NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science - Electricity and Circuits
Q1: Fill in the blanks:
(a) A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called _______________.
(b) An electric cell has _______________ terminals.
Ans:
(a) A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called a switch.
(b) An electric cell has two terminals.
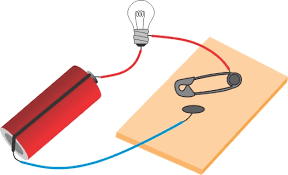 Simple switchQ2: Mark 'True' or 'False' for the following statements:
Simple switchQ2: Mark 'True' or 'False' for the following statements:
(a) Electric current can flow through metals.
Ans: True
(b) Instead of metal wires, a jute string can be used to make a circuit.
Ans: False
(c) Electric current can pass through a sheet of thermo Col.
Ans: False
Q3: Explain why the bulb would not glow in the arrangement shown in Fig. Ans: The handle of the screw is made up of an insulator, which does allow to current to flow. That is why the bulb is not glowing.
Ans: The handle of the screw is made up of an insulator, which does allow to current to flow. That is why the bulb is not glowing.
Q4: Complete the drawing shown in Fig. to indicate where the free ends of the two wires should be joined to make the bulb glow.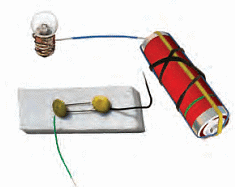 Ans:
Ans:

Q5: What is the purpose of using an electric switch? Name some electrical gadgets that have switches built into them.
Ans: An electric switch serves the purpose of either opening or closing an electric circuit for a specific appliance. This allows us to control the usage of an appliance, turning it on or off as needed. The switch provides a convenient way to manage the flow of electricity to the appliance, offering control and ease of use. Common devices with built-in switches include lights, fans, and televisions.
Q6: Would the bulb glow after completing the circuit shown in Fig. if instead of safety pin we use an eraser?
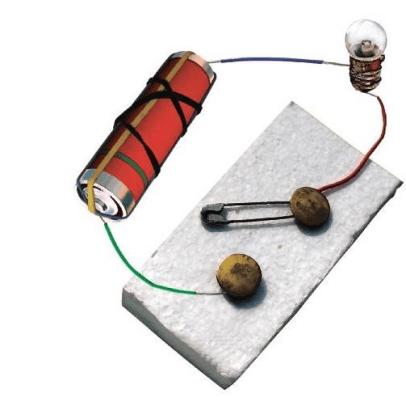
Ans: No, since the eraser is an insulator it does not allow the current to pass. Hence the bulb will not glow.
Q7: Would the bulb glow in the circuit shown in Fig?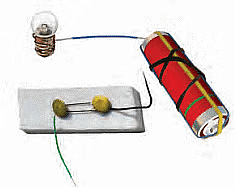
Ans: No, the bulb will not glow.
Q8: Using the "conduction tester" on an object it was found that the bulb begins to glow. Is that object a conductor or an insulator? Explain.
Ans: If an object is a good conductor of electricity, the current will flow through a conduction tester, causing the bulb to glow. Therefore, the object can be identified as a conductor of electricity. The conductivity test using the bulb glow is a simple and effective way to determine whether a material allows the passage of electric current.
Q9: Why should an electrician use rubber gloves while repairing an electric switch at your home? Explain.
Ans: As our body is a good conductor of electricity and rubber acts as an insulator, accidents can occur when the body comes into contact with a current-carrying wire during repair work. To prevent such accidents, electricians use rubber gloves, which do not allow the passage of electric current. This protective measure ensures the electrician's safety while working on an electric switch.
 Rubber gloves for repairing electric switch
Rubber gloves for repairing electric switch
Q10: The handles of the tools like screwdrivers and pliers used by electricians for repair work usually have plastic or rubber covers on them. Can you explain why?
Ans: Plastic or rubber, being insulators, prevents the flow of electric current. To ensure safety, electricians use tools like screwdrivers and pliers with handles covered in plastic or rubber. This covering prevents electric current from passing through the tools to the electrician's body, protecting them from harm.
|
70 videos|150 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science - Electricity and Circuits
| 1. What is an electric circuit and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of electric circuits? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between conductors and insulators? |  |
| 4. How do you calculate the total resistance in a series circuit? |  |
| 5. What is Ohm's Law and how is it used in circuits? |  |






















