Class 6 History Notes - Traders Kings and Pilgrims
Chapter Notes - History Traders Kings and Pilgrims
- Around 1,000 BC when the Second Urbanisation characterized North India, the area around Deccan Peninsula and South India saw ht eco-habitation of both Iron Age and Megalithic Age leading to a strong civilization.
Sangam Age:
(i) The Iron Age laid roots of a golden period in South India from 300 BC to 300 AD, popularly known as the Sangam Age.
(ii) The rich poetry of this period reflects the glory of Tamil culture and society.
(iii) Tamils had good contacts and trade relations with distant lands like Rome and Cambodia.
Fig: Sangam Age
Sangam Literature:
i) The word ‘Sangam’ means assembly. The Tamil literature reveals three literary gatherings of poets and scholars around
(ii) 2,200 years ago under the patronage of the Pandyan Kings.
iii) Of the second assembly, only the Tamil grammar ‘Tolkappiyam’ has survived. The third assembly at Madurai led to the creation of over 2,000 poems together which is called the Sangam Literature.
Southern Kingdoms:
(i) The Sangam literature mentions three Kingdoms in the Tamilakam territory: The Cheras, the Cholas, and the Pandyas.
ii) The Cheras were Alsop called Keralaputras and traded in spices, cattle, and turmeric.
iii) The Cholas ruled Kaveri delta and even captured parts of Sri Lanka.
iv) The Pandyas centered around Madurai. Madurai was famous for its third Tamil assembly.
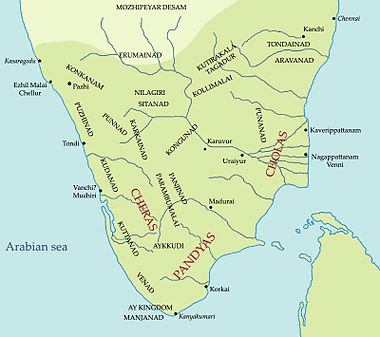
Fig: Kingdom of Acient India
Foreign Trade:
i) Tamilakam had extensive trade with distant lands.
ii) Greeks text like Pliny’s periplus History also confirm these trade relations.
iii) The Sangam literature uses the word ‘Yavana’ for Greek and Romans.
iv) Historians confirm that Christianity came to South India due to these contacts.
v) Trade route was through North India front Taxila to Pataliputra via Ujjain which linked to Tamralipti seaport.
(vi) The Tamil Kingdom even had trade with South and South-East regions of Ceylon, Malaya, Java, Cambodia, Sumatra, etc.
Conquerors from Distant Lands:
i) In North-West India, the main conquerors were Sungas, Indo-Greeks, Parthians, Kushanas, and Shakas.
ii) Sungas came in 185BC, after defeating the last Mauryan ruler Brihadratha and captured Magadha. They spread Buddhism.
iii) The Indo-Greeks or Bactrians were from Northern Afghanistan. They captured Punjab.
iv) The Parthians came from Central Asia and established Gandhara as their capital. The Kushanas were nomadic Yueh-chi tribes of North-West China. They defeated the
(v) Indo-Greeks, Parthians and Shakas. Their greatest ruler was Kanishka.
(vi) Shakas came through Hindu-kush mountains and established Ujjain as their capital.
The most famous Shaka ruler was Rudradaman.
(vii) In central India, the Satavahanas were the main rulers. Gautamipurtra, Sri Satkarni was their most important ruler.
Trade:
(i) Trade flourished during this period. All the kingdoms issued a number of gold, silver and copper coins to promote trade.
(ii) Broach, Sopara and Kalyan were the important port cities.
(iii) The most important reason for development and prosperity during the age was the Silk Route which linked India to Rome via Central Asia.
Religion:
i) In India, Buddhism and Hinduism were the two main religions.
ii) Buddhism was divided into two cults Hinayana and Mahayana.
iii) Menander, the Indo-Greek king, and Kanishka, the Kushana ruler helped in the promotion of Buddhism.
iv) Bamiyan, one of the tallest statues of Buddha.
(v) Hinduism was patronized by Satavahana ruler who worshipped Vishnu, Shiva, and Mother Goddess.
(vi) Emphasis was now laid on loving devotion to God called Bhakti.
(vii) Deities were kept in special homes called temples.
(viii) Bhagavad Gita became famous text during this period.
FAQs on Class 6 History Notes - Traders Kings and Pilgrims
| 1. How did trade influence the rise of civilizations during ancient times? |  |
| 2. What were some of the key goods traded along the Silk Road? |  |
| 3. How did the pilgrimage to Mecca impact the spread of Islam in ancient times? |  |
| 4. Who were some of the prominent rulers during ancient times who were known for their support of trade and commerce? |  |
| 5. How did the exchange of goods and ideas along trade routes contribute to the development of art and architecture in ancient civilizations? |  |















