Motion and Measurement of Distances Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 7
| Table of contents |

|
| Story of Transport |

|
| Measuring Length and Distance |

|
| Some Measurements |

|
| Measuring the Length of a Curved Line |

|
| Types of Motion |

|
| Frequently Asked Questions |

|
Wherever there is a change in the position of the object or body we termed it as motion. Whereas the case of measurement has different concepts with respect to motion. In the case of measurement, we quantify objects or anything.
Example: distance of your school from your home.
Story of Transport
- Before the invention of the wheel, the only means of transportation was walking. For transporting goods, people used animals like donkeys, horses, mules, elephants, oxen, sled dogs, and even bison.
- Boats were also used as a means of transportation on water. The earliest boats were simple logs of wood with a hollow cavity.
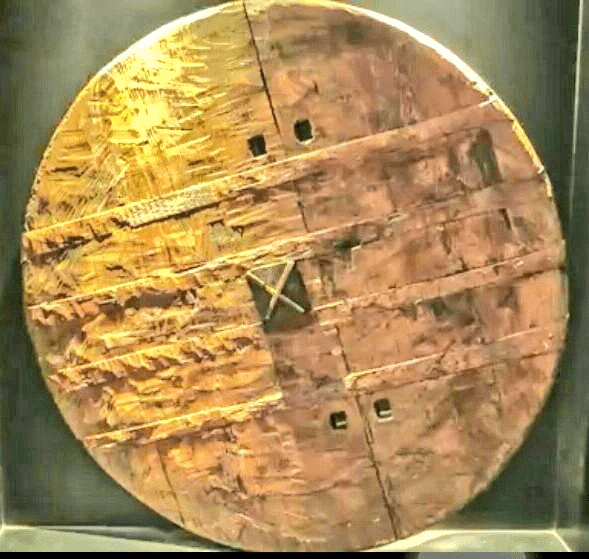 Oldest Wheel
Oldest Wheel
- The oldest wheel was discovered in Mesopotamia and is believed to be over 5,500 years old. Fixed wheels for carts were invented around 3500 BC, according to some historians.
- After the invention of the wheel, man started using animals to pull vehicles that moved on wheels, and thus, bullock carts and chariots came into existence.
- Till the 19th century, most forms of transport used only animals. The bicycle was invented in the late 18th century bicycles.
- Later on, motors were fitted to bicycles, and thus, mopeds came into existence. Further research and development led to the invention of the motor car.
- The steam engine and the railroad were invented in the 19th century. Apart from these, motorized boats and ships were used as a means of water transport. Roads, railroads, and water remained the major means of transport for a very long time.
- The Wright brothers invented the airplane and gave the world another means of transport - airways. In his effort to explore his universe, a man even stepped into space and invented the spaceship to travel in space.
- There are various means of transport, such as roads, railways, waterways, and airways. The mode of transport can be chosen, usually depending upon the distance to be traveled, but sometimes also upon how fast you want to get to your destination.
 Modes of Transport
Modes of Transport
Measuring Length and Distance
- Various means of measurement, such as the palms, fingers, arm length and feet, were used to measure length and distance before standardized systems were introduced.
- Distance is the measure of how far or long something is. For example, the length of a table or a soccer field or, how far is Mumbai from Delhi?
Standards need to be set to ensure consistency and to standardize measurements.
Some Measurements
- Length can be measured in terms of a unit.
- A unit is a comparison of an unknown quantity with that of a known quantity.
- It is required to establish a common standard or convention in order to make calculations and analysis easier worldwide.
Standard Units of Measurement
- In ancient times, various body parts were used as units of measurement, such as the foot, finger, and step.
- The Indus valley civilization used precise measurements of length, as evidenced by excavations of geometrical constructions.
- The cubit, which is the length from the elbow to the fingertips, was used in ancient Egypt and other parts of the world. The foot was also commonly used as a unit of length, although its measurement varied slightly from region to region.
- The Romans measured with their pace or steps.
- In ancient India, small length measurements were based on body parts like the finger or fist. Even today, body parts are used as units of length in certain situations.
- In 1790, the French introduced the metric system as a standard unit of measurement.
- Scientists worldwide have accepted the International System of Units (SI units) for uniformity, with the meter as the SI unit of length.
- The meter is divided into 100 equal divisions called centimeters, and each centimeter has ten equal divisions called millimeters.
- For measuring large distances, the kilometer is used as a larger unit of length, where 1 kilometer is equal to 1000 meters.
- Using standardized scales and measuring in SI units allows for consistency and accuracy in measurements.
 Measuring the width of a table with a handspan
Measuring the width of a table with a handspan
Correct Measurement of Length
- A ruler is used to measure the length of an object. It is also used to measure the length of a straight line.
- A ruler is used to measure the length of an object. It is also used to measure the length of a straight line. A non-stretchable string or thread is used to measure the length of a curved line.
Procedure to Measure the Length of an Object (or) a Straight Line:
- First place the ruler along the edge of the object that is to be measured, with the zero mark of the ruler placed at one end of the object.
- On the ruler, note the reading at the other end of the object.
- Correct position of the eye is also important for taking measurement. Your eye must be exactly in front of the point where the measurement is to be taken.
- This gives the measure of the length of the object.
- The same procedure can be followed to measure the length of a straight line.
Accuracy
Whatever method you use, always look at the ruler with the eyes directly in the line with the reading and not in an oblique way to obtain the readings accurately.
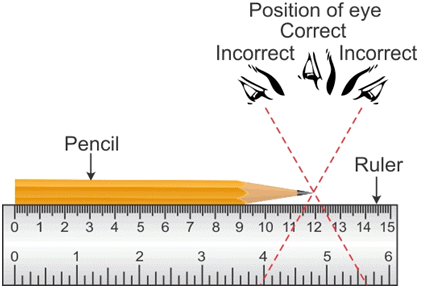 Proper position of the eye for taking reading of the scale
Proper position of the eye for taking reading of the scale
Measuring the Length of a Curved Line
It is not possible to directly measure the length of a curved line using a meter scale. A thread can be used as an alternative method to measure the length of a curved line.
Procedure to Measure the Length of a Curved Line:
- Take a non-stretchable string or a thread and tie a knot at one of its ends.
- Place the knotted end of the thread at one end of the curved line.
- Holding the thread steadily with your fingers, and stretch it along the curved line until you reach the other end.
- Now make a mark on the thread where it reaches the other end.
- Finally, place the thread along a metre scale and measure the length between the knot and the marked point.
- This gives the length of the curved line.
- Length is one of the fundamental quantities.
Moving Things Around Us
Rest
- When a body remains in one position for a long time, it is said to be at rest.
- For example, the chairs of the dining table are at rest unless and until they are moved, and the flower vase, table, and the blackboard in the classroom are all at the position of rest.
Motion
- The act, process or state of the change in place or position of a body with respect to time and relative to the observer is said to be motion.
- For example, the blades of a rotating fan, the hands of a working wall clock, a moving car, a spinning top and satellites are all in motion.
Rest and Motion are Relative Terms
- A body seems to be at rest with respect to one object but may appear to be in motion with respect to some other object.
- For example, a person on a railway platform is at rest with respect to another person on the same platform but is in motion with reference to a person looking at him from a train crossing that platform.
- Similarly, a passenger sitting in the train will appear at rest to another passenger on the same train.
Types of Motion
The various types of motion are:
1. Rectilinear Motion
- Rectilinear motion is the motion of an object that moves in a straight line. For example, a train moving on a track, a parade, coins tossed in the air are all in rectilinear motion.
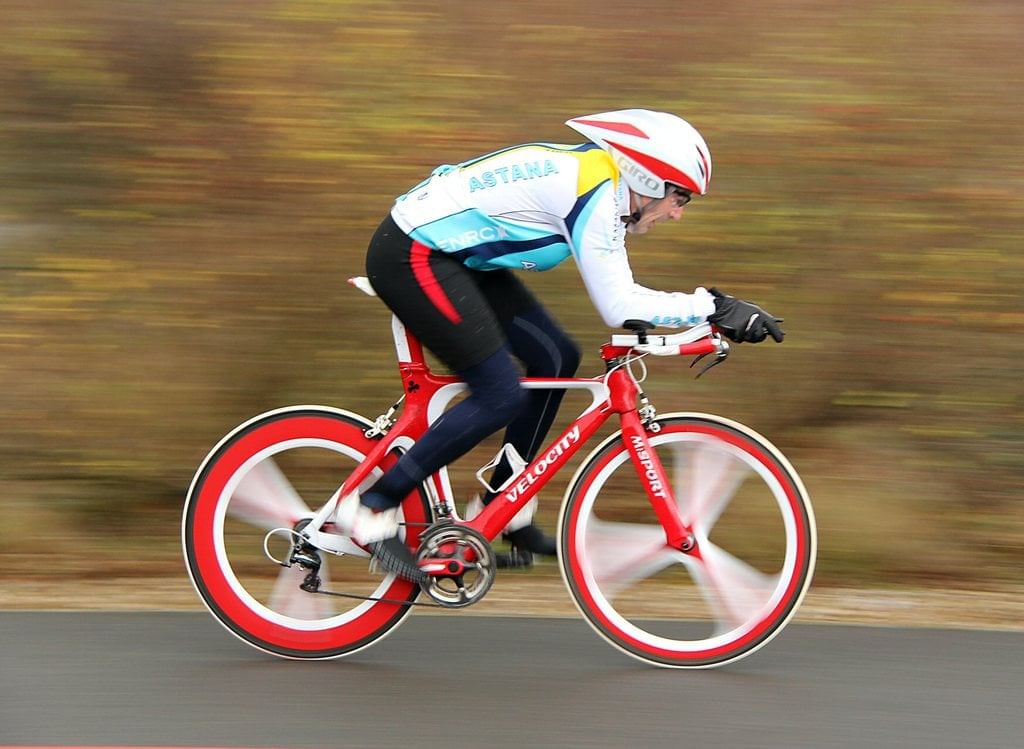 Bike moves in a rectilinear position
Bike moves in a rectilinear position
2. Circular Motion
- Circular motion is the motion of an object that moves at a fixed distance from a fixed point. Here, all objects rotate in a circular motion. So, circular motion is a motion in which the body traverses a circular path. The hands of a clock, a merry-go-round, the blades of a fan, the wheel of a moving vehicle, satellites, a spinning top, are all good examples of circular motion.
 A fan shows circular motion
A fan shows circular motion
3. Periodic Motion
- Periodic motion is a motion that repeats itself at regular intervals of time. Every body executing circular motion can be said to be executing periodic motion. For example, the pendulum of a wall clock moves at regular intervals, the bells in a church, a bouncing ball, a vibrating string and a swinging cradle are all in periodic motion.
 Pendulum shows periodic motion
Pendulum shows periodic motion
- A moving car that moves straight on the road displays rectilinear motion but at the same time, the wheels of the car which are moving in circles display circular motion. So a moving car displays both rectilinear and circular motion.
- In a sewing machine, the needle is in periodic motion whereas the wheels of the sewing machine are in a circular motion. So a sewing machine displays circular and periodic motions.
- If a body does not change its position with respect to time, then it is said to be at rest. If a body changes its position with respect to time, then it is said to be in motion. There are different types of motion. Rest and motion are relative terms. If you consider a passenger in a moving train, he is at rest with respect to his co-passengers but is in motion with respect to an observer on the ground.
- There are many examples of bodies that are relatively at rest. Trees, buildings and mountains are some examples of bodies that are relatively at rest with respect to each other. Some examples of bodies in motion are flying birds, moving trains, and the rotating blades of a ceiling fan.
- There are different types of motion. They are rectilinear motion, circular motion and periodic motion.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1. Why is it important to know how far a place is?
It is important to know how far a place is, so that we can have an idea how we are going to reach that place – walk, take a bus or train, a ship, an aeroplane or even a spacecraft.
Q.2. What is estimation?
To guess the dimensions of an object without actual measuring is known as estimation. It is difficult to make near about correct estimate. It needs a lot of experience.
Q.3. Explore and find out what kind of scale is used by cloth merchants, tailors, carpenters and mechanics to measure length.
The kind of scale used by:
- Cloth merchants use iron/steel metre scale.
- Tailors use plastic metre scale tape.
- Carpenters use plastic metre tape and iron metre scale both.
|
70 videos|150 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on Motion and Measurement of Distances Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 7
| 1. How can we measure the length of a curved line? |  |
| 2. What are some standard units of measurement used for length and distance? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of motion that objects can exhibit? |  |
| 4. How do we ensure the correct measurement of length when using a ruler or measuring tape? |  |
| 5. What are some common measurements that can be taken using length and distance? |  |
















