Class 8 Geography Notes - Mineral and Power Resources
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Mineral? |

|
| Types of Minerals |

|
| Extraction of Minerals |

|
| Distribution of Minerals |

|
| Uses of Minerals |

|
| Conservation of Minerals |

|
| Power Resources |

|
What is a Mineral?
A naturally occurring substance with a definite chemical composition is a mineral, and minerals are not evenly distributed over space. Minerals are concentrated in a particular area or rock formations. A few of these minerals are found in areas which are not easily accessible, such as the Arctic ocean bed and Antarctica.
 Minerals are also formed in several types of geological environments under varying conditions. They are created by natural processes without any human interference. They can be identified on the basis of their physical properties such as colour, density, hardness and chemical properties such as solubility.
Minerals are also formed in several types of geological environments under varying conditions. They are created by natural processes without any human interference. They can be identified on the basis of their physical properties such as colour, density, hardness and chemical properties such as solubility.
Types of Minerals
There are 3000 various types of Minerals and based on their composition, they can be classified into metallic and non-metallic minerals. 
Metallic Minerals
1. Metallic minerals contain metal in the raw form.
2. Metals are hard substances that conduct heat and electricity and have a characteristic luster or shine.
3. Iron ore, bauxite, manganese ore are some examples.
4. Metallic minerals may be ferrous or non-ferrous.
- Ferrous minerals like iron ore, manganese and Chromite contain iron.
- A non-ferrous mineral does not contain iron but may contain some other metal such as gold, silver, copper or lead.
Non-Metallic Minerals
1. Non-metallic minerals do not contain metals.
2. These metals are soft and non-lustrous.
3. They are bad conductors of heat and electricity.
4. Limestone, mica and gypsum are examples of such minerals. The mineral fuels like coal and petroleum are also non-metallic minerals.
Extraction of Minerals
Mineral extraction means the removal of topsoil, gravel, rock, clay, sand or other earth material, including accessory activities such as washing, sorting, screening, crushing and stockpiling. Minerals can be extracted by mining, drilling or quarrying.
Open Cast Mining:
Minerals that lie at shallow depths are taken out by removing the surface layer; this is known as open-cast mining. Open cast mining is the process of making a large pit in the ground and extracting minerals. This technique is used in places where the mineral or the ore is close to the ground or near the surface of the earth. Open pits are called ‘quarries’ sometimes.
Shaft Mining:
When deep bores (called shafts) are made to reach the mineral deposits at great depth, the process is called shaft mining.
Shaft mining, or shaft sinking, involves driving vertical shafts into the earth. Once a desired depth is reached, auxiliary tunnels, or drifts, are dug in all directions to access ore and mineral deposits. Shaft mines are dug when there are concentrated mineral deposits embedded deep underground.
Drilling:
When deep wells are bored to take out the mineral, the process is called drilling. Petroleum and natural gas are extracted by this method.
Drilling is the process of penetrating through the ground and extracting rocks from various depths beneath the surface for confirming the geology beneath and/or providing samples for chemical analysis.
Quarrying:
When minerals are simply dug out from near the surface, the process is called quarrying.
Quarrying refers to extracting materials directly from the surface. In mining and quarrying, water is used and gets polluted in a range of activities, including mineral processing, dust suppression, and slurry transport.
Distribution of Minerals
- Minerals can generally be found in the various types of rocks. Few types of minerals can also be found in igneous rocks & other kinds are found in metamorphic rocks. The other forms of minerals are normally found in sedimentary rocks.
- Generally, metallic minerals can also be identified in igneous & metamorphic rocks. Non-metallic minerals are generally found in the sedimentary rocks of plains & young fold mountains.

Asia
1. China and India have large iron ore deposits.
2. The continent produces more than half of the world’s tin.
China, Malaysia and Indonesia are among the world’s leading tin producers.
3. China also leads in production of lead, antimony and tungsten.
4. Asia also has deposits of manganese, bauxite, nickel, zinc and copper.
Europe
1. It is the leading producer of iron-ore in the world.Russia, Ukraine, Sweden and France have large deposits of iron ore.
2. Minerals deposits of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel are found in eastern Europe and European Russia.
North America
Mineral deposits in North America are located in three zones:
- The Canadian region north of the Great Lakes: Iron ore, nickel, gold, uranium and copper
- The Appalachian region: Coal
- The mountain ranges of the west: Copper, lead, zinc, gold and silver
South America
- Iron Ore: Brazil
- Copper: Chile and Peru
- Tin: Brazil and Bolivia
- Mineral Oil: Venezuela, Argentina, Chile, Peru and Columbia
- South America also has large deposits of gold, silver, zinc, chromium, manganese, bauxite, mica, platinum, asbestos and diamond.
Africa
- It is the world’s largest producer of diamonds, gold and platinum.
- Gold: South Africa, Zimbabwe and Zaire
- Oil: Nigeria, Libya and Angola.
- Other minerals found in Africa are copper, iron ore, chromium, uranium, cobalt and bauxite.
Australia
- It is the largest producer of bauxite in the world.
- It is a leading producer of gold, diamond, iron ore, tin and nickel.
- It is also rich in copper, lead, zinc and manganese.
- Kalgoorlie and Coolgardie areas of western Australia have the largest deposits of gold.
Antarctica
- Deposits of coal in the Transantarctic Mountains and iron near the Prince Charles Mountains of East Antarctica is predicted
- Iron ore, gold, silver and oil are also present in commercial quantities.
Uses of Minerals
- Minerals for gems-hard set in various jewelry styles
- Copper is used in making coins and pipes.
- Silicon used in the computer industry is obtained from quartz.
- Aluminium extracted from its ore bauxite is used in automobiles and aeroplanes, bottling industry, buildings and kitchen cookware.
Conservation of Minerals
Minerals are a non-renewable resource. It takes thousands of years for the formation and concentration of minerals. The rate of formation is much smaller than the rate at which the humans consume these minerals. It is necessary to reduce wastage in the process of mining because it creates pollution and ultimately global warming. Recycling of metals is another way in which the mineral resources can be conserved. We need to move towards sustainable development to save our environment as well.

Power Resources
Power or energy plays a vital role in our lives. We need power for industry, agriculture, transport, communication and defense. Hence conservation of energy is also essential. Power resources may be broadly categorized as conventional and non-conventional resources.
Conventional Resources
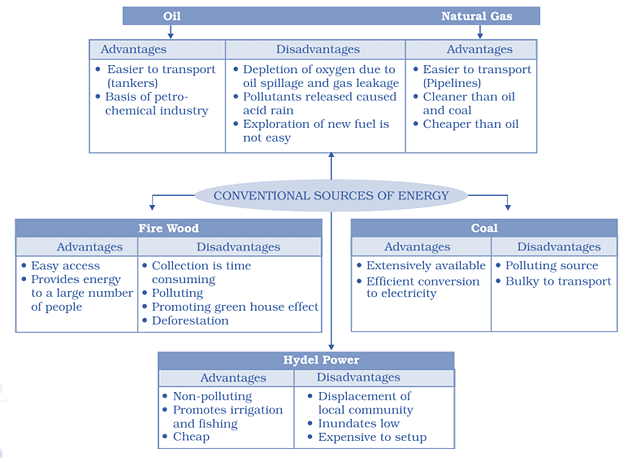
Resources which can been commonly used for a long time are known as conventional sources. The primary conventional energy resources are firewood and fossil fuels.
Firewood
- It is widely used for cooking and heating
- More than 50% of the energy used by villagers comes from firewood.
Fossil Fuels
- Remains of plants and animals which were buried under the earth for millions of years got converted by the heat and pressure into fossil fuels
- Coal, petroleum and natural gas are the fossils fuels which are the main sources of conventional energy.
- Fossil fuels are in limited quantities and the rate at which the growing world population is consuming them is far greater than the rate of their formation.
 Conventional Sources of Energy
Conventional Sources of Energy
 Conventional Sources of Energy
Conventional Sources of Energy
1. Coal
- The most abundantly found fossil fuel on earth is coal.
- Coal is generally utilised as domestic fuel in various industries like iron and steel, steam engines, and to produce electricity.
- Electricity generated from coal is called "thermal power."
- Another name for coal is “buried sunshine” because of its formation procedure.
- The largest coal producers in India are the areas of Raniganj, Jharia, Dhanbad and Bokaro.
2. Petroleum
- Petroleum is also identified between the layers of rocks and is drilled from oil fields situated in off-shore and coastal regions.
- Different types of products such as diesel, petrol, kerosene, wax, plastics, and lubricants are produced by the crude oil refined from petroleum.
- It is so valuable that it is called "black gold."
- The largest producer of petroleum in India is Digboi in Assam. Apart from that, Bombay High in Mumbai and the Krishna and Godavari river deltas are also rich in petroleum.
3. Natural Gas
- Natural gas can be formed in deposits of Petroleum and is discharged at the time of bringing crude oil to the surface.
- It can be utilized in the form of domestic and industrial fuel.
- Jaisalmer, Krishna and Godavari delta etc are rich in natural gas resources.
4. Hydel Power
- The stored rainwater or the river water in dams is generally prepared to fall from heights.
- The water with the help of turbine blades then produces electricity. This is termed as hydroelectricity.
- The water discharged after the generation of electricity is used for irrigation.
- The famous hydel power projects of India are Bhakra Nangal, Gandhi Sagar and Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC) projects.
Non-Conventional Resources
Fossil fuels which are falling short due to their increasing usage right now. There is also a huge possibility of conventional sources of energy of being getting exhausted. Another demerit of using conventional sources of energy is increasing environmental pollution. For that purpose, the requirement of non-conventional sources of energy is being realized now.

1. Solar Energy
- The sun is the biggest source of energy that we have, it’s radiating very high energy constantly for very long time and will continue to do so. The energy we obtain from the sun is called solar energy.
- Solar energy can be harnessed using several devices like solar cooker and solar panel.
- Solar energy trapped from the sun can be used in solar cells to produce electricity.
- Many of these cells are joined into solar panels to generate power for heating and lighting purpose.
- The technology of utilising solar energy benefits a lot of tropical countries that are blessed with abundant sun shine.
- Solar energy is also used in solar heaters, solar cookers, solar dryers besides being used for community lighting and traffic signals.

Advantages of Solar Energy:
- Solar energy is available to us in infinite amount. Since, sun will be there and will continuously emit energy for the next few hundred million years.
- Solar energy can protect the nature and reduce global warming. Solar energy is a green form of energy which can be converted to electricity and used in different energy and this process of creating electricity is much cleaner than from burning coal which emits harmful gases into our atmosphere.
- Solar devices (like solar panels and solar cookers) though expensive now are one time investment and saves a good amount money in long term.
- Proper harnessing of solar energy is also a very crucial aspect of our space exploration as the artificial satellites and other orbiters that we sent on outer space and different planets operate using solar energy.
2. Wind Energy
- The energy obtained from the wind is called wind energy.
- The wind contains kinetic energy which can used to harness energy by converting it to mechanical energy by the use of wind mill.
- The high speed winds rotate the wind mill which is connected to a generator to produce electricity.
- Wind farms having clusters of such wind mills are located in coastal regions and in mountain passes where strong and steady winds blow
Although, wind energy has been used by us for a long time , it was used in propelling the sails of the ship in the ancient times.
Advantages of Wind Energy
- Like solar energy , it is also a renewable form of energy.
- It does not cause any air pollution and global warming by releasing harmful gases.
- It is space efficient and requires very little space on the land surface and the land between two windmills can be used for agriculture and other different purposes.
Disadvantages of Wind Energy
- It is very location specific as wind mills cannot be setup in all places. It can only be installed at places where there is strong winds
- It is very costly to setup and difficult for repair.
- Storms and cyclones cause great damage to windmills.
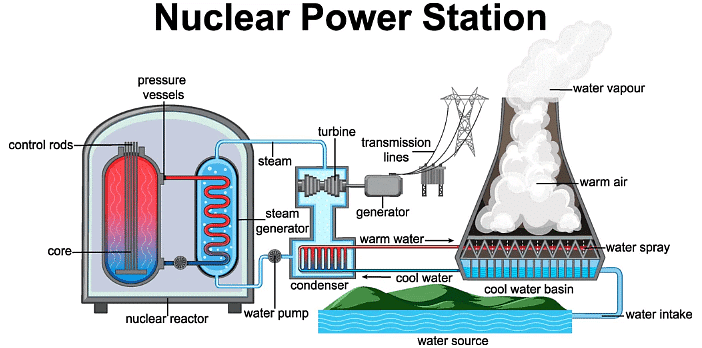
3. Nuclear Energy
- Nuclear energy is the energy produce when one heavy nucleus splits into two light nuclei or two light nuclei fuses to one heavy nucleus producing enormous amount energy in form of heat and light.
- Nuclear reaction are of two types : Nuclear Fission & Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear Fission- The process in which one heavy nucleus (e.g uranium , polonium) splits into two light nuclei producing large amount of energy and neutrons along with it.
Nuclear Fusion- The process in which two light nuclei fuses into one heavy nucleus at a very high temperature and pressure, producing large amount of energy
 Advantages of nuclear energy:
Advantages of nuclear energy:
- Nuclear energy is a green source of energy which does not produces any harmful gases .
- The amount of energy obtained from a single nuclear reaction is very high.
Disadvantages of nuclear energy:
- Nuclear reactions are very hard to control, as they are chain reactions and even a slight mistake can cause huge risks.
- The elements used in the reaction are radioactive and the radiation can cause severe health issues like cancer and other genetical deformation.
- Unfortunately, this is also used in nuclear weapons. An atomic bomb is based on nuclear fission reaction where the reaction is uncontrollable. It was used two times in World War2 and cause the deaths of millions of people.
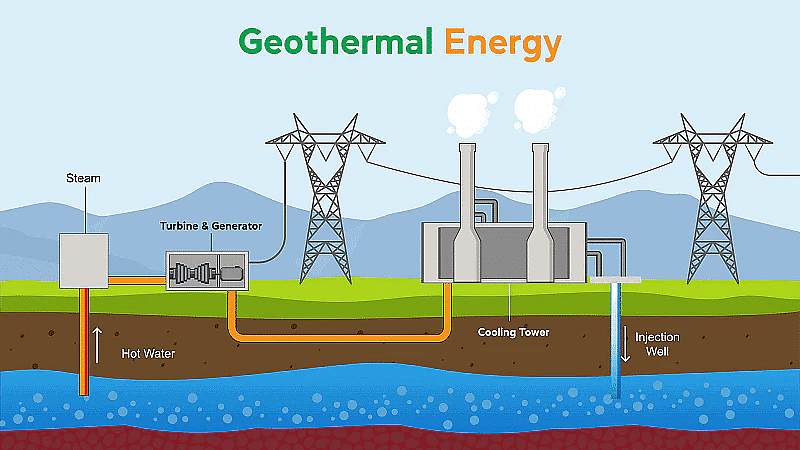
4. Geo-Thermal Energy
- Geo-thermal energy is the heat energy possessed by the rocks inside the earth.
- The places where the rocks inside the hot is very hot are called hotspot.
- Now, the heat of these rocks heats up the underground water and turns it into steam.
- Steam is extracted by drilling hole into the ground and connecting pipeline to rotate the turbine with the help of the steam and produce electricity for use.
- In India, only one place is Madhya Pradesh has a hotspot . But in US there are a no. of geo-thermal power plants. The Pacific ring of fire is also a suitable spot for geo-thermal energy sites.
 Advantages of Geo-Thermal Energy:
Advantages of Geo-Thermal Energy:
- They are renewable and completely environment friendly.
- They are also energy of future and new research to harness geothermal energy more efficiently is going on in different parts of the world.
Disadvantages of Geo-Thermal Energy:
- The largest single disadvantage of geothermal energy is that it is location specific.
- Although geothermal energy does not typically release greenhouse gases, there are many of these gases stored under the Earth’s surface which are released into the atmosphere during digging. These gas emissions are still far lower than those associated with fossil fuels.
- Geothermal energy also runs the risk of triggering earthquakes. This is due to alterations in the Earth’s structure as a result of digging.
- Geothermal energy is an expensive resource to tap into, with price tags ranging from around $2-$7 million for a plant with a 1 megawatt capacity.
5. Tidal Energy
- Tides is the periodic movement of the ocean waters due to the gravitational force of the moon and the sun. Tides are of two types – high tides i.e the rise of water and low tides i.e the fall in the level of water.
- The tidal energy from tides are obtained and used to generate electricity using a machine called Tidal Energy Generator.
- Tidal barrages or dams are built over a limited sea entrance. When the sea level rises, water pours into the dam. This causes the turbine blades, which are connected at the dam’s entrance, to shift. As a consequence, power is generated.

Advantages of Tidal Energy
- Tidal energy is a renewable energy source, which implies that it does not deteriorate as it is consumed.
- Tidal power plants, in addition to being a sustainable energy source, do not release greenhouse gases during electricity generation.
- The tidal currents are quite predictable. Low and high tides follow predictable patterns, making it easy to predict when electricity will be generated throughout the day.
- Tidal power plants are capable of producing large amounts of electricity. One of the key reasons for this is because water is extremely dense – over 800 times denser than air.
- Also, the system established to obtain tidal energy has low operational and maintenance costs.
Disadvantages of Tidal Energy
- The possible installation location must fulfill extremely precise conditions in order for a tidal power plant to be developed.
- Because of the high density of water, tidal energy turbines must be substantially more robust than wind turbines. The cost of building a tidal power producing facility varies based on the technology used.
- While tidal power generates predictable power, it does not produce steady power. We can predict when the tidal power plant will create electricity, but that output may not match the demand for energy.
6. Bio-Gas
- Biogas is the energy that is obtained from organic materials like dead plants, kitchen waste, cow dung, and other organic materials.
- These organic wastes are put in large containers or pits called biogas digesters and are decomposed by bacterial action.
- After certain days, the digester emits biogas which is a mixture of methane gas and carbon dioxide.
- Biogas is considered as an excellent fuel used for cooking. It produces a high amount of heat and light.

Advantages of Bio-Gas:
- It is an efficient technology which produces fuels from our wastes.
- It reduces our dependencies on fossil fuels as bio-gas produced from biomass plants can be directly used as fuel
- It is very cost effective and cheap.
- It is carbon neutral. Carbon dioxide is released on burning bio-waste but no carbon is released into the atmosphere on burning bio-fuels like bio-gas etc.
Disadvantages of Bio-Gas:
- It releases methane in the environment which causes greenhouse effect and global warming.
- It is not as effective as fossil fuels.
- Building of bio-gas plant requires a lot of space.
|
24 videos|33 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Geography Notes - Mineral and Power Resources
| 1. What is a mineral? |  |
| 2. What are the types of minerals? |  |
| 3. How are minerals extracted? |  |
| 4. How are minerals distributed? |  |
| 5. What are the uses of minerals? |  |

















