Light Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 13
| Table of contents |

|
| Light Travels Along a Straight Line |

|
| Reflection of Light |

|
| Playing With Spherical Mirrors |

|
| Images Formed by Lens |

|
| Sunlight - White or Colored? |

|
Have you noticed sunlight shining into a room through a small hole, or the bright lights from a car at night? These beams of light help us see and show how light travels. Let's learn more about how light works and why it’s important!
What is light?
Light is a form of energy that allows us to see the world around us. It travels in straight lines and can move through different mediums like air, water, and glass.
Light Travels Along a Straight Line
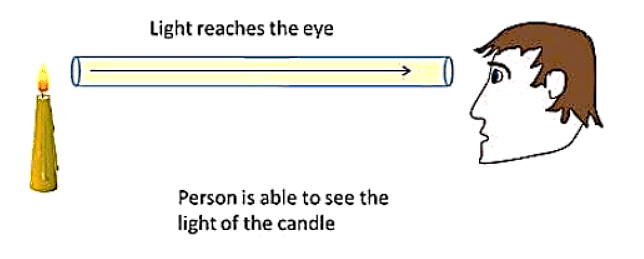
This characteristic of light can be explained by a Candle and Pipe Experiment.
- Look at the candle through a straight pipe. The light from the candle can travel directly through the straight pipe to your eyes. So, you can see the candle flame clearly.
- If you bend the pipe, the light from the candle can't reach your eyes because it hits the sides of the pipe and gets blocked. That's why you can't see the flame.
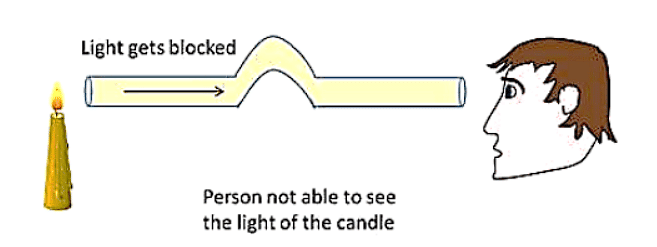
Conclusion: So, when the light's path is blocked or bent, you won't be able to see the light source, just like with the candle and the bent pipe.
Reflection of Light
When light hits a shiny surface like a stainless-steel plate, steel spoon, or even the surface of water, it can change direction. This is known as reflection.
- You might have seen pictures of trees or buildings reflected in water.
- Any smooth or shiny surface can act like a mirror.
- When light hits a mirror, it changes its direction, creating what we know as light reflection.
 Reflection of light from a mirror
Reflection of light from a mirror
- The mirror changes the direction of light according to the angle at which light of torch hits the mirror.
Image and Object
- Look at the flame of the candle in the mirror, when it is placed in front of a mirror.
- You will see what seems like another candle placed behind the mirror.
- The candle that you see behind the mirror is actually the image of the original candle formed by the mirror.
- The original candle is called the object.
- Now, move the candle to different positions in front of the mirror.
- Observe how the image changes each time you move the candle.
 Candle in front of a plain mirror
Candle in front of a plain mirror
- If we increase or decrease the distance between the object and the mirror, the distance between the image and the mirror also increases or decreases, respectively.
- However, the size of the image formed on the mirror can vary with respect to the distance between the object and the mirror.
- If the distance between the object and the mirror increases, the size of the image decreases and vice-versa.
Erect: An image is said to be erectif the image is formed the same side up as that of the object.
Inverted: The image will be called Inverted if it is formed upside down compared to the object.
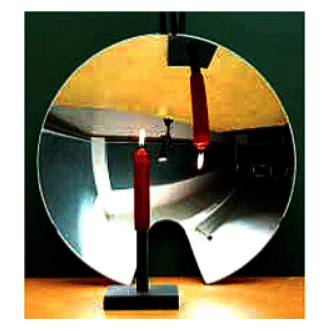 Inverted image of a candle
Inverted image of a candle
Right or Left!
When you stand in front of a mirror and raise your left hand, it looks like the person in the mirror is raising their right hand. If you touch your right ear, it seems like the person in the mirror is touching their left ear. This happens because the mirror switches left and right sides. So, what looks like left in the mirror is actually right, and what looks like right is actually left.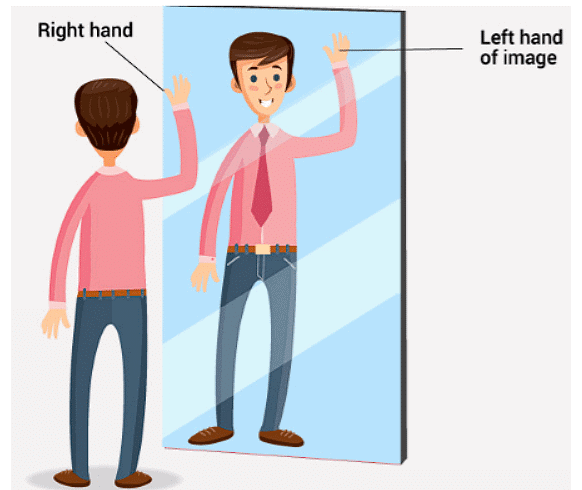 Left- Right Inversion
Left- Right Inversion
Interesting Fact:Why is the word ‘AMBULANCE’ painted on an ambulance left-right inverted?
The left-right reversal of images in a mirror causes the word "ambulance" to be easily readable for the driver of a vehicle ahead when seen in the rearview mirror.
 Left-Right Reversal of Images
Left-Right Reversal of Images
Playing With Spherical Mirrors
Spherical mirrors are mirrors that have a curved surface, like a part of a sphere (a round object like a ball).
Types of Spherical Mirrors: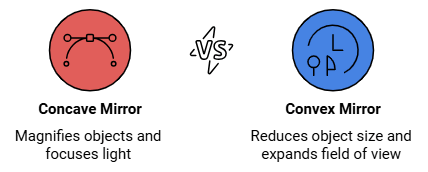
Concave Mirror:
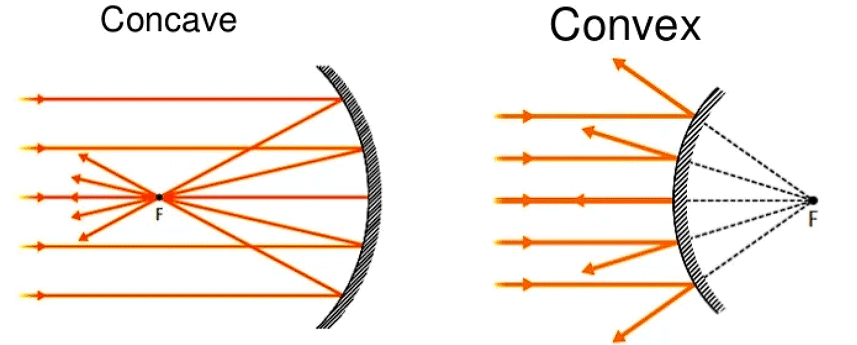
- If the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is concave, it is called a concave mirror.
- A concave mirror curves inward, like the inside of a spoon. It can make things look bigger when you bring them close to the mirror.
- The reflecting surface is concave
Convex Mirror:
- If the reflecting surface is convex, then it is a convex mirror.
- A convex mirror curves outward, like the back of a spoon. It makes things look smaller and shows a wider area.
- The reflecting surface is convex.
Where You See Them:
- Concave mirrors are used in things like makeup mirrors and car headlights because they focus light, used by dentists to see things up close, in torches. They can make things look bigger or smaller and can create real or virtual images.
- Convex mirrors are used as side mirrors on cars because they give a wider view of the road.
 Types of Mirrors
Types of Mirrors
- If the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is concave, it is called a concave mirror.
- If the reflecting surface is convex, then it is a convex mirror.
Types of Images
There are two types of images formed
1. Real Image: Images that can be captured on a screen are known as real images. For example, in a camera, images are real and can be captured on the negative, which acts as a screen.
2. Virtual Image: The image formed by a plane mirror cannot be captured on a screen and is called a virtual image.
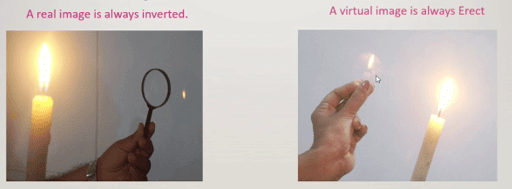 Real and Virtual Image
Real and Virtual Image
Images Formed by Lens
A lens is a piece of transparent material, usually glass or plastic, that bends light to help us see things more clearly. Lenses are used in many everyday objects like spectacles (glasses), telescopes (to see faraway things), and microscopes (to see very tiny things).
Depending upon its shape a lens can be categorized as:
1. Convex Lens- A Convex Lens is curved outwards. It is thicker in the centre and narrows down at the edges. It merges the light rays passing through it at a certain point. Therefore, it is also called a Converging Lens.
2. Concave Lens - A Concave Lens is curved inwards. It has wider edges and a thinner centre. It reflects back the light that travels through it in different directions. Therefore, it is also called a Diverging Lens.
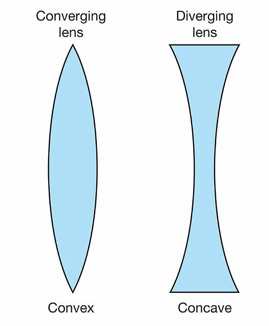 Lens
Lens
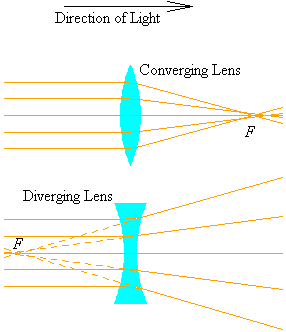 Converging and Diverging Lens
Converging and Diverging Lens
Applications of Lenses
Lenses are used in magnifying glasses, peepholes, cameras, bioscopes, binoculars, telescopes, microscopes and projectors. A refracting telescope uses a concave mirror and a convex lens.
 Image by a convex lens for object placed at different distance from it
Image by a convex lens for object placed at different distance from it Virtual image by convex lens Image by a concave lens
Virtual image by convex lens Image by a concave lens
CAUTION
Be careful not to look through a lens at the Sun or any bright light. Avoid focusing sunlight with a convex lens on your skin.
Activity Instructions
- Take a convex lens or magnifying glass and place it in the path of sunlight.
- Put a sheet of paper as shown, adjusting the distance between the lens and paper until you see a bright spot. Hold this position for a few minutes. Does the paper start to burn?
- Now replace the convex lens with a concave lens. Do you see a bright spot on the paper? Why not?
Similar to mirrors, the position of the object affects the nature and size of the image in lenses as well.
In summary, a convex lens can create real, upside-down images, while a concave lens always produces upright, virtual, and smaller images than the object.
Sunlight - White or Colored?
A band of colors extending from violet to red is a rainbow. A rainbow is formed by the reflection of the sun's rays through raindrops.
Rainbow
A rainbow is a natural event where sunlight is reflected by water droplets in the air. It forms an arc in the sky and showcases seven distinct colors: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
This occurrence shows that sunlight is actually composed of seven different colored lights, which become visible through reflection.
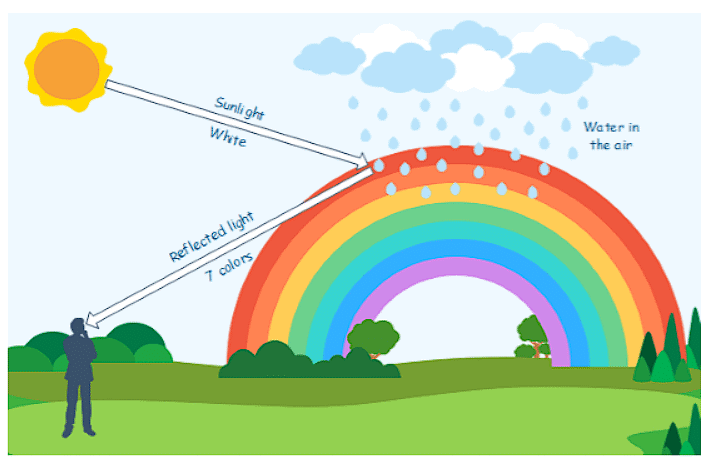
Just like how the soap bubbles and CDs show different colors when light hits them, sunlight is made up of many colors that can be separated and seen. This is why we can create rainbows or see colorful reflections!
Note:If you divide a disk into 7 parts and paint each part with a different color of the rainbow, when you spin the disk really fast in bright light, the colors all blend together, and the disk looks white.
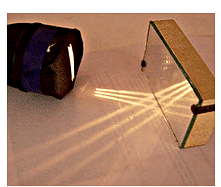
Let's understand this with interesting activity through a Prism:
- Take a glass prism.
- Allow a narrow beam of sunlight to pass through a small hole in the window of a dark room to fall on one face of the prism.
- The light bends when it passes through the prism.
- Now allow the light coming out of the other face of the prism to fall on a white sheet of paper or a white wall.
- Different component colors of white light bend differently, and so the constituent colors can be seen separately.
- This indicates that sunlight is made up of seven colors. Sunlight is referred to as white light, which means that white light comprises seven colors.
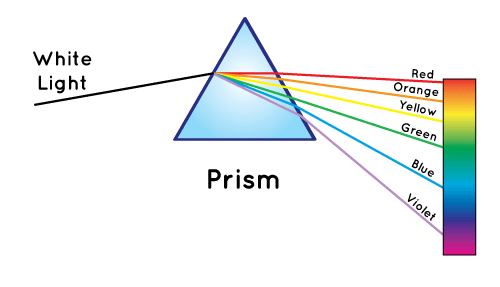 A prism splits a beam of sunlight into seven colors
A prism splits a beam of sunlight into seven colors
Newton's Disc
When you divide a disk into seven sections and paint each with a different color of the rainbow, you get what's known as Newton's disc. When you spin the disc quickly in daylight, the colors blend together, giving the appearance of a whitish color.
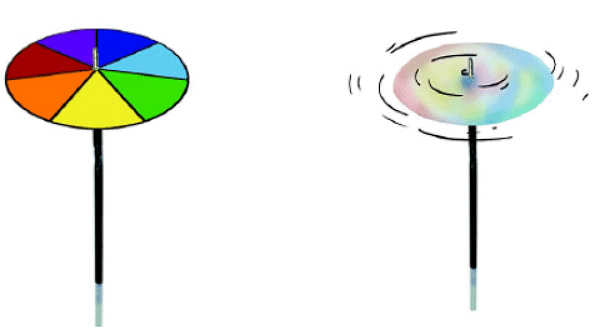 Newton's Disc
Newton's Disc
|
111 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Light Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 13
| 1. What is the law of reflection and how does it apply to mirrors? |  |
| 2. How do convex and concave mirrors differ in terms of image formation? |  |
| 3. What are the characteristics of images formed by converging and diverging lenses? |  |
| 4. Why is sunlight considered to be white light, and how can it be separated into colors? |  |
| 5. What role does the focal point play in the behavior of light in optical systems? |  |
















