NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science - Rights in the Indian Constitution
Q1: Write true or false against each of these statements:
(a) A Bill of Rights lays down the rights enjoyed by the people of a country.
(b) A Bill of Rights protects the liberties of an individual.
(c) Every country of the world has a Bill of Rights.
(d) The Constitution guarantees remedy against violation of Rights.
Ans:
(a) True:
The bill of rights is the first ten amendments to the constitution. They are amendments or additions to the original text. The bill of rights lays down the different rights that are to be enjoyed by the people of a country. It protects the citizen from excess government power and secures their rights. This is achieved by ensuring the separation of powers between different government branches.
 (b) True:
(b) True:
The Bill of Rights contains rights designed to guarantee the liberties of the individual. The purpose of the bill is to prevent the federal government from taking away our rights as humans and citizens when the government (state or national) does something that violates our rights it is up to the Supreme Court to use its power of judicial review to strike down the act citing the bills of rights. Only then bill of right protect outright and liberties as citizens.
(c) False:
It is not necessary for all countries to have a bill of rights. All countries with a legal and political systems similar to Australia have a Bill or Charter of Human Rights. For example, Canada, The United States, and South Africa all have a bill of rights in their constitution and the United Kingdom and New Zealand have Human Rights. Bill of rights may be fixed or flexible.
(d) True:
The constitution guarantees remedy against violations of Rights. In the Indian constitution article 32 provides constitutional remedies against the violation or transgression of fundamental rights. The fundamental rights are of the highest importance to individuals. They are basic conditions for the fullest development of personality. When any of our rights are violated we can seek a remedy through courts.
Article 32 of the Indian constitution provides for constitutional remedies against the violation or transgression of fundamental rights. The fundamental rights are of the highest importance to individuals. They are basic conditions for the fullest development of personality.
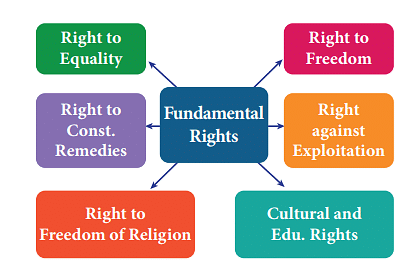
Q2: Which of the following is the best description of Fundamental Rights?
(a) All the rights an individual should have.
(b) All the rights given to citizens by law.
(c) The rights given and protected by the Constitution.
(d) The rights given by the Constitution that cannot ever be restricted.
Ans: (c)
- Fundamental Rights are the basic rights of the people and the charter of rights contained in part III of the constitution of India.
- Taking the example of India, it guarantees civil liberties such that all Indians can lead their lives in peace and harmony as citizens of India.
- These include individual rights common to most liberal democracies such as equality before the law, freedom of speech and expression, religious and cultural freedom, freedom to practice religion, etc.
- Mainly it also has constitutional remedies for protection of the civil rights by means of writs such as Habeas Corpus, Mandamus, Prohibition, Certiorari, and Quo Warranto. Violation of these rights results in punishment as prescribed in the Indian Penal code or other special laws, subject to the discretion of the judiciary.
- The fundamental rights are defined as basic human freedoms that every citizen of India has the right to enjoy for proper and harmonious development of personality.
Q3: Read the following situations. Which Fundamental Right is being used or violated in each case and how?
(a) Overweight male cabin crew are allowed to get promotion in the national airlines but their women colleagues who gain weight are penalized.
(b) A director makes a documentary film that criticizes the policies of the government.
(c) People displaced by a big dam take out a rally demanding rehabilitation.
(d) Andhra society runs Telugu medium schools outside Andhra Pradesh.
Ans:
(a) Overweight male cabin crew are allowed to get promotion in the national airlines but their women colleagues who gain weight are penalized. The right being violated in this situation is the right to equality, specifically, the right to equality of opportunity in employment. As in the Right to Equality, it is mentioned that all the citizens are considered equal in all aspects of life. Nobody should be discriminated against on the basis of sex, caste creed, and color etc.
(b) A director makes a documentary film that criticizes the policies of the government. In this situation, the right being used is the freedom of speech and expression. As the director makes a documentary in which he goes against the government by criticizing the policies of the government freely.
(c) People displaced by a big dam take out a rally demanding rehabilitation. In our constitution, the right to reside and settle in any part of India is given to the citizens in Right to Freedom People have to right to take out rallies and assemble peacefully. But the government can maintain law and order impose some restrictions on such rally if it creates violence or disturbance in the working of the government. In this case, central and educational rights are being inviolate.
(d) All linguistic minorities can set up their own educational institutions to preserve and develop their own culture. The right being used is the Cultural right to represent and protect one’s own language and culture. Thus, the Andhra Society has every right to run Telugu medium schools outside Andhra Pradesh.
Q4: Which of the following is a correct interpretation of the Cultural and Educational Rights?
(a) Only children belonging to the minority group that has opened educational institutions can study there.
(b) Government schools must ensure that children of the minority group will be introduced to their belief and culture.
(c) Linguistic and religious minorities can open schools for their children and keep it reserved for them.
(d) Linguistic and religious minorities can demand that their children must not study in any educational institution except those managed by their own community.
Ans: (b)
Linguistic and religious minorities can open schools for their children and keep it reserved for them, which is the correct interpretation of Cultural and Educational Rights.
In the Indian constitution, Article 29 (i) provides that any sections of the citizens residing in the territory of India or any part thereof having a distinct language, script, or culture of its own shall have the right to conserve the same. The article also protects the interest of minorities in India. According to Article 29 (ii) no citizen of India shall be denied admission into any government institution or government-aided institution.
Article 80 provides that all minorities whether based on religion or language shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice. The state shall not grant aid to these institutions, which discriminate against any Educational institutes.
So linguistic and religious minorities can open schools for their children and keep it reserved for them. It is a correct interpretation.
Q5: Which of the following is a violation of Fundamental Rights and why?
(a) Not paying minimum wages
(b) Banning of a book
(c) Banning of loudspeakers after 9 pm.
(d) Making a speech
Ans: (a)
- Not paying minimum wages is a violation of Fundamental Rights as it is a form of exploitation of the labor and not providing him his minimum wage and also because this violation of this act comes under the Rights against exploitation in the Indian constitution.
- In our country, there are millions of people who are underprivileged and deprived.
- Beggar of forced labor-without payment or not paying the minimum wages or some form of bonded labor- these are the examples of such exploitation.
Q6: An activist working among the poor says that the poor don't need Fundamental Rights. What they need are Directive Principles to be made legally binding. Do you agree with this? Give your reasons.
Ans: Any answer supported with an argument or explanation would solve the purpose. It is strongly recommended that you prepare the solution on your own. However, one sample solution has been provided for your reference:
- No, I do not agree with this statement. Fundamental Rights cannot be denied to any section of the society and this is applicable to the poorer sections as well. While implementation of directive principles is required for improving the condition of the poor, fundamental rights are universal as they ensure dignity to every citizen and form the basis for equality among people.
- Certain rights like the right to constitutional remedy are important to secure protection for the poorest and weakest sections of the society from the arbitrary action of the state.
- Enforcement of directive principles is important for ensuring social, economic and political justice. However, freedom of expression is still required to raise voice against any form of discrimination or injustice.
Q7: Several reports show that caste groups previously associated with scavenging are forced to continue in this job. Those in positions of authority refuse to give them any other job. Their children are discouraged from pursuing education. Which of their Fundamental Rights are being violated in this instance?
Ans:
- Fundamental right against exploitation, such as prohibition of forced labour, is violated in this situation by forcing certain castes to continue in the same job that is associated with their caste.
- Right to practice any profession is violated as they are refused any other jobs by the authorities.
- Prohibition of employment of children in hazardous jobs is also violated in this instance.
Q8: A petition by a human rights group drew the attention of the court to the condition of starvation and hunger in the country. Over five crore tonnes of food grains were stored in the godowns of the Food Corporation of India. Research shows that a large number of ration cardholders do not know about the quantity of food grains they can purchase from fair-price shops. It requested the court to order the government to improve its public distribution system.
(a) Which different rights does this case involve? How are these rights interlinked?
(b) Should these rights form part of the right to life?
Ans:
(a)
(i) The case involves the use of Right to speech and expression and constitutional remedy. These rights were used by the human rights group to inform the court about the prevailing condition of hunger and starvation, thus requesting the court to order the government to improve public distribution system.
(ii) The right to life of people is also invoked to address hunger and starvation.
(iii) These rights are interlinked as freedom of speech provides the basis for constitutional remedies.
(b) Yes, these rights should form part of the right to life as they are necessary for the sustenance of people.
Q9: Read the statement by Somnath Lahiri in the Constitutent Assembly quoted in this chapter. Do you agree with him? If yes, give instances to prove it. If not, give arguments against his position.
Ans: Any answer supported with an argument or explanation would solve the purpose. It is strongly recommended that you prepare the solution on your own. However, one sample solution has been provided for your reference:
 Somnath LahiriYes. Somnath Lahiri said that minimum rights have been conceded and are almost invariably followed by a proviso and have been framed from the point of view of the police constable. This is visible in certain provisions that are invoked to place restrictions on fundamental rights.
Somnath LahiriYes. Somnath Lahiri said that minimum rights have been conceded and are almost invariably followed by a proviso and have been framed from the point of view of the police constable. This is visible in certain provisions that are invoked to place restrictions on fundamental rights.
- The provision of preventive detention contradicts the right to life and personal liberty and has often been misused by the government.
- There are several rights under the right to freedom that are restricted by the government in various ways. For example, the provision of restriction over the assembly of five or more people in certain areas can be misused by the administration.
Q10: Which of the Fundamental Rights is in your opinion the most important right? Summarise its provisions and give arguments to show why it is most important.
Ans: The right to constitutional remedies is the most important right. The provisions of this right include the right to move the courts for issuance of writs. The Supreme Court and High Courts can issue directives to the government for the implementation of rights. The special orders issued by courts for enforcement of rights are as follows:
Habeas Corpus: The court can order the arrested person to be presented before it under the writ of Habeas Corpus. It can also order the release of a person arrested on unlawful grounds.
Mandamus: This writ is issued by courts when a particular office does not perform the assigned legal duty and violates the rights of the individual.
Prohibition: This writ is issued by a higher court when a case is beyond the jurisdiction of the lower court.
Quo Warranto: This writ is issued by the court when it finds an individual holding the office, which is not entitled to him.
Certiorari: The court orders the transfer of a pending matter from a lower court or another authority to the higher court.
The Right to Constitutional Remedies provides a legal solution within the framework of the constitution, to the violation of fundamental rights and provides a check on state power.
This is the most important right as it safeguards the other fundamental rights.
It ensures the realization of other rights as well as providing a defense for them. According to Dr. Ambedkar, this right is the 'Heart and Soul of the Constitution.
|
44 videos|202 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science - Rights in the Indian Constitution
| 1. What are the fundamental rights guaranteed by the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 2. Can fundamental rights be suspended in India? |  |
| 3. How can an individual enforce their fundamental rights in India? |  |
| 4. Are there any limitations to fundamental rights in India? |  |
| 5. Can non-citizens of India avail fundamental rights? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Humanities/Arts exam
|

|













