Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Notes Science
What are Fibres?
Fibres can be generally defined as the thread-like structures that are thin, long, and flexible strands. The two main sources of Fibres are plants and animals.
 Fibres
Fibres
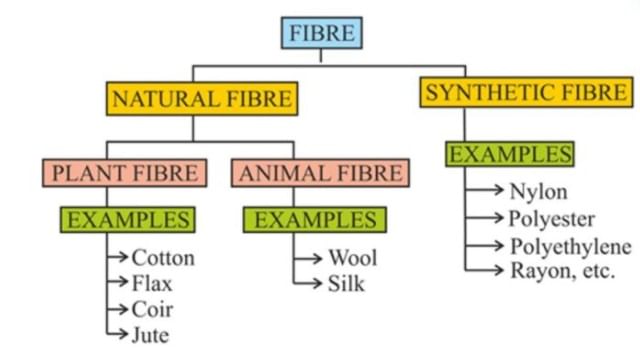
Classification of Fibres
Fibres can be classified into the following:
- Natural Fibres
- Synthetic Fibres
What are Natural Fibres?
The Fibres obtained naturally from both plants and animals are termed as the Natural Fibres. These Fibres are hair-like raw material directly obtainable from different plants and animals.
Natural fibres have the following characteristics:
- They can be twisted into yarn to make a fabric.
- They are comfortable and durable.
- They are strong.
- They are highly capable of absorbing moisture.
- They provide an excellent look and feel.

The natural fibres are further classified into:
- Plant Fibre
- Animal Fibre
- Mineral Fibre
What are Synthetic Fibres?
Synthetic fibres are made only from polymers found in natural gas and the by-products of petroleum.
- Synthetic fibres are man-made fibres, most of them are prepared from raw material petroleum called petrochemicals.
- All fabrics are obtained from fibres, while fibres are obtained from artificial or man-made sources. They consist of a small unit or a polymer that is made from many repeating units known as monomers.
- They include nylon, acrylics, polyurethane, and polypropylene. Millions of tons of these fibres are produced all over the world each year.
Classification of Synthetic Fibers
Following are some of the most commonly used synthetic fibres:
1. Rayon
- This is a type of synthetic fibre obtained from wood pulp.
- Rayon fabric is soft, absorbent, and comfortable.
- It is easy to dye in a wide range of colours.
- Rayon is mixed with cotton to make bedsheets.
- Rayon is mixed with wool to make carpets.
Characteristics of rayon
- Cheaper than silk and can be woven like silk fibres.
- Highly absorbent, soft, and comfortable.
- Easy to dye in a wide range of colours, and drapes well.
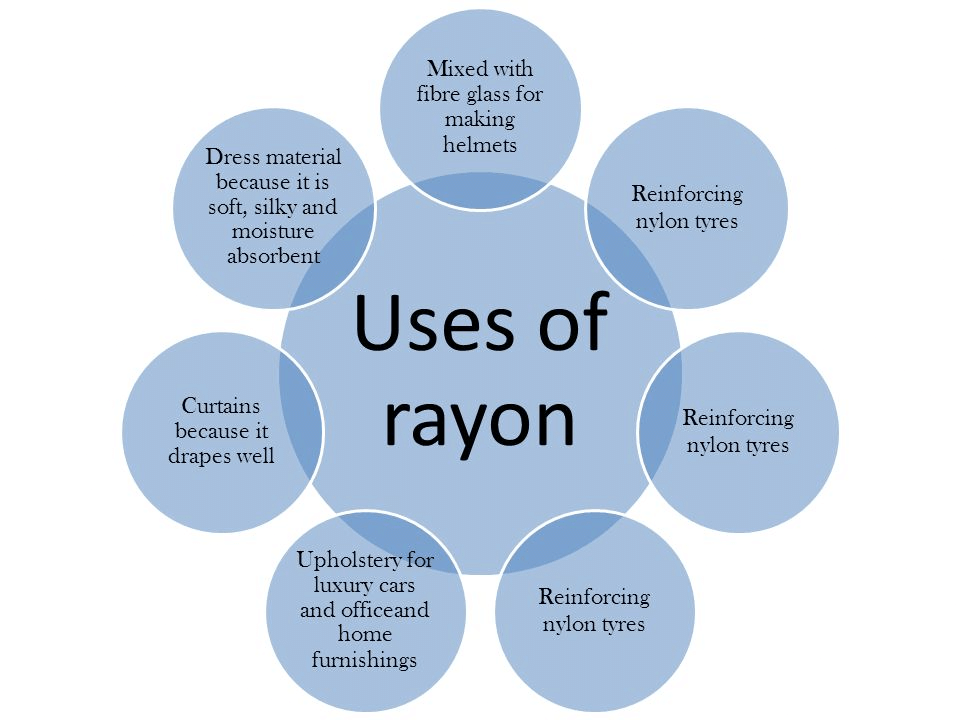
Uses of Rayon
Widely used in all types of clothing and home furnishings. Mixed with cotton to make bedsheets and curtains, or with wool to make carpets.
 2. Nylon
2. Nylon
- This type of synthetic fibre is obtained from coal, water and air.
- Nylon is very lustrous, easy to wash, and elastic.
- It dries quickly and retains its shape.
- Nylon finds its application in seat belts of car, sleeping bags, socks, ropes, etc.
- Nylon is also used in ropes for rock climbing, making parachutes, and fishing nets.
 Nylon
Nylon
Characteristics of Nylon:
- Nylon is a synthetic fibre made from coal, water and air.
- Cloths from nylon are very strong elastic and light lustrous and easy to wash.
Uses of nylon:
- To make seat belts in cars, curtains, sleeping bags, tents, toothbrushes, socks and ropes
- To make parachutes and ropes for rock climbing.
3. Polyester
- This type of synthetic fibre is obtained from coal, water, air and petroleum.
- Polyester is made from repeating units of a chemical known as esters.
- Polyester is easy to wash and it remains wrinkle-free and it is quite suitable in making dress material.
- Polyester retains its shape and remains crisp.
- Polyester is used in making ropes, nets, raincoats, jackets, etc.
 Polyester
Polyester
Characteristics of Polyester:
- Polyester is a synthetic fibre, derived from coal, air, water and petroleum. Polyester is made of repeating chemical units called esters.
- Polycot is a mixture of polyester and cotton, and poly wool is a mixture of polyester and wool. Fabric made from polyester retains its shape and remains crisp. Polyester is easy to wash and dry.
- Terylene is a popular form of polyester, which can be drawn into very fine fibres. These fibres can be woven like any other yarn.
- PET, or polyethene terephthalate, is another familiar form of polyester, which is used to make bottles, utensils, films and wires. Polyester is also used for making hoses, ropes, nets, thread, raincoats, fleece jackets, clothing and medical textiles. Acrylic is a synthetic polymer of methyl methacrylate. Fabric made from acrylic is warm to wear, retains its shape and is durable.
- Acrylic is easy to wash and dries quickly. Acrylic is used in apparel like sweaters and socks, and in-home furnishings such as furniture, carpets, blankets and upholstery fabrics. Industrial uses of acrylic include craft yarns, awnings, boat and vehicle covers, and luggage.
Advantages of Synthetic Fibres
- Synthetic fibres are very durable and do not wrinkle easily
- They are elastic and can be easily stretched out
- They are strong and can sustain a heavy load.
- They are soft and hence used in clothing material.
- They are cheaper than compared to natural fibres.
- Disadvantages of Synthetic Fibres
- Most synthetic fibres do not absorb moisture.
- Synthetic fibre can be affected if washed using hot water.
- They catch fire easily as compared to natural fibre.
Disadvantages of Synthetic Fibres
- Most synthetic fibres do not absorb moisture.
- Synthetic fibre can be affected if washed using hot water.
- They catch fire easily as compared to natural fibre.
Advantages of Natural Fibres over Synthetic Fibres
- Natural Fibres are biodegradable.
- They have a low specific weight due to which they possess higher strength.
- They possess good electrical resistance.
- They are skin-friendly and cause no irritation.
- Their production requires less energy and emits low carbon dioxide.
- Cost-effective.
- They possess good thermal and insulating properties.
What is Plastic?
Plastic is defined as a material that contains as an essential ingredient an organic substance of large molecular weight. It is also defined as polymers of long carbon chains.

- Plastic was discovered by famous German chemist Christian Schonbein in 1846. Plastics were actually discovered accidentally.
- Christian was experimenting in his kitchen and by accident, he spilt a mixture of nitric acid and sulphuric acid. To mop that solution (a mixture of nitric and sulphuric acid) he took a cloth and after moping he kept it over the stove. After some time, the cloth disappeared and from their plastic got its name.
Characteristics of plastics
- Do not corrode easily - Light in weight - Strong - Durable
- Can be easily moulded into different shapes and sizes.
- Poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Types of Plastics
Depending on physical properties, plastics are divided into two types: Thermoplastic and thermosetting.
- Thermoplastic: Plastics that can be deformed easily upon heating and can be bent easily. Linear polymers and a combination of linear and cross-linked polymers come under thermoplastics.
Example: PVC, nylon, polythene, etc. - Thermosetting: Plastics that cannot be softened again by heating once they are moulded. Heavily cross-linked polymers come under the category of thermosetting plastics.
Example: Bakelite, melamine, etc.
Bakelite is used for making electrical switches whereas melamine is used for floor tiles.
Recycling of Plastic
- Recycling of plastic is very important. If they are not recycled at the proper time, then they get mixed with other chemicals or materials and hence become more difficult to recycle and become a source of pollution.
- They are non-biodegradable, and they do not get decomposed by the microbial action.
- To avoid this, it is important to use biopolymers or biodegradable polymers.
Properties of Plastic
- Strong and ductile
- Poor conductors of heat and electricity
- Easily moulded into different shape and size
- Resist corrosion and are resistant to many chemicals.
Some Uses of Plastic in Various Fields
- Plastics find extensive use in the healthcare industry. Plastics are used for the packaging of tablets, threads used for stitching wounds, syringes, doctors’ gloves and a number of medical instruments.
- Special plastic cookware is used in microwave ovens for cooking food without affecting the plastic vessel.
- Teflon is a special plastic on which oil and water do not stick. It is used for making non-stick coating on cookware.
- Fire-proof plastics: Synthetic fibre catches fire easily. The uniforms of firemen have a coating of melamine plastic to make them flame resistant.
Plastics & the Environment
- Plastic is a non-biodegradable material. It takes many years to get decomposed or either does not get decomposed.
- Due to the non-biodegradable property of plastic, it is a very major problem for the environment.
Problem
- Nowadays, plastic is very popular and used it for many purposes. As a result, we generate a large amount of plastic waste. Since plastic has non-biodegradable property, so plastic waste is getting accumulated in the environment. It causes environmental pollution.
- Accumulated plastic waste is a major concern as it does not get completely burnt easily. In the process, it releases lots of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere causing air pollution.
Ways to Reduce the Use of Plastic Materials
Reduce: Avoid the use of disposable plastic bags, instead make use of cotton or jute bags for shopping.
Reuse: Plastic items should be reused wherever possible.
Recycle: It is better to recycle plastic waste. Most thermoplastics can be recycled.
Biodegradable & Non-Biodegradable Materials

- Material that gets decomposed through natural processes, such as by the action of bacteria, is termed biodegradable.
Example: Peels of vegetables, fruits, other foodstuff, paper and pieces of clothes. - Material that is not easily decomposed by natural processes is termed non-biodegradable.
Example: plastic, polythene covers, thermocol, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1. How Synthetic Fibres are made?
Ans: Synthetic fibers are made from small molecules synthesized polymers. The substances used to produce such fibres are extracted from raw materials such as chemicals based on petroleum or petrochemicals. Such materials are polymerized into a chemical that ties together two adjacent atoms of carbon.
Q.2. What are Natural Fibres In short? What are examples of Natural Fibres?
Ans: Plants, animals, and geological processes create natural fibres, often known as natural fibres. They can be utilized in composite materials where the orientation of the fibres affects the characteristics. Natural fibres can be flattened into sheets and used to produce paper or felt.
Seed hairs, such as cotton, stem (or bast) fibres, such as flax and hemp, leaf fibres, such as sisal, and husk fibres, such as coconut, are all examples of plant fibres. Wool, hair, and secretions, such as silk, are examples of animal fibres.
Q.3. Explain the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.| Thermosetting plastic | Thermoplastic |
| Cannot be bent, it will break if we attempt to bend thermo setting plastic | Thermoplastic can be bent easily |
| On heating thermosetting plastics, it cannot be softened. This is the reason it cannot be reshaped once it is molded. | On heating the thermoplastics, it becomes softened and can be molded and reshaped easily. |
|
18 videos|34 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Notes Science
| 1. What are some common examples of natural fibres? |  |
| 2. What are some common uses of synthetic fibres? |  |
| 3. What are some benefits of recycling plastics? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials? |  |
| 5. How do plastics impact the environment? |  |

















