questions - Introduction Micro Economics - Economics Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are high order thinking skills in microeconomics? |  |
| 2. Why are HOTS important in microeconomics exams? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of HOTS questions in microeconomics exams? |  |
| 4. How can students develop HOTS in microeconomics? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of HOTS in the field of microeconomics? |  |






















