Class 6 Geography Chapter 5 Notes - Water
| Table of contents |

|
| How much Water do we Use? |

|
| Water Cycle |

|
| What happens if it does not rain for a long period? |

|
| What if it Rains Heavily? |

|
| Rainwater Harvesting |

|
How much Water do we Use?
It is common knowledge that water is important on our Earth and without water, life as we know it would cease to exist. While Earth has an abundant reservoir of water, covering three-fourths of its surface, freshwater is a mere 2.6% of the total water. Water is said to be a renewable resource but the rate at which humans and animals are using water, fresh water might be a scarce resource in the recent future. Our body is also made up of 70% water and we use water for a number of reasons from cooking to cleaning and of course drinking it.
Water Cycle
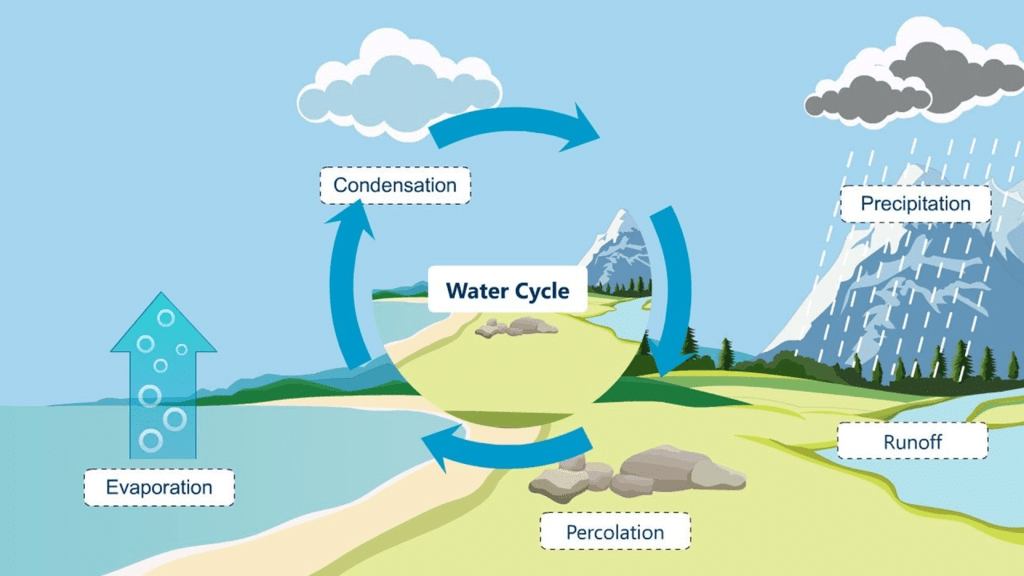
Water cycle is defined as the process through which water gets evaporated from open surfaces like oceans and seas, gets condensed as it rises in cool atmosphere and ultimately pours down as rain back into oceans, lakes, rivers and ponds.
Disappearing Trick of Water
Evaporation: The process of conversion of water into its gaseous state i.e. vapours is known as evaporation. The water present on the surface of the ocean evaporates by the sun's heat. The sun warms up the surrounding air as well. Evaporation takes place faster in direct sunlight, than in a shady area. Evaporation also takes place from wet clothes, fields, ponds, lakes and rivers. A variety of salts, like sodium chloride, calcium, magnesium and potassium, are left behind during the process of evaporation.
Condensation: The process of conversion of vapours into water is referred to as condensation.
Loss of Water by Plants
Plants take in water to grow as well as to prepare their food. They retain the water they need and release the excess water into the air as water vapour through the stomata of the leaves and the stem. This process is called transpiration.
Thus, water is mainly evapo-transpirated to the air from land, water bodies and plants.
How are clouds formed?
The evaporated water is carried away by warm air. As the warm air moves higher from the surface of the Earth, it starts to cool down. It is because the water vapour present starts to condense to form tiny water droplets. These droplets float in the air and form clouds and fog. Back to the Oceans
All these droplets collect to form bigger drops of water. Some of them may become too heavy to remain in the sky and fall down as rain. This process is known as precipitation. If the air is too cold, the water drops can become snow or hail and may settle on the top of a mountain. When this snow or hail melts, it can become part of a river or a stream.
Thus, the water that is evaporated from the oceans or seas is again condensed to form water and fills up the rivers and seas. Rainwater also seeps into the ground to form groundwater. Thus, the water cycle is a continuous process.
Uses of Water
Water is used in our day to day life. Water is used for everyday needs such as brushing, bathing, washing, cleaning etc. Farmers use groundwater to water their fields.
Many industries use groundwater to produce everything from paints and fabric to leather and chemicals. So groundwater is used for many purposes. Moreover, the decline in the number of trees, excess usage of water and the presence of concrete in the areas does not allow the rainwater to seep into the ground which is the reason for the shortage of water.
What happens if it does not rain for a long period?
Droughts
Due to lack of rains the wells, lakes, ponds get dried up and thereby creating water scarcity and as result droughts are possible. If there are no rains, then the soil becomes more dry and patchy. Droughts occur when there are no rains for a longer period of time. There is less rainfall because trees are cut down.
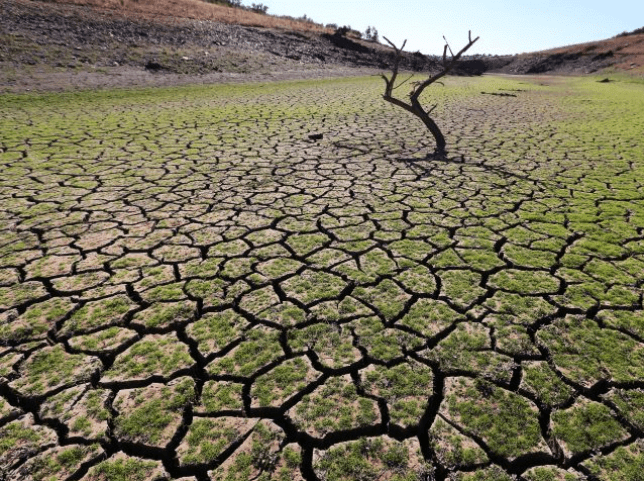 Dried Fields as a result of Droughts
Dried Fields as a result of Droughts
Droughts result in the drying up of the crops and vegetation and this affects the availability of food for villages and food for the other animals. Finally, this leads to malnutrition in humans.
What if it Rains Heavily?
Floods
Due to heavy rainfall the water levels in ponds, lakes rises to a greater extend and the rise in the water level of these water bodies causes the excess water to spread across causing floods.
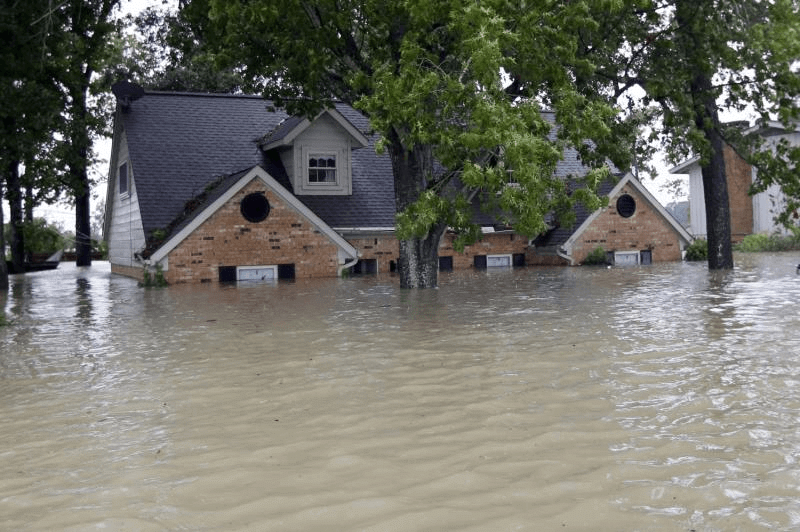 FloodsFloods wash out living beings such as fish and other animals etc. and they create great havoc to mankind. Once the rains stop the flood water receded, fish, cattle and other animals were left dead. Floods cause a lot of harm to the living beings and there will be loss of property also.
FloodsFloods wash out living beings such as fish and other animals etc. and they create great havoc to mankind. Once the rains stop the flood water receded, fish, cattle and other animals were left dead. Floods cause a lot of harm to the living beings and there will be loss of property also.
Rainwater Harvesting
Harvesting is a method to collect rainwater and store the rainwater. The purpose of harvesting rainwater is that two-thirds of the earth is covered with water. Ocean and seawater contain many dissolved salts and cannot be used for drinking, agriculture and domestic purposes. So constant use of groundwater results in scarcity of groundwater. So rain harvesting clears the problem of depleting the groundwater.
 Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater Harvesting
Technique involved in Rainwater Harvesting
First, collect the rainwater at the rooftop and then allow the rainwater to travels through the pipes or drains and then attach a wire mesh to the mouth pipe which filters large fragments such as leaves etc. This water is transported to the water tanks. These tanks contain layers of sand, gravel, charcoal that will filter the dirt and other impurities from rainwater.
Advantages
The benefits of the rainwater harvesting system are listed below.
- Less of cost.
- Helps in reducing the water bill.
- Decreases the demand for water.
- Reduces the need for imported water.
- Promotes both water and energy conservation.
- Improves the quality and quantity of groundwater.
- Does not require a filtration system for landscape irrigation.
- This technology is relatively simple, easy to install and operate.
- It reduces soil erosion, stormwater runoff, flooding, and pollution of surface water with fertilizers, pesticides, metals and other sediments.
- It is an excellent source of water for landscape irrigation with no chemicals and dissolved salts and free from all minerals.
Disadvantages
In addition to the great advantages, the rainwater harvesting system has few disadvantages like unpredictable rainfall, unavailability of the proper storage system, etc.
Listed below are few more disadvantages of the rainwater harvesting process.
- Regular Maintenance is required.
- Requires some technical skills to install.
- Limited and no rainfall can limit the supply of Rainwater.
- If not installed correctly, it may attract mosquitoes and other waterborne diseases.
- One of the significant drawbacks of the rainwater harvesting system is storage limits.
|
237 docs|47 tests
|
FAQs on Class 6 Geography Chapter 5 Notes - Water
| 1. How much water do we use? |  |
| 2. What is the water cycle? |  |
| 3. What happens if it does not rain for a long period? |  |
| 4. What if it rains heavily? |  |
| 5. What is rainwater harvesting? |  |





















