Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Extra Question Answers - Development
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. On the basis of the given table answer the following questions:
(a) Calculate the average income of country A and B.
(b) Are both the countries equally developed?
(c) Which country is better and why?

Ans: (a) The average income of Country A is calculated as follows:
Average income = (9500 + 10500 + 9800 + 10000 + 10200) / 5 = Rs. 10,000
The average income of Country B is: Average income = (500 + 500 + 500 + 500 + 48000) / 5 = Rs. 10,000
(b) No, the two countries are not equally developed.
(c) Country A is better because:
- Income distribution is more equitable.
- Most citizens are neither very rich nor extremely poor.
- In Country B, the majority are poor, with one person being extremely rich.
Q2. In what respect is the criterion used by UNDP for measuring development different from the one used by the World Bank?
Ans: The World Bank and the UNDP measure development using different criteria:
- The World Bank relies solely on per capita income to assess a country's development.
- In contrast, the UNDP considers multiple factors, including: Health status, Education status, Per capita income
For example, consider two individuals in India: Mukesh Ambani, with an annual income of Rs. 50 crore. A rickshaw puller, earning Rs. 12,000 annually.
When calculating per capita income, both would appear to have similar incomes, which is misleading:
- Ambani's income would suggest Rs. 25 crore per person.
- The rickshaw puller's would show Rs. 6,000.
The UNDP's approach offers a more accurate picture of a country's development by including various indicators, thus reflecting the true status of its citizens.
Q3. Why are public facilities needed for the development of the country? Explain any four public facilities.
Ans: Public facilities are crucial for a country's social and economic development. They enable individuals to reach their full potential and contribute to society. Here are four key public facilities:
- Infrastructure: Building roads, railways, and ports is essential for transportation and trade, facilitating movement and commerce.
- Affordable Goods: The government should provide essential goods at low prices, ensuring that even low-income families can access them.
- Health and Education: It is the government's duty to offer adequate health and education services. A healthy and educated population is vital for national progress.
- Basic Needs: Providing safe drinking water, housing, and nutritious food for children is fundamental for their development and well-being.
Q4. What are the two basic criteria used for comparing an underdeveloped country with a developed one?
Ans: The two basic criteria for comparing an underdeveloped country with a developed one are:
- Per capita income: This criterion classifies countries based on their average income. According to the 2006 World Development Report, countries with a per capita income of Rs. 4,53,000 or more are considered rich, while those with Rs. 37,000 or less are classified as low-income countries.
- Human Development Index (HDI): This criterion ranks countries based on factors such as life expectancy, literacy rate, and overall health status.
Q5. What do you mean by Human Development Index? What are its three components?

Ans: The Human Development Index (HDI) is a measure created by the UNDP to assess and compare the development of countries. It focuses on three key components:
- Education: The educational levels of the population.
- Health: The overall health status of the people.
- Income: The per capita income of the citizens.
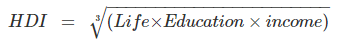
Q6. Why is sustainability important for development? Give two suggestions to achieve the sustainability of development.
Ans: Sustainability is crucial for development because neglecting environmental and natural factors can lead to serious consequences for humanity. For instance, if we continue to deforest without restraint, it could exacerbate global warming, jeopardising our planet's future. In such a scenario, the purpose of development becomes questionable.
To achieve sustainability, we can:
- Reduce reliance on non-renewable resources.
- Adapt our lifestyles to natural conditions and utilise local resources whenever possible.
Q7. How does World Bank classify different countries? Is it an adequate indicator?
Ans: The World Bank classifies countries based on their per capita income. The categories are:
- Rich countries: Average per capita income of Rs 4,53,000 or more.
- Poor countries: Average per capita income of less than Rs 37,000.
However, this classification is inadequate because:
- It does not provide a full picture of development.
- It assigns a notional amount of money to poor people that may not reflect their actual financial situation.
Q8. What is development? What are the two aspects of development?
Ans: Development refers to positive growth or change in a country's economy, society, and politics.
The two main aspects of development are:
- Economic development: This involves an increase in the income of the population.
- Social development: This includes improvements in education, health, and public services.
Q9. Why are countries of the Middle East not called ‘developed’ in spite of high per capita income?
Ans: Countries in the Middle East are often not classified as developed despite their high per capita income due to several factors:
- Wealth Alone: High income from oil does not equate to overall development.
- Social Factors: Development also includes education, individual freedom, and gender equality.
- Political Aspects: Many Middle Eastern countries lack democratic governance.
Thus, while financial wealth is significant, it is not the sole indicator of a country's development.
Q10. Explain the concepts of Human Development Index (HDI) and that of the per capita income.
Ans: Human Development Index (HDI) and Per Capita Income are both measures of a country's development, but they differ significantly.
- Human Development Index (HDI):Developed by the U.N.D.P., HDI assesses a country's development based on three key factors:
- Health status
- Educational status
- Per capita income
- Per Capita Income:This measure, used by the World Bank, categorises countries as rich or poor based on their average income:
- Countries with a per capita income above Rs. 4,53,000 are considered rich.
- Countries with a per capita income below Rs. 37,000 are classified as poor.
Q11. What is the main criterion used by the World Bank in classifying different countries? Write the limitations of this criterion.
Ans: The main criterion used by the World Bank to classify countries is per capita income. This is calculated by dividing a country's total income by its total population. Countries with a per capita income of more than Rs. 4,53,000 per year are classified as rich, while those with less than Rs. 37,000 are considered poor.
However, there are limitations to this criterion:
- It does not provide a complete picture of development.
- Average income figures can be misleading, as they assume everyone earns the same amount.
- In reality, many individuals in a country may earn significantly less than the average, highlighting income inequality.
Q12. How can more jobs be created in the field of education? Give any three reasons.
Ans: More jobs can be created in the field of education through the following means:
- Literacy Rate: In India, only 65% of the population is literate. To provide quality education to everyone, more schools are needed.
- Teacher Demand: An increase in schools will require a greater number of teachers, thereby creating more job opportunities.
- Support Staff: More schools will also need thousands of supporting staff, such as administrative personnel, leading to additional job creation.
Q13. Mention any three characteristics of development.
Ans:
Different individuals have their own developmental goals.
What constitutes development for one person may not be the same for another; it could even be harmful.
People often consider a mix of goals when thinking about development.
Q14. ‘For development people look at a mix of goals.’ Support the statement with suitable examples.
Ans: It is true that when women engage in paid work, their dignity within the household and society increases. However, respect for women can lead to:
- More sharing of household work.
- Greater acceptance of women working outside the home.
- A safe and secure environment that encourages women to take various jobs or start businesses.
Thus, developmental goals encompass not only better income but also other significant aspects of life.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. Why Kerala has a better human development ranking than Punjab in spite of lower per capita income?
Ans: Keralahas a lower per capita income but a better human development ranking than Punjab due to several factors:
- Literacy Rate: Kerala boasts the highest literacy rate in India.
- Infant Mortality Rate: Kerala's rate is significantly lower (11) compared to Punjab's (49).
- Net Attendance Ratio: Kerala has a higher attendance ratio (91) than Punjab (81).
- Infrastructure: Kerala offers superior health and educational facilities.
- Public Services: The state provides better public amenities.
Q2. Mention any five conditions or aspects that one would consider before accepting a job.
Ans: Before accepting a job, there are several important factors to consider:
- Salary: A competitive salary is essential for most job seekers. It allows individuals to meet their needs and desires.
- Working Environment: A peaceful and safe workplace is crucial. A positive atmosphere enhances productivity for both the employee and the company.
- Job Security: While a job with lower pay may offer regular employment, it can provide a sense of security that many find valuable.
- Benefits: Access to medical facilities and paid leave for illnesses is important. Other benefits like a provident fund and gratuity also play a significant role in decision-making.
- Learning Opportunities: The chance to learn and grow during employment is beneficial for both the individual and the employer.
In summary, job seekers value not only material rewards but also various non-material aspects that contribute to their overall well-being.
Q3. What is the meaning of Infant Mortality Rate? Give two reasons for low infant mortality rate in Kerala.
Ans: Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) refers to the number of children who die before their first birthday, measured per 1,000 live births in a given year.
Kerala has a low IMR due to:
- Access to healthcare: The state provides adequate basic health facilities.
- Public Distribution System: A well-functioning system ensures people receive essential food and commodities at subsidized rates.
These factors contribute to better health and nutrition, helping to keep the IMR low.
Q4. ‘Human development is the essence of social development’. Explain.
Ans: Human development is essential for social development as it prioritises the quality of life for individuals. It focuses on:
- Enhancing well-being through meeting people's needs, choices, and aspirations.
- Building human capabilities to ensure a long, healthy life.
- Providing access to education and adequate livelihood opportunities.
- Expanding basic choices for individuals.
A society is considered ideal when all its members enjoy a quality life, reflecting the importance of human development in creating a thriving community.
Q5. Distinguish between developed and developing countries.
Ans: The following differences can be observed between developed and developing countries:
- Economic Status: Developed countries have a high average income, while developing countries typically have lower incomes.
- Infrastructure: Developed nations possess advanced infrastructure, including transportation and communication systems, whereas developing nations often face challenges in these areas.
- Healthcare: Citizens in developed countries generally enjoy better healthcare services and longer life expectancy compared to those in developing countries.
- Education: Higher literacy rates and better educational facilities are common in developed countries, while developing countries may struggle with access to quality education.
- Industrialisation: Developed countries are highly industrialised, whereas developing countries may rely more on agriculture and have less diversified economies.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Extra Question Answers - Development
| 1. What is the significance of development in a country? |  |
| 2. What are the key indicators of development? |  |
| 3. How does sustainable development differ from traditional development? |  |
| 4. What role does education play in development? |  |
| 5. How can governments promote development effectively? |  |

















