Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 10 > Key Concepts: Forest & Wildlife Resources
Key Concepts: Forest & Wildlife Resources | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Flora and Fauna in India |

|
| Conservation of Forest and Wildlife in India |

|
| Types and Distribution of Forest and Wildlife Resources |

|
| Community and Conservation |

|
Flora and Fauna in India
- Humans and living organisms form a complex web of ecological system in which we are dependent on the system for our own existence.
- Forests play a key role in the ecological system as primary producers on which all other living things depend.
 A NASA photo of India's North Sentinel Island covered with forest
A NASA photo of India's North Sentinel Island covered with forest - India is one of the world’s richest countries in terms of its vast array of biological diversity and has nearly 8% of the total number of species in the world.
- At least 10% of India’s recorded wild flora and 20% of its mammals are on the threatened list.
- Based on the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) the existing plants and animal species can be classified as Normal, Endangered, Vulnerable, Rare, Endemic and Extinct species.
- The greatest damage inflicted on Indian forests was during the colonial period due to the expansion of the railways, agriculture, commercial and scientific forestry, and mining activities.
- Large-scale development projects have also contributed significantly to the loss of forests.
- The destruction of forests and wildlife is not just a biological issue but is strongly correlated with the loss of cultural diversity.
Conservation of Forest and Wildlife in India
- Conservation in the background of rapid decline in wildlife population and forestry has become essential.
- Conservation preserves the ecological diversity and our life support systems — water, soil, and air.
- The Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act was implemented in 1972.
- The conservation projects focus on biodiversity rather than on a few of its components.Forest around Nohkalikai fall in Meghalaya, an eastern state of India
Types and Distribution of Forest and Wildlife Resources
- For administration, forests have been classified into three types—
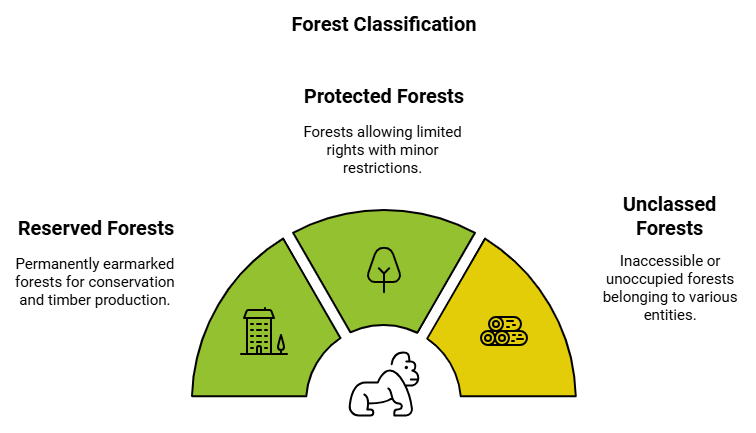
- Reserved Forests are forests that are permanently earmarked and regarded as most valuable for the conservation of forests and wildlife resources either for the production of timber or other forest products. Grazing and cultivation is seldom permitted in a reserved forest.
- In Protected Forests, these rights are allowed subject to a few minor restrictions.
- Unclassed Forests consist of inaccessible forests or unoccupied wastes belonging to both government and private individuals and communities.
Community and Conservation
- In India, forests are also home to some of the traditional communities.
- Belief of tribes that all creations of nature must be protected has led to the reservation of virgin forests in a pristine form called Sacred Groves (the forests of Gods and Goddesses).
- In India, sacred qualities are often ascribed to springs, mountain peaks, plants, and animals which are closely protected.
- Chipko Movement in the Himalayas resisted deforestation. Farmers and citizen groups like the Beej Bachao Andolan in Tehri and Navdanya have shown that adequate levels of diversified crop production without the use of synthetic chemicals are possible and economically viable.
- In India, the Joint Forest Management (JFM) program furnishes a good example of involving local communities in the management and restoration of degraded forests.
The document Key Concepts: Forest & Wildlife Resources | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
95 videos|815 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts: Forest & Wildlife Resources - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What are the main types of forest resources? |  |
Ans. The main types of forest resources include timber, fuelwood, non-timber forest products (such as fruits, nuts, and medicinal plants), and wildlife. Each of these resources plays a crucial role in the economy and ecology, providing materials for construction, energy, food, and a habitat for various species.
| 2. How do forests contribute to biodiversity? |  |
Ans. Forests are home to a vast array of plant and animal species, making them vital for biodiversity. They provide habitats and food for wildlife, support various ecosystems, and help maintain ecological balance. Conserving forests is essential to protect the numerous species that depend on them for survival.
| 3. What are the major threats to forest and wildlife resources? |  |
Ans. Major threats to forest and wildlife resources include deforestation, habitat destruction, climate change, pollution, and illegal poaching. These factors lead to loss of biodiversity, disruption of ecosystems, and contribute to climate change, necessitating urgent conservation efforts.
| 4. Why is sustainable forestry important? |  |
Ans. Sustainable forestry is important because it ensures that forest resources are managed in a way that meets current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs. It involves practices that maintain the health of forest ecosystems, promote biodiversity, and support local communities.
| 5. What role do protected areas play in wildlife conservation? |  |
Ans. Protected areas play a critical role in wildlife conservation by providing safe habitats for endangered and threatened species. They help to preserve biodiversity, maintain ecological processes, and protect ecosystems from human activities. Establishing and managing these areas is essential for effective conservation strategies.
Related Searches
















