NCERT Solution (Part - 2) - Recording of Transactions-I | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Q3 : Describe how accounts are used to record information about the effects of transactions?
Answer :
Every transaction is recorded in the original book of entry (journal) in order of their occurrence; however, if we want to know that how much we receive from our debtors or how much to pay to the creditors, it is not possible to determine at a single movement. Hence, we prepare accounts to know the position of business activities in the meantime.
There are some steps to record transactions in accounts; it can be easily understood
with the help of an example.
Sold goods to Mr A worth Rs 50,000 on 12th April and received payment Rs 40,000 on
25th April. The following journal entries will be recorded:

Step 1- Locate the account in ledger, i.e., Mr A's Account.
Step 2- Enter the date of transaction in the date column of the debit side of Mr A's
Account.
Step 3- In the 'Particulars' column of the debit side of Mr A's Account, the name of
corresponding account is to be written, i.e., 'Sales'.
Step 4- Enter the page number of the ledger in the Journal Folio (J.F.) column of Mr A's
Account.
Step 5- Enter the amount in the 'Amount' column.
Step 6- Same steps are to be followed to post entries in the credit side of Mr A's
Account.
Step 7- After entering all the transactions for a particular period, balance the account by
totalling both sides and write the difference in shorter side, as 'Balance c/d'.
Step 8- Total of account is to be written on either sides.
Q4 : What is a journal? Give a specimen of journal showing at least five entries.
Answer:
Journal is derived from the French word Jour, means daily records. In this book,
transactions are recorded in order of their occurrence, i.e., in chronological order from
the source document. It is also termed as the book of original entry and each
transaction is termed as journal entry.
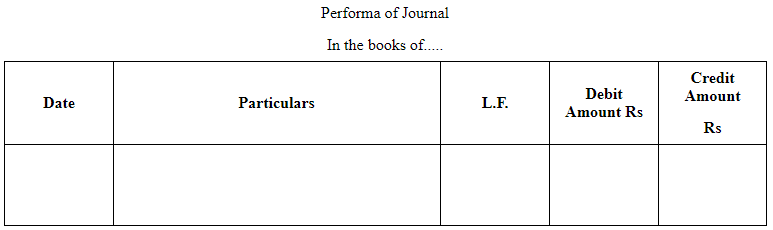
Date- Date of transaction is recorded in the order of their occurrence.
Particulars- Details of business transactions like, name of the parties involved and the
name of related accounts, are recorded.
L.F.- Page number of ledger account when entry is posted.
Debit Amount- Amount of debit account is written.
Credit Amount- Amount of credit account is written.
Recording of a Journal Entry




Q5 : Differentiate between source documents and vouchers.
Answer :
Basis of Difference | Source Documents | Vouchers |
Meaning | It refers to the documents in writing, containing the details of events or transactions. | When source document is considered as evidence of an event or transaction, then it is called voucher. |
Purpose | It is used for preparing accounting vouchers. | It is used for analysing the transactions. |
Recording | It acts as a basis for preparing accounting voucher that helps in recording. | It acts as a basis for recording transactions. |
Preparation | It is prepared at the time when an event or a transaction occurs. | It can be prepared either when an event or a transaction occurs, or later on. |
Legality/Validity | It can be used as evidence in the court of law. | It can be used for assessing the authentication of transactions. |
Prepared By | It is prepared by the persons who are directly involved in the transactions, or who are authorised to prepare or approve these documents. | It is prepared by the authorised persons or by the accountants. |
Examples | Cash memo, invoice, and pay-in-slip, etc. | Cash memo, invoice, pay-in-slip (if used as evidence), debit note, credit note, cash vouchers, transfer vouchers, etc. |
Q6 : Accounting equation remains intact under all circumstances. Justify the
statement with the help of an example.
Answer :
According to the dual-aspect concept, every transaction simultaneously, has two effects of equal amount, i.e. debit and credit. However, in any case, the equality of total assets with the total claims of business (sum of capital and liabilities) is not disturbed. This equality is algebraically represented as:
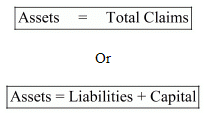
or, Liabilities = Asset - Capital
or, Capital = Assets - Liabilities
In any circumstance the above equation cannot be changed. For example,
1. Business started with cash Rs 1,00,000
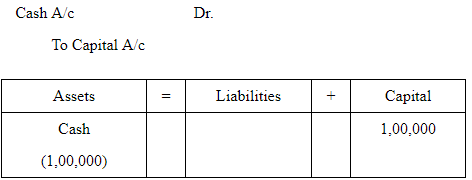
Assets decrease, as cash is invested into the business and capital increases. Thus the
equality between LHS and RHS remains intact.
2. Goods purchased on credit Rs 20, 000


Assets increase as well as liability increases, without disturbing the equality.
3. Goods purchased with cash 25000
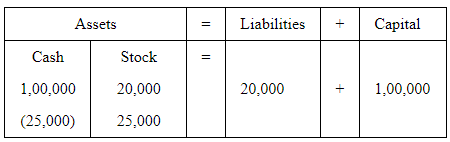
As goods are purchased for cash, so cash balance reduces by Rs 25,000, but on the other hand, stock balance increases by Rs 25,000. Thus the total balance of LHS remains equal to the total claims.
Q7 : Explain the double entry mechanism with an illustrative example.
Answer :
Double entry system is based on the dual aspect concept. It means every transaction
has two-sided effects, i.e., every debit has its credit.
This system is explained by Luca Pacioli in his book Summade Arithmetica
Geometria Proportioni et Proportionalita, 1494. He said if one is receiver, then the
other should be the giver.
In double entry system, accounts are classified as shown below.

1. Personal Accounts: It includes individual persons, firms, companies, and other institutions,
such as Mr. A, M/s ABC & Co. etc.
Rule of double entry system for personal accounts:
- Debit the receiver.
- Credit the giver.

2. Impersonal Accounts: It relates to non living things. Impersonal accounts are further classified as real accounts and nominal accounts.
1. Real Account- It includes all types of assets.

i. Tangible assets that can be seen and touched; for example, machinery, building, etc.
ii. Intangible assets that cannot be seen and touched; for example, goodwill, patent, etc.
Rule of double entry system for real accounts:
- Debit what comes in.
- Credit what goes out.
For example:
Furniture purchased for cash
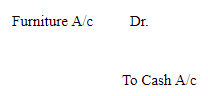
2. Nominal Account: It includes all expenses, losses, incomes and gains. Rule of double entry system for nominal accounts:
- Debit all losses and expenses.
- Credit all gains and incomes.

Numerical questions
Q1: Prepare accounting equation on the basis of the following:
(a) Harsha started business with cash Rs 2,00,000
(b) Purchased goods from Naman for cash Rs 40,000
(c) Sold goods to Bhanu costing Rs 10,000/- Rs 12,000
(d) Bought furniture on credit Rs 7,000
Answer:
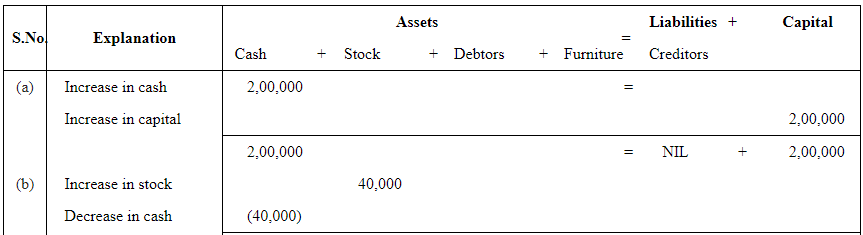
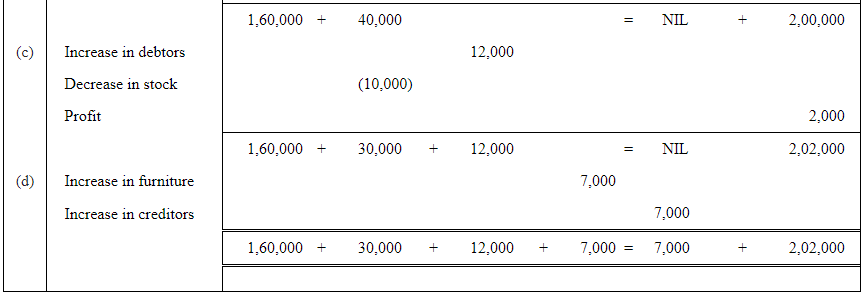
Q2 : Prepare accounting equation from the following:
| Rs | ||
| (a) | Kunal started business with cash | 2,50,000 |
| (b) | He purchased furniture for cash | 35,000 |
| (c) | He paid commission | 2,000 |
| (d) | He purchases goods on credit | 40,000 |
| (e) | He sold goods (costing Rs 20,000) for cash | 26,000 |
Answer:
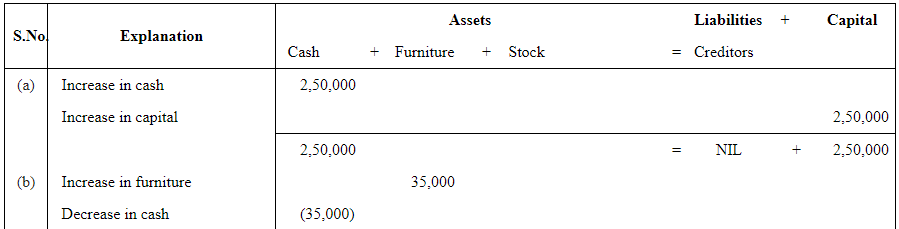
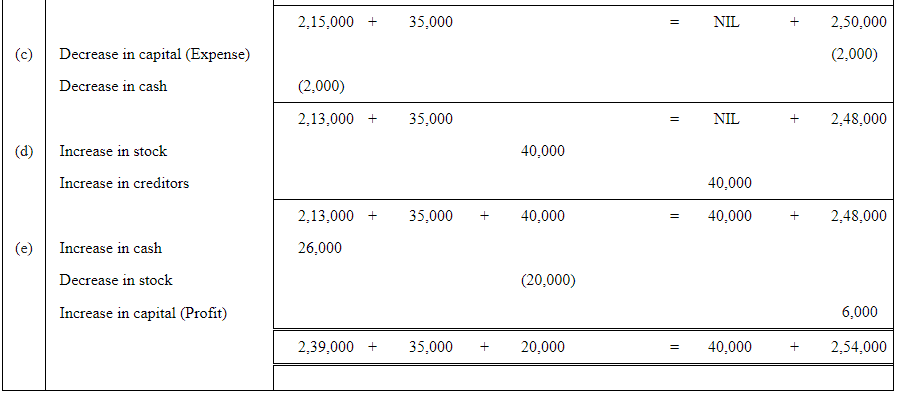
Page No 89:
Q3: Mohit has the following transactions, prepare accounting equation:
| Rs | ||
| (a) | Business started with cash | 1,75,000 |
| (b) | Purchased goods from Rohit | 50,000 |
| (c) | Sales goods on credit to Manish (Costing Rs 17,500) | 20,000 |
| (d) | Purchased furniture for office use | 10,000 |
| (e) | Cash paid to Rohit in full settlement | 48,500 |
| (f) | Cash received from Manish | 20,000 |
| (g) | Rent paid | 1,000 |
| (h) | Cash withdrew for personal use | 3,000 |
Answer:
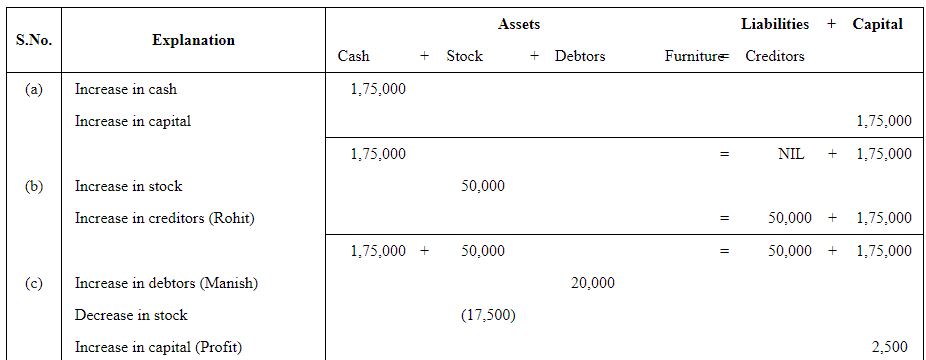
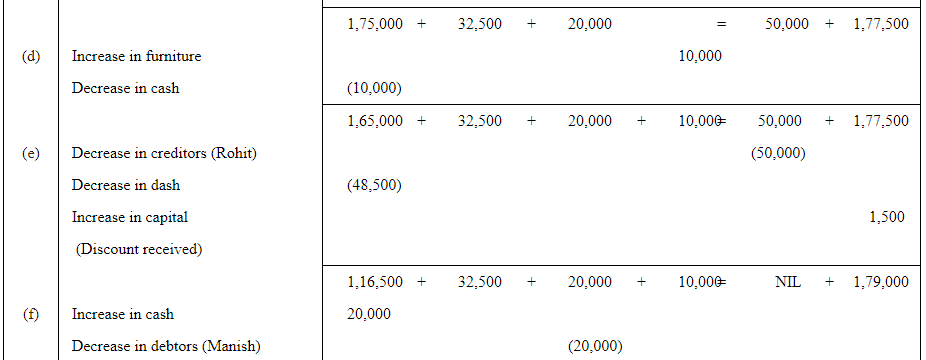
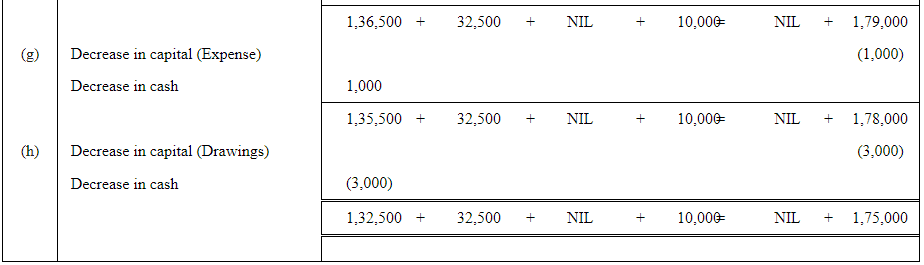
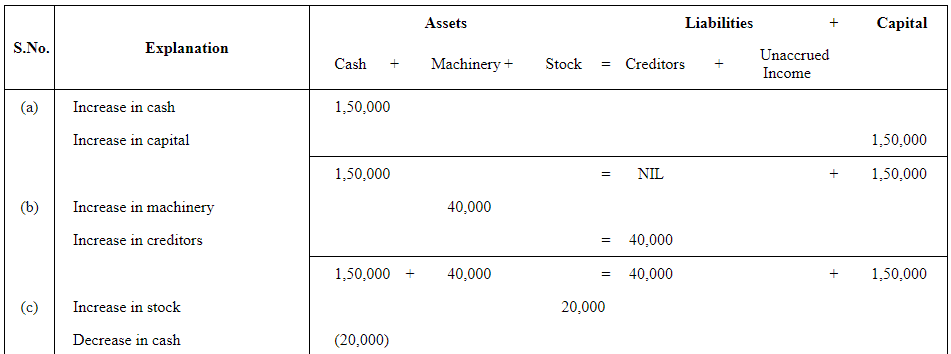
Q4: Rohit has the following transactions:
| Rs | ||
| (a) | Commenced business with cash | 1,50,000 |
| (b) | Purchased machinery on credit | 40,000 |
| (c) | Purchased goods for cash | 20,000 |
| (d) | Purchased car for personal use | 80,000 |
| (e) | Paid to creditors in full settlement | 38,000 |
| (f) | Sold goods for cash costing Rs 5,000 | 4,500 |
| (g) | Paid rent | 1,000 |
| (h) | Commission received in advance | 2,000 |
Prepare the Accounting Equation to show the effect of the above transactions on the assets, liabilities and capital.
Answer:
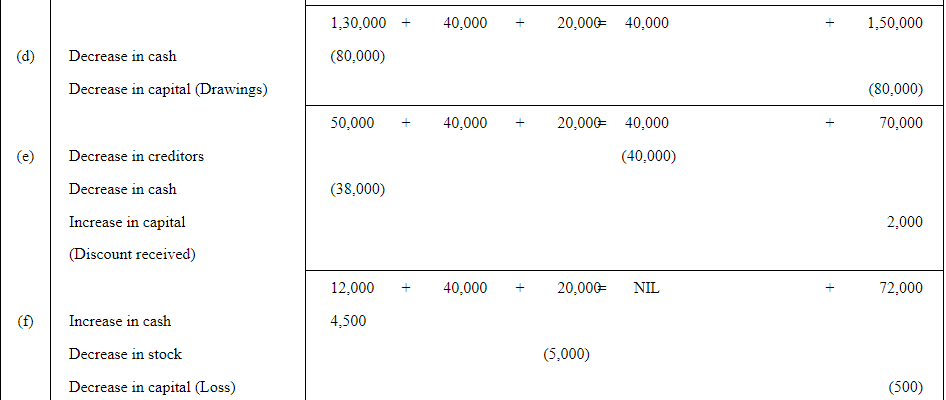
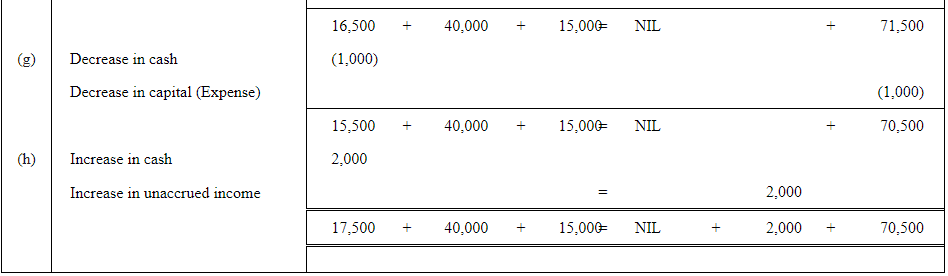
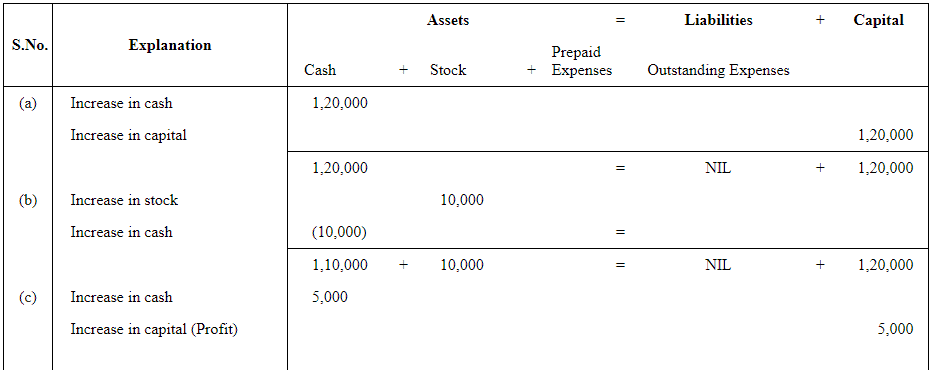
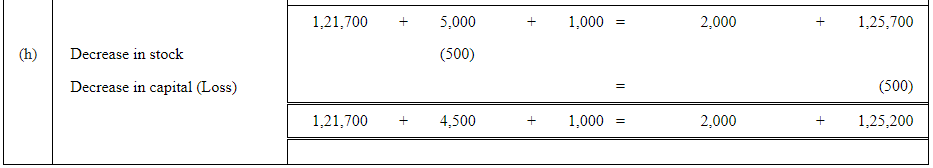
Q5: Use accounting equation to show the effect of the following transactions of M/s Royal Traders:
| Rs | ||
| (a) | Started business with cash | 1,20,000 |
| (b) | Purchased goods for cash | 10,000 |
| (c) | Rent received | 5,000 |
| (d) | Salary outstanding | 2,000 |
| (e) | Prepaid Insurance | 1,000 |
| (f) | Received interest | 700 |
| (g) | Sold goods for cash (costing Rs 5,000) | 7,000 |
| (h) | Goods destroyed by fire | 500 |
Answer :
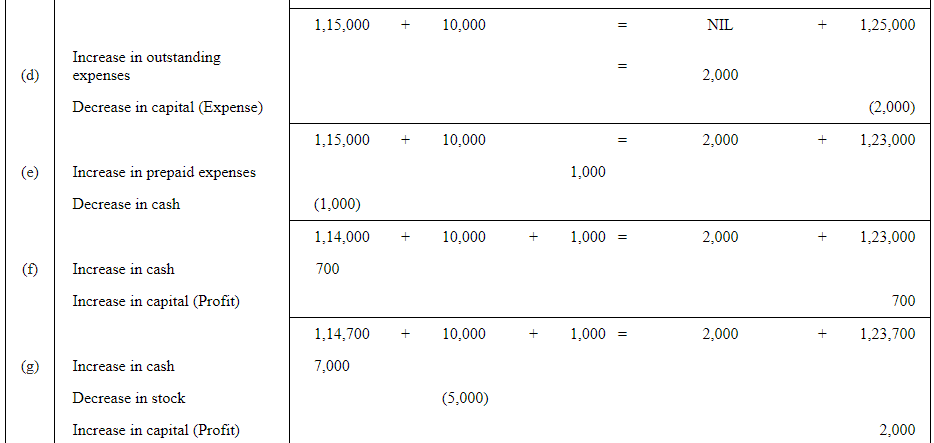
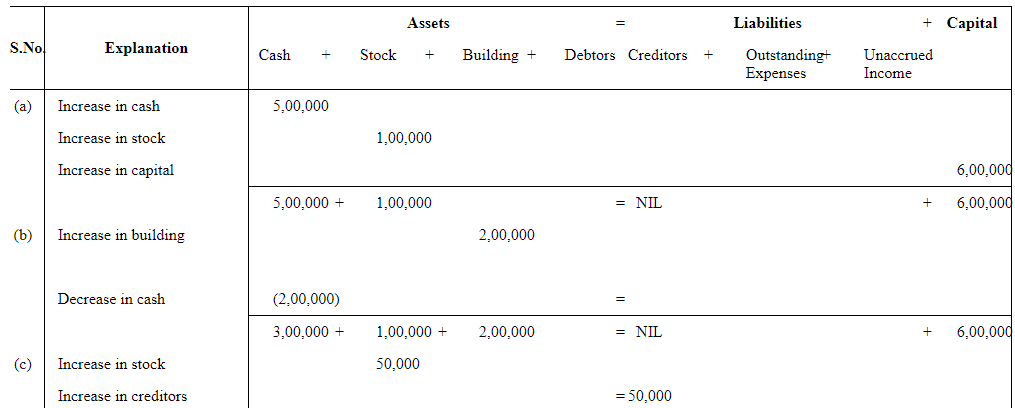
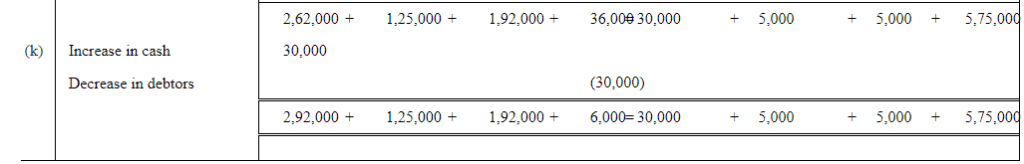
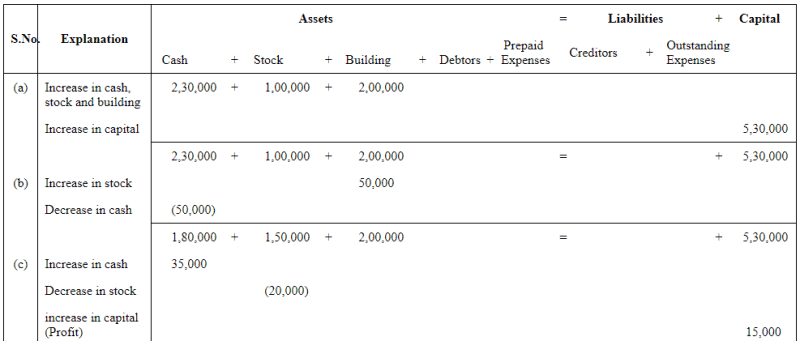
Q6: Show the accounting equation on the basis of the following transaction:
| (a) | Udit started business with: | Rs | |
| (i) | Cash | 5,00,000 | |
| (ii) | Goods | 1,00,000 | |
| (b) | Purchased building for cash | 2,00,000 | |
| (c) | Purchased goods from Himani | 50,000 | |
| (d) | Sold goods to Ashu (Cost Rs 25,000) | 36,000 | |
| (e) | Paid insurance premium | 3,000 | |
| (f) | Rent outstanding | 5,000 | |
| (g) | Depreciation on building | 8,000 | |
| (h) | Cash withdrawn for personal use | 20,000 | |
| (i) | Rent received in advance | 5,000 | |
| (j) | Cash paid to Himani on account | 20,000 | |
| (k) | Cash received from Ashu | 30,000 | |
Answer:
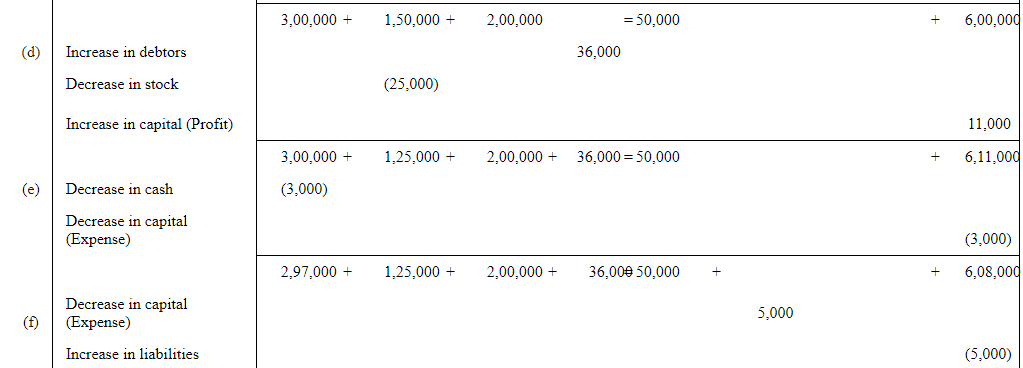
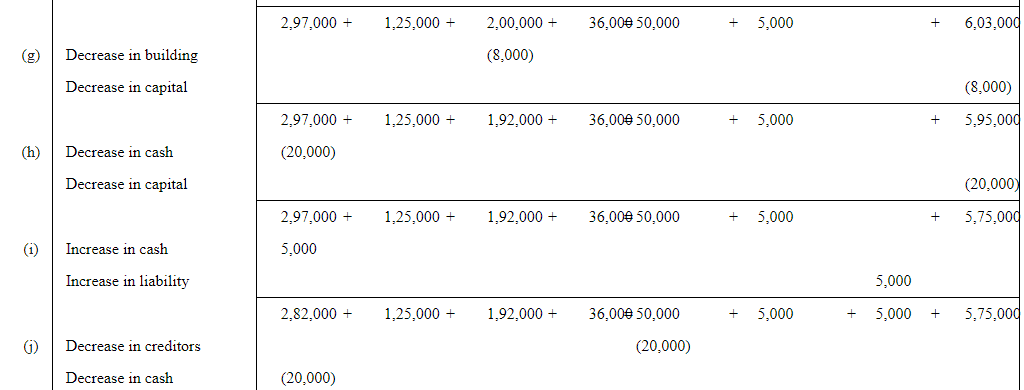
Page No 90:
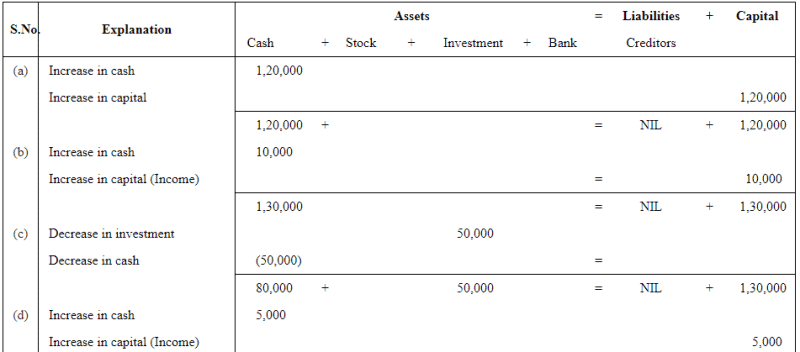
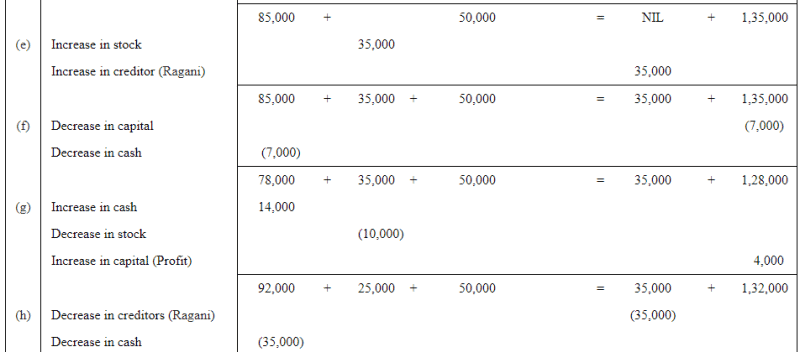
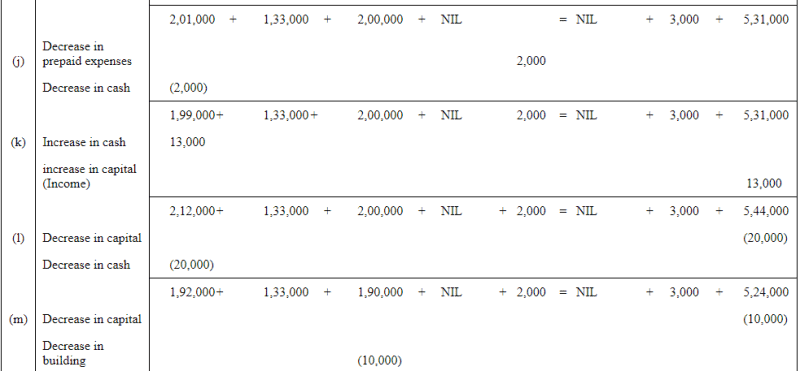
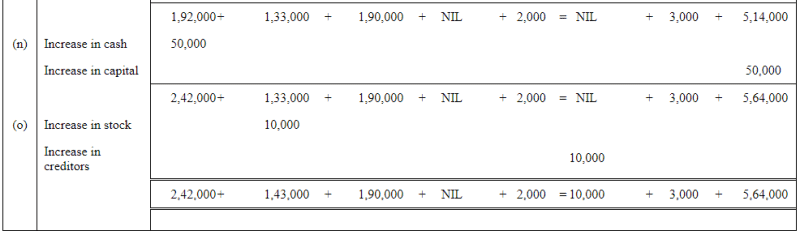
Question 7: Show the effect of the following transactions on Assets, Liabilities and Capital through accounting equation:

ANSWER:


QUESTION 8: SHOW THE EFFECT OF FOLLOWING TRANSACTION ON THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION:


ANSWER:
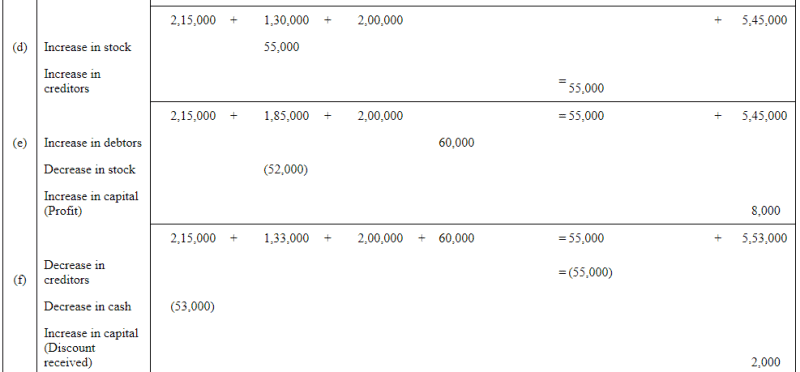

|
64 videos|152 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solution (Part - 2) - Recording of Transactions-I - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is recording of transactions? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of recording transactions in a business? |  |
| 3. What are some of the commonly used methods for recording transactions? |  |
| 4. What is the role of a bookkeeper in recording transactions? |  |
| 5. What are some of the common mistakes that businesses make while recording transactions? |  |