Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Extra Question Answers - Resources and Development
Short Question Answer
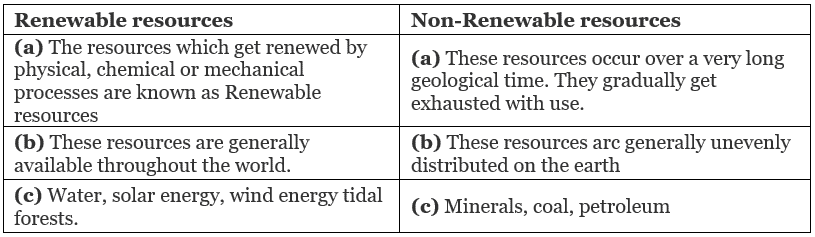
Q 1. Distinguish between renewable and non-renewable resources.
Q 2. Explain the resources on the basis of origin and exhaustibility.
Resources on the basis of origin:
- Biotic: Those resources which are available in the biosphere and have life.
Example: Human beings, flora and fauna etc.- Abiotic: All those things which are non-living are called abiotic resources.
Example: Rocks, soils, and minerals.Resources on the Basis of Exhaustibility:
- Renewable resources: The resources which can be renewed are Renewable resources.
Example: Water, forest, wind, etc- Non-renewable resources: These resources occur over a very long time and get exhausted.
- Example: Minerals and fossil fuels.
Q 3. What is soil erosion? Write two human activities that lead to soil erosion.
The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is described as soil erosion.
Two human factors leading to soil erosion are:
- Deforestation: Due to heavy deforestation, soil erosion is increasing.
- Overgrazing: In many regions, people still practice grazing cattle, goats, and sheep. Gradually this leads to soil erosion.
Q 4. Explain any three steps that can be taken to solve the problem of land degradation?
(a) Contour Ploughing: Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes.
Contour Ploughing(b) Terrace cultivation: Steps can be cut out on the slopes, making terraces. Terrace cultivation restricts erosion.
(c) Strip cropping: Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. This breaks up the force of the wind reducing its effect.
Q 5. Explain the role of humans in resource development.
- Humans are at the center of resource development. Actually, all resources become resources only when they are put to use by humans.
- It is humans who make natural things usable with help of technology. Had no technology been there, the development would not have been possible.
- There are regions where natural resources are in abundance but the regions are not developed, for example, Africa.
- When humans interact with Nature through technology and create institutions, they accelerate the economic development of the region, for example, Japan.
Q 6. Explain the importance of the conservation of resources.
Conservation of resources is necessary because of the following reasons:
(a) Resources are vital for any developmental activity but irrational consumption and overutilization of resources may lead to socio-economic and environmental problems. To overcome these problems, resource conservation at various levels is important.
(b) If resources are not conserved at this point in time, then our future generations will be left with no resources at all. So it is very important to think about the conservation of resources.
Q 7. Why is it important to raise the land area under forests?
It is very important to raise the area under forest because forests are essential for the maintenance of the ecological balance. The livelihood of millions of people who live on the fringes of these forests depends upon it. Forest also provides a number of goods that are required for industry and medicines etc. Forest also helps in soil conservation and rainfall.
Q 8. Describe any three main characteristics of the arid soil of India.
Characteristics of Arid soils in India are:
- They range from red to brown in colour.
- They are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature.
- In some areas, the salt content is higher and common salt is obtained by evaporation of water.
- Due to the dry climate, high temperature, evaporation is faster and the soil lacks humus and moisture.
Q 9. Highlight any three problems associated with the indiscriminate use of resources by human beings.
Indiscriminate use of resources creates the following problems:
- Global ecological crises such as global warming.
- It has also led to the depletion of the ozone layer.
- It has also caused environmental pollution and land degradation.
The resultant threat to ecology and the environment has put the future of our planet in danger. Natural disasters have become very frequent. Many species of flora and fauna have already become extinct.
Q 10. “Consequences of environmental degradation do not respect national or state boundaries.” Justify the statement.
As the environment belongs to the Earth, its impact felt by the whole planet. For example, if carbon dioxide is being released by some rich countries global warming is affecting the lives of all the people on the planet. Air pollution moves along with air and cannot be restricted to any place or country.
Ozone layer depletion has serious consequences for people all over the world.
Q 11. Describe any three types of soil available in India.
Three important soils of India are:
(a) Alluvial Soils
- It is the most important and widespread soil of India. The entire northern plain is made of this soil.
Alluvial soil- Alluvials have been deposited by three important Himalayan rivers— Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus.
- These soils consist of various proportions of sand, silt, and clay.
- These are of two types: Khadar and Bangar.
- They contain potash, phosphoric acid, and limestone.
(b) Black Soil:
- These soils are black in colour and are also known as Regur or cotton soils.
- This type of soil is found in the Deccan plateau region and is made up of lava flows.
- They are well known for their capacity to hold moisture.
- They are rich in calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, and lime.
(c) Laterite Soil:
- Laterite soil develops in areas of high temperature and heavy rainfall. This is the result of intense leaching. The Humus content of the soil is very low.
- These are found in Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, and the hilly areas of Orissa and Assam.
Q 12. What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in hilly areas?
- Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes. This is contour ploughing.
- Steps can be cut out on the slopes mapping terraces. Terrace cultivation restricts erosion.
- Strip cropping is a very effective method of soil conservation or controlling soil erosion. Large fields are divided into strips and strips of grass are left to grow between the crops.
Q 13. Mention any three characteristics of black soil.
- The black soils are made of clayey material and are well-known for their capacity to hold moisture.
- They are rich in soil nutrients, such as calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, and lime. But black soils are poor in phosphoric contents.
- Black soil develops deep cracks during summer which helps in the proper aeration of the soil. These soils are sticky when wet and difficult to work on unless tilted just after the first shower.
Q 14. “India’s vast and diverse size is the most important resource.” Support the statement.
India has land under a variety of relief features such as plains, plateaus, mountains, and islands. About 43 per cent of land areas are plain, which provides facilities for agriculture and industry. Mountains account for 30 per cent of the total surface area of the country and ensure the perennial flow of some rivers, provide facilities for tourism and ecological aspects. About 27 per cent of the area is the plateau region. It possesses rich reserves of minerals, fossil fuels, and forests.
Q 15. Suggest any three measures of soil conservation.
The three measures of soil conservation are:
(a) Contour ploughing: ploughing along the contour lines can lead to soil conservation.
(b) Terrace cultivation: steps can be cut out on the slopes making terraces. Terrace cultivation leads to soil conservation.
(c) Creating shelterbelts: planting of trees to create shelter. Rows of such trees are called shelterbelts.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q 1. What does the term ‘land degradation’ mean? Which human activities have contributed significantly to land degradation? Suggest measures to solve the problems of land degradation.
OR
What are the reasons for land degradation? Describe any four measures to conserve land.
Continuous use of land over a prolonged period of time, without taking necessary steps to conserve and manage it, has resulted in land degradation, i.e., qualitative degradation of land. The quality of the land becomes poorer due to gradual loss of fertility due to unplanned use. Unplanned use and over-exploitation by humans have led to the degradation of land and have also aggravated the pace of natural forces to cause damage to the land.
Land Degradation
- Human activities such as deforestation, over-grazing, mining, and quarrying have contributed significantly to land degradation.
- Faulty methods of cultivation and over-irrigation have also caused land degradation in some areas.
- Mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry, industrial effluents, and wastes cause pollution and lead to land degradation.
The problem of land degradation may be tackled by adopting certain measures to conserve land:
(a) Afforestation or large-scale plantation of trees and proper management of grazing.
(b) Planting of shelterbelts of plants and stabilization of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes in windy, arid areas like a desert of Rajasthan.
(c) Proper management of wasteland and control of mining activities.
(d) Proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and waste after treatment in industrial and suburban areas.
Q 2. What is resource planning? Why is resource planning essential? Explain three reasons.
Resource planning is the widely accepted strategy for judicious use of resources.
It is a complex process that involves:(i) Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country through surveying, mapping, and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of resources.
(ii) Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill, and institutional set-up for implementing resource development plans.
(iii) Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
Resource Planning is essential mainly because of the following reasons:
- Resources are not equally distributed throughout the world. Within a country also some regions may be rich in resources and self-sufficient in terms of availability of resources while some other regions may have an acute shortage of some vital resources. There are regions that are rich in certain types of resources but are deficient in some other resources.
- Some regions in the country that are rich in natural resources may be included among the economically backward regions. On the contrary, there are some regions that have a poor resource base but are economically developed.
- Technology, quality of human resources, and the historical experiences of the people influence resource development. In a country like India which has enormous diversity in the availability of resources, resource planning is indispensable.
Q 3. Explain any four human activities which are mainly responsible for land degradation in India.
Continuous use of land over a prolonged period of time without taking necessary steps to conserve and manage it has resulted in land degradation.
Four human activities responsible for land degradation in India are as follows:
- In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Orissa deforestation due to mining has caused severe land degradation. Mining sites are dug, drilled or quarried, and abandoned after excavation work is over, leaving the land overburdened and in a highly degraded state.
- Mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generates the huge quality of mineral dust in the atmosphere which ultimately settles down on the land. It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil, thus, degrading the land. Discharge of industrial effluents and wastes cause pollution and land degradation in industrial regions.
- In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation.
- In Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh over-irrigation is responsible for land degradation. It leads to waterlogging which in turn increases salinity and alkalinity in the soil and reduces its fertility.
Q 4. Give the importance of soil. Explain any three factors responsible for soil formation.
Soil is the medium of plant growth and supports different types of living organisms, including animals and human beings, by providing them with food for their survival. Human existence and settlement are determined by soil fertility as it determines the agricultural productivity of an area. Soil determines the natural vegetation and type of crop production of an area. It also influences the land use of an area. Areas of fertile soil are agriculturally productive and densely populated. It is one of the most important renewable natural resources. Relief, nature of parent rock or bedrock, climate, vegetation, and other forms of life (especially decomposers), and time are important factors in the formation of soil.
The three most important factors of soil formation are:
- Nature of parent rock. It influences the colour and texture of the soil. The mineral content of the soil also depends on the parent rock from which it is formed.
- Climate influences the rate and types of weathering and erosion of the rocks. Weathering of the parent rocks due to climatic factors and natural forces leads to the disintegration of rocks which leads to the formation of soil.
- Time determines the maturity of the soil. The soil is a living system. It takes millions of years to form soil up to a few centimetres in depth.
Q 5. Classify resources on the basis of ownership into four categories. Mention the main features of each.
On the basis of ownership, resources can be classified into the following categories:
(a) Individual resources are owned privately by individuals or groups of individuals. Plots of lands owned by farmers, pasture lands, ponds, orchards, water in wells, are examples of resources owned by individuals in the villages. Plots of land, houses, cars and other property are some examples of individual resources in urban areas. Plantations are also individual resources. Its plot of land, management, revenue, products, and profits are under individual ownership.
(b) Community-owned resources are accessible to all members of the community. These resources can be used by all people living in the area. Picnic spots, maidans, village ponds, grazing grounds, burial grounds, etc., in villages; playgrounds, public parks, markets, etc in urban areas are examples of community-owned resources.
(c) National Resources mean all resources owned by a nation. All the forests, wildlife, minerals, water resources, land within the political boundaries of a nation, and oceanic area up 12 nautical miles, i.e., 19.2 km, from the coast termed as territorial water, and resources therein belong to the nation and are termed as national resources.
(d) International Resources are under the jurisdiction and regulation of international organizations. The oceanic resources beyond 200 km of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open oceans and no individual country can utilize these without the concurrence of international institutions, e.g. manganese nodules in the bed of the Indian Ocean.
|
66 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Extra Question Answers - Resources and Development
| 1. What are the key resources involved in development? |  |
| 2. How does resource management impact economic development? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of renewable and non-renewable resources? |  |
| 4. Why is sustainable development important in resource utilization? |  |
| 5. What role does education play in resource and development management? |  |