Symmetry Class 7 Notes Maths Chapter 12
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Line of Symmetry for Regular Polygon |

|
| Rotational Symmetry |

|
| Line Symmetry and Rotational Symmetry |

|
Introduction
Symmetry is a crucial concept found in nature and utilized across various fields. From art and design to manufacturing and architecture, symmetry plays a significant role. The word symmetry comes from the Greek word 'symmetros', which means even.
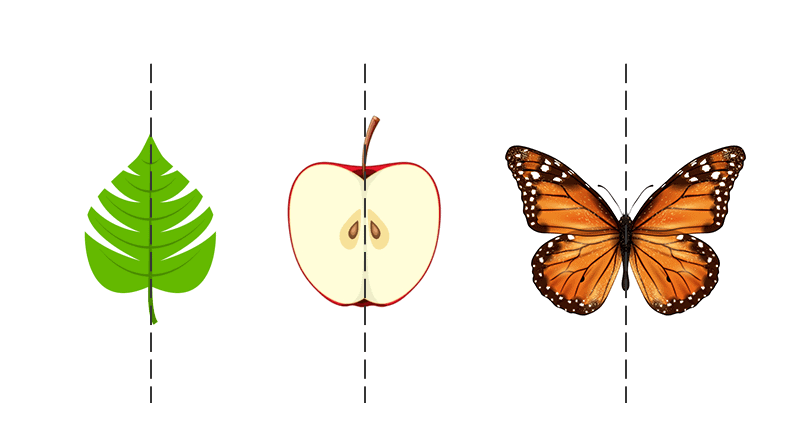 Symmetry
Symmetry
- Symmetry is a geometric concept that is found in most cases, including in nature.
- Any geometric shape can be said to be symmetric or asymmetric
- A shape is said to be symmetric if an imaginary line passes through that divides the shape into halves and these halves overlap each other completely.
- In other words, fold the shape about the imaginary line to check if the two halves completely overlap each other or not. If they overlap each other completely the shape is symmetric, if not, then it is asymmetric.
- The imaginary line is called the line of symmetry.
- The symmetry observed in the above example is called a line or bilateral symmetry.
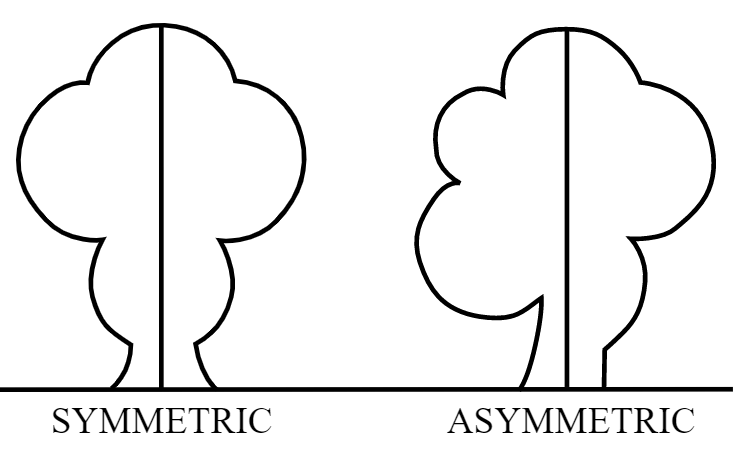
Line of Symmetry for Regular Polygon
A figure has line symmetry if a line can be drawn dividing the figure into two identical parts.The line is called the line of symmetry or axis of symmetry.
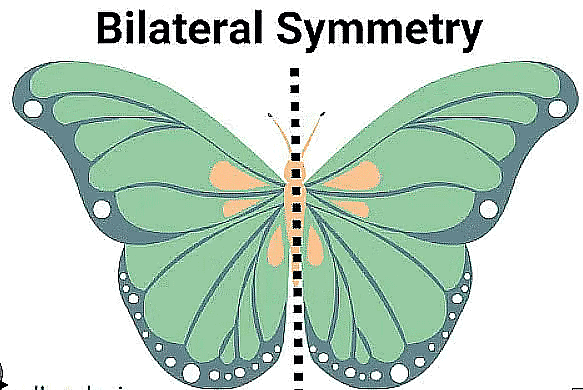 Line Symmetry Line symmetry is also known as 'reflection symmetry' because a mirror line resembles the line of symmetry, where one-half is the mirror image of the other half.
Line Symmetry Line symmetry is also known as 'reflection symmetry' because a mirror line resembles the line of symmetry, where one-half is the mirror image of the other half. Mirror Symmetry
Mirror Symmetry
Remember, while looking at a mirror, an object placed on the right appears to be on the left, and vice versa.
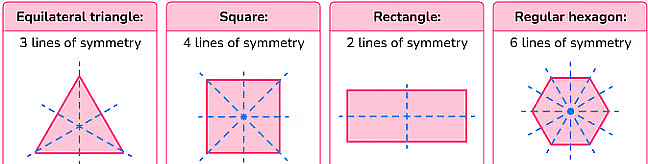
- Line segment - The perpendicular bisector is the line of symmetry.
- Equilateral triangle - Bisectors of the internal angles are the lines of symmetry.
- Square - lines of symmetry are the diagonals and the lines joining the mid-points of the opposite sides.
- Rectangle - lines joining the mid-points of the opposite sides are the lines of symmetry.
- Isosceles triangle - the perpendicular bisector of the non-equal side are line of symmetry.
A scalene triangle, in which all the sides are of different lengths, doesn't have any line of symmetry.
Example: Copy the figures with punched holes and find the axis of symmetry for the following:
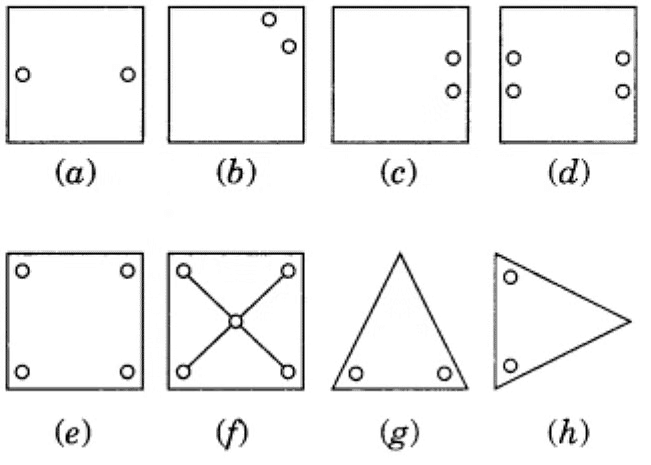
Ans: The axis of symmetry is shown by the following line.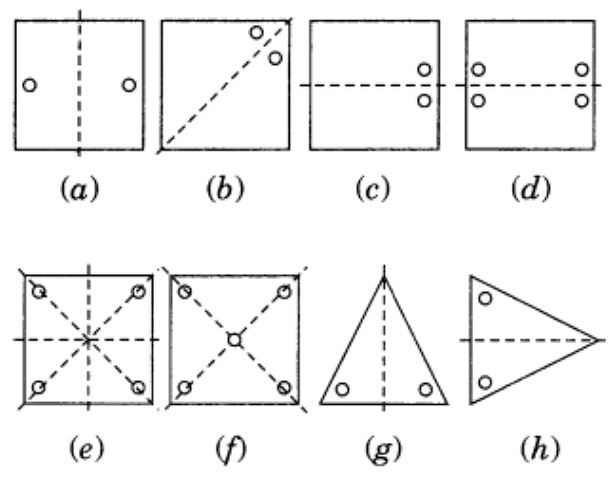
Example: Give three examples of shapes with no line of symmetry.
Ans:
- A scalene triangle has no line of symmetry.
- A non regular quadrilateral has no line of symmetry.
- Alphabet R has no line of symmetry.
Regular Polygons
A polygon is said to be a regular polygon if all its sides are equal in length and all its angles are equal in measure. Only regular polygons have lines of symmetry.
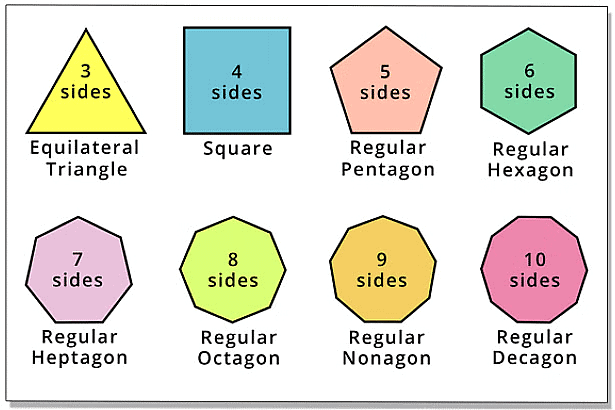 Regular Polygons
Regular Polygons
An equilateral triangle is regular because each of its sides has the same length, and each of its angles measures sixty degrees.
The number of lines of symmetry in a regular polygon is equal to the number of sides that it has.
A rectangle has two lines of symmetry, and an isosceles triangle has one line of symmetry.
A pentagon has five lines of symmetry.
Similarly, a regular octagon has eight sides, and therefore, it will have eight lines of symmetry, while a regular decagon has ten sides, so it will have ten lines of symmetry.
Example: Identify multiple lines of symmetry, if any, in each of the following figures: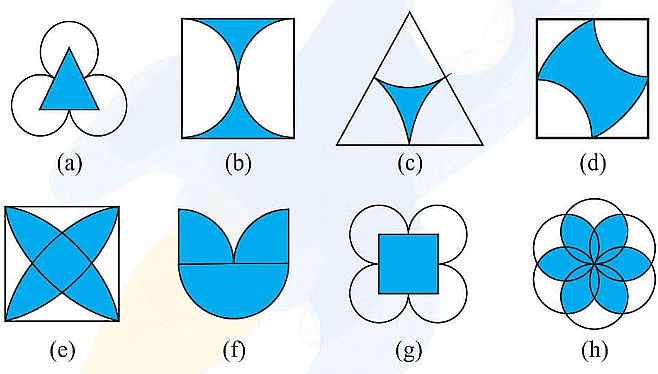
Ans: 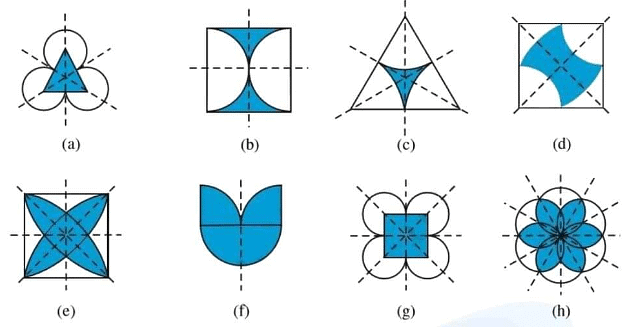 (a) It has 3 lines of symmetry.
(a) It has 3 lines of symmetry.
(b) It has 2 lines of symmetry.
(c) It has 3 lines of symmetry.
(d) It has 2 lines of symmetry.
(e) It has 4 lines of symmetry.
(f) It has 1 line of symmetry.
(g) It has 4 lines of symmetry.
(h) It has 6 lines of symmetry.
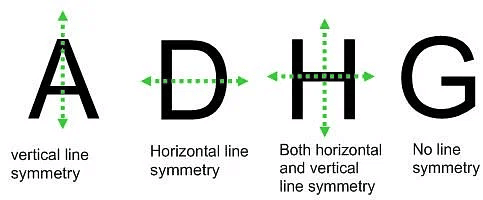
Example: What letters of the English alphabet have reflectional symmetry (i.e. symmetry related to mirror reflection) about
(а) a vertical mirror
(b) a horizontal mirror
(c) both horizontal and vertical mirrors.
Ans:
(a) Alphabet of vertical mirror reflection symmetry are A, H, I, M, O, T, U, V, W, X, Y
(b) Alphabet of horizontal mirror reflection symmetry are B, C, D, E, H, I, K, O, X
(c) Alphabet of both horizontal and vertical mirror reflection symmetry are H, I, O, X.
Irregular Polygons
If a polygon is not a regular polygon, then it is said to be an irregular polygon. Most irregular polygons do not have line symmetry. However, some of them do.
 Irregular polygons
Irregular polygons
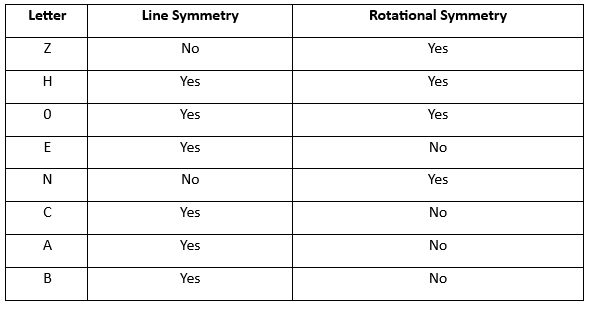
Some letters also have line symmetry.
- The letters A, B, C, D, E, I, K, M, T, U, V, W and Y have one line of symmetry.
- The letter H overlaps perfectly both vertically and horizontally. So it has two lines of symmetry. Similarly, the letter X has two lines of symmetry.
- The letters F, G, J, L, N, P, Q, R, S and Z have no line of symmetry.
 Some of the letters' lines of symmetry
Some of the letters' lines of symmetry
Rotational Symmetry
Any object or shape is said to have rotational symmetry if it looks exactly the same at least once during a complete rotation through 360o .
Rotation may be clockwise or anti-clockwise.
- A full turn refers to a rotation of 360o.
- A half turn refers to a rotation of 180o.
- A quarter turn refers to a rotation of 90o.
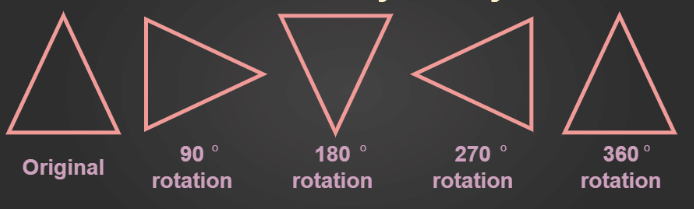 Rotational Symmetry of Triangle
Rotational Symmetry of Triangle
When identifying rotational symmetry, consider:
(i) Center of rotation: During the rotation, the object rotates around a fixed point. Its shape and size do not change. This fixed point is called the center of rotation.
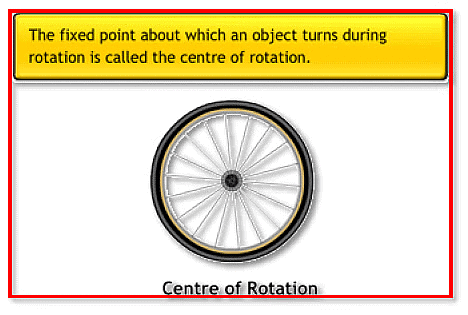
(ii) Angle of rotation: It is the angle at which a shape or an object looks exactly the same during rotation.
(iii) Direction of rotation: The direction of rotation is also referred to as the sense of rotation and indicates the direction (clockwise or anti-clockwise) in which bodies rotate around an axis.
(iv) Order of rotational symmetry: It can be defined as the number of times that a shape appears exactly the same during a full 360o rotation.
The centre of rotation of a square is its center. The angle of rotation of a square is 90 degrees, and its order of rotational symmetry is 4.
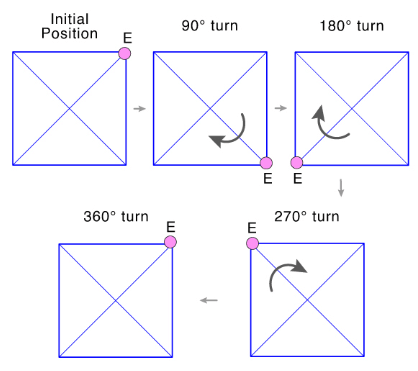 Rotation of a square
Rotation of a square
The circle is the most symmetrical figure. It has an infinite number of lines of symmetry, as any line passing through its center serves as a line of symmetry. Additionally, the circle has rotational symmetry around its center for every possible angle. The center of rotation of a circle is the center of the circle.
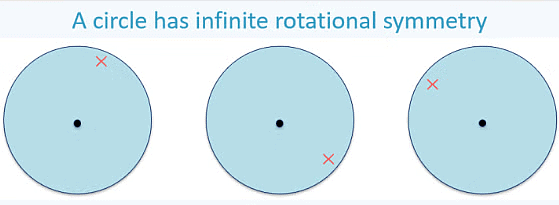 Rotation of a circle
Rotation of a circle
Line Symmetry and Rotational Symmetry
- There are many shapes that have only line symmetry and no rotational symmetry at all.
- Some objects and shapes have both, line symmetry as well as rotational symmetry.
The Ashok Chakra in the Indian national flag has both, line symmetry and rotational symmetry.
Ashok Chakra
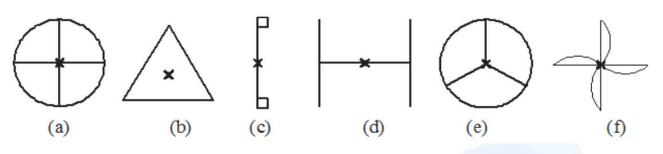
Example: Which of the following figures have rotational symmetry of order more than 1:
Ans:
(a) The given figure can be rotated four times at 90o angles each to produce the symmetrical figures. The above figure has a rotational symmetry of order 4.
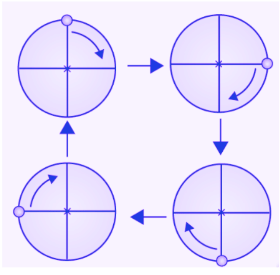
(b) The given figure can be rotated three times at 120o angles. The above figure has a rotational symmetry of order 3.
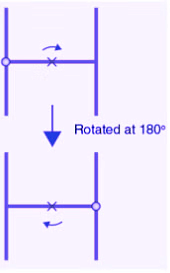
(c) The given figure can be rotated once at 180o angles each to produce the symmetrical figures. The above figure has a rotational symmetry of order 1.
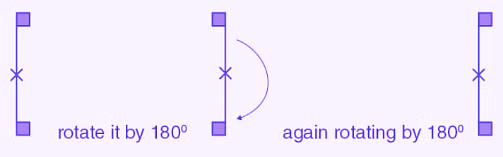
(d) The given figure can be rotated two times at 180o angles each to produce the symmetrical figures. The above figure has a rotational symmetry of order 2.
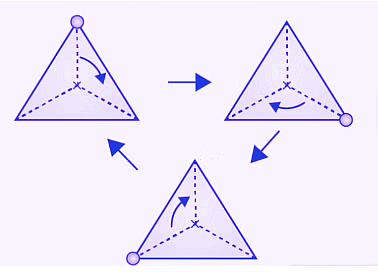
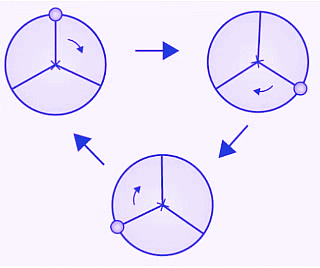
(e) The given figure can be rotated three times at 120o angles each to produce the symmetrical figures. The above figure has a rotational symmetry of order 3.
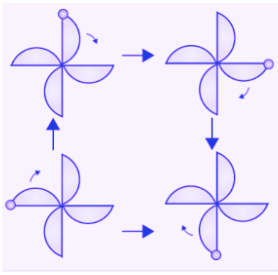
(f) The given figure can be rotated four times at 90o angles each to produce the symmetrical figures. The above figure has a rotational symmetry of order 4.
|
76 videos|386 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Symmetry Class 7 Notes Maths Chapter 12
| 1. What is line symmetry? |  |
| 2. How can you determine if a regular polygon has line symmetry? |  |
| 3. What is rotational symmetry? |  |
| 4. How do you determine the number of lines of symmetry in a regular polygon? |  |
| 5. Are all regular polygons also have rotational symmetry? |  |
















