Scanner Chapter 3 & 4 - (Macro Economics) | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
C.B.S.E. PAPER 2013
(Q1) Give two examples of intermediate goods. (1 M)
Ans: Two examples of intermediate goods are:
- Wood used in furniture manufacturing
- Flour used by a bakery to make bread
Explanation: Intermediate goods are products used as inputs in the production of final goods and are not counted in GDP separately to avoid double counting.
(Q2) Distinguish between “real” gross domestic product and “nominal” gross domestic product. Which of these is a better index of the welfare of the people and why? (4 M)
Ans: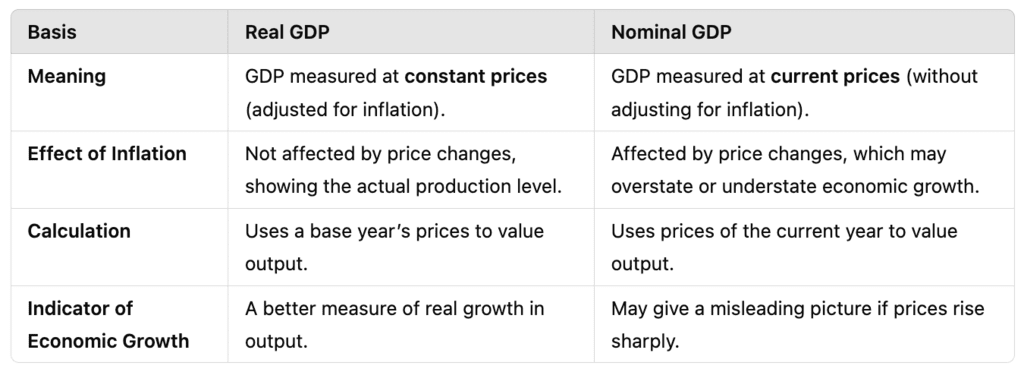
Real GDP is a better index of people's welfare because:
- It reflects the actual increase in goods and services produced rather than changes in price levels.
- It helps compare economic growth over different years without the distortion of inflation.
- A rise in Real GDP indicates an actual improvement in the standard of living, whereas Nominal GDP may increase just due to inflation, without real economic progress.
(Q3) Calculate ‘Sales’ from the following data : (4 M)
Ans: 5000
(Q4) Calculate “Gross National Product at Market Price” from the following data : (6 M)
Ans: 5700
(Q5) Calculate “Gross National Disposable Income” from the following data :
Ans: 3500
(Q6) Calculate ‘Sales’ from the following data : (4 M)
Ans: 1710
C. B. S. E. PAPER 2014 & SAMPLE PAPER
(Q1) What are externalities? Give an example of a positive externality and its impact on the welfare of the people.
Ans: Externalities refer to the positive or negative effects of economic activities on third parties who are not directly involved in the transaction. These effects are not reflected in market prices.
Example of Positive Externality:
The use of a public park for leisure increases people's well-being by providing a clean environment, relaxation, and health benefits.
Impact on Welfare:
Positive externalities improve social welfare by enhancing the quality of life, public health, and environmental benefits without additional costs to individuals.
(Q2) What are externalities? Give an example of a Negative externality and its impact on welfare of the people.
Ans: Example of Negative Externality:
Air pollution from a factory affects the health of nearby residents by causing respiratory diseases.
Impact on Welfare:
Negative externalities reduce social welfare by creating health hazards, environmental degradation, and economic burdens (e.g., medical expenses).
(Q3) What are non-monetary exchanges? Give an example. Explain the impact on the use of GDP as an index of the welfare of the people.
Ans: Non-monetary exchanges refer to goods and services produced that aren't traded for money, such as domestic help provided by family members. These are hard to measure and thus aren't included in national income estimates, but they positively impact welfare.
(Q4) Explain the difference between final goods and intermediate goods. Give one example of each.
Ans:
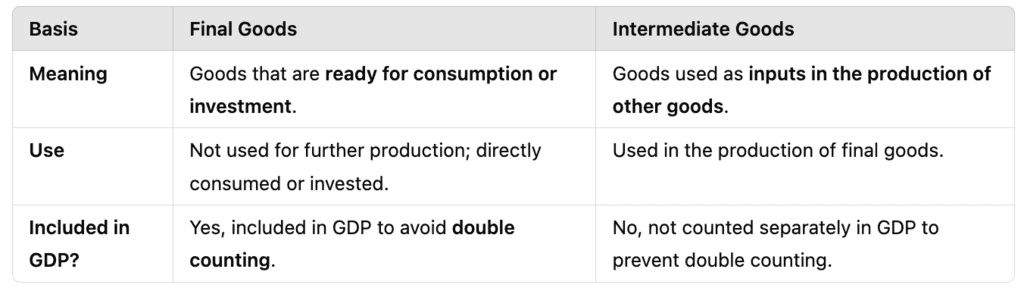
Examples:
- Final Good: A car purchased by a customer for personal use.
- Intermediate Good: Steel used by an automobile company to manufacture cars.
(Q5) An Increase in per capita real income means an increase in per capita availability of goods and services. Does it necessarily mean a rise in the welfare of the people of the country? Give any one argument in support of your answer and explain the same. (3 marks)
Ans. An increase in per capita availability of goods and services does raise the standard of living and, consequently, welfare. But it may not necessarily always be so. For example, manufacturing, etc., does raise output but at the same time also leads to water pollution and air pollution, which reduces the welfare of the people. Such a reduction in welfare may outweigh the increase in welfare and thus lead to an overall reduction in welfare.
(Q6) During a given year, nominal national income increased by 14 per cent while the real national income increased by only 6 per cent. Population increased by 2 per cent. What has caused the difference between nominal income and real income? What is real per capital income? (3 marks)
Ans. Change in nominal income over a year is on account of
(a) change in quantity of goods and services and
(b) change in price level. However, change in real income refers to change in the quantity of goods and services only. Therefore, a change of 14 percent in nominal income over the year is partly on account of a 6 percent change in the quantity of goods and services, and the remaining 8 per cent must be on account of a rise in the general price level.
Real per capita income rise = Rise in real national income - Rise in population
= 6 - 2 = 4 per cent
(Q7) How should the following be treated in estimating national income of a country ? You must give reason for your answer.
(i) Taking care of aged parents
(ii) Payment of corporate tax
(iii) Expenditure on providing police services by the government. (6 marks)
Ans: yes , no , yes
(Q8) Giving reasons explain how the following are treated while estimating national income :
(i) Payment of fees to a lawyer engaged by a firm;
(ii) Rent free house to an employee by an employer;
(iii) addition to stock during year
(iv) Purchase of taxi by taxi driver
Ans: No , Yes, Yes , yes
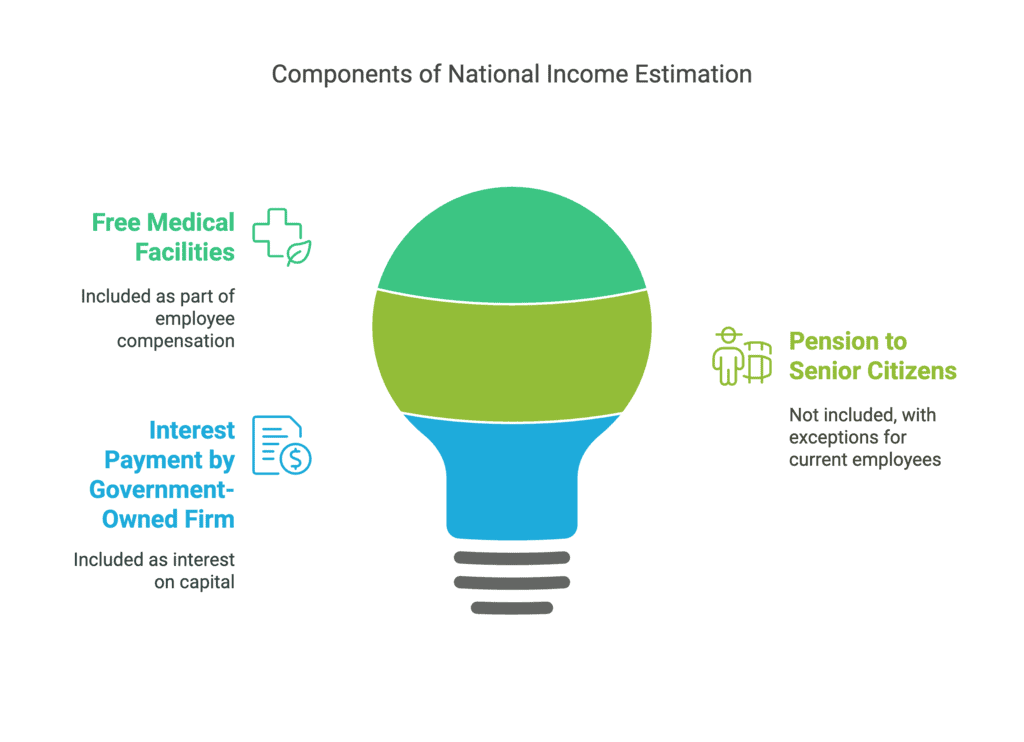
(Q9) How should the following be treated in estimating national income? Give reason :
(i) Free medical facilities to employees.
(ii) Pension to senior citizens.
(iii) Interest payment by a government-owned firm. (6 marks)
Ans: Treatment of Items in National Income Estimation
1. Free Medical Facilities to Employees
- Included in National Income as part of Compensation of Employees (a component of Factor Income).
- Reason: This is a benefit provided by employers to employees in return for their work, making it part of their total earnings.
2. Pension to Senior Citizens
- Not Included in National Income (except in certain cases).
- Reason: Pensions given to retired individuals are transfer payments because they are not given in exchange for current productive work.
- Exception: If a pension is given to a current employee (e.g., employer’s contribution to a pension fund), it is included in Compensation of Employees.
3. Interest Payment by a Government-Owned Firm
- Included in National Income as Interest on Capital (a component of Factor Income).
- Reason: Interest paid on loans used for productive purposes is considered factor income, whether the firm is privately owned or government-owned.
(Q10) How should the following be treated in estimating national income?
Give reason :
(a) Exp. by a firm on payment of government fees to a chartered accountant
(b) Payment of corporate tax by firm
(c) Purchase of refrigerator by a firm for own use
Ans:
(a) Expenditure by a Firm on Payment of Government Fees to a Chartered Accountant
Included in National Income as part of Factor Income (Compensation of Employees or Payment for Services).
Reason: The fees paid to a chartered accountant for professional services is a payment for productive work and is included in GDP as a part of service sector output.
(b) Payment of Corporate Tax by a Firm
Not Included in National Income (Direct Tax).
Reason: Corporate tax is a transfer payment to the government. It does not reflect production or income earned by factors of production, so it is excluded from national income.
(c) Purchase of Refrigerator by a Firm for Own Use
Included in National Income under Gross Domestic Capital Formation (Investment).
Reason: When a firm purchases a refrigerator for its own use, it is considered a capital good as it will be used for business operations. Investments in capital goods are counted in GDP.
(Q11) Calculate ‘Net National Product at Factor Cost’ and ‘Gross National Disposable Income’ from the following : (4, 2 marks)
Ans: 2050, 2530
(Q12) Calculate ‘National Income’ and ‘Net National Disposable Income’ from the following :
Ans: 630, 720
(Q13) Calculate ‘Net National Product at Market Price’ and ‘Gross National Disposable Income’ from the following : (Rs. in Arab)
Ans: 730, 780
(Q14) Find (a) National Income and (b) Gross National Disposable Income.
Ans. Rs. 315 crore.
(Q15) Calculate ‘Net National Product at Market Price’ and ‘Gross National Disposable
Income’ form the following data : (Rs. in Arab)
(Q16) Find Net Value Added at Factor Cost : (3 marks)
(Rs. in Lakh)
(i) Sales 100
(ii) Closing Stock 20
(iii) Excise 15
(iv) Opening Stock 10
(v) Depreciation 12
(vi) Intermediate Consumption 50
Ans. Rs. 33 Lakh
C. B. S. E. PAPER 2015 & SAMPLE PAPER
(Q1) Which of the following is a characteristic of a good?
(a) Intangible (b) Can be stored
(c) Production and consumption must happen simultaneously
(d) Cannot be transferred
Ans : (b)
(Q2) State the various components of the Expenditure Method that are used to calculate national income.
Ans: Components of Expenditure Method:
(a) Private Final Consumption Expenditure
(b) Government Final Consumption Expenditure
(c) Investment Expenditure
(d) Net Exports ( 1X 4)
(Q3) Discuss any two differences between GDP at constant prices and GDP at current Prices.
Ans: The two main differences between GDP at current prices and constant prices are:
(1) GDP at current prices are measured at Current Year’s Prices, whereas GDP at constant prices are measured at base year’s prices. (2m)
(2) GDP at current prices may increase even if there is no flow of goods and services, whereas GDP at constant prices will only increase when there is an increase in the flow of goods and services. (2m)
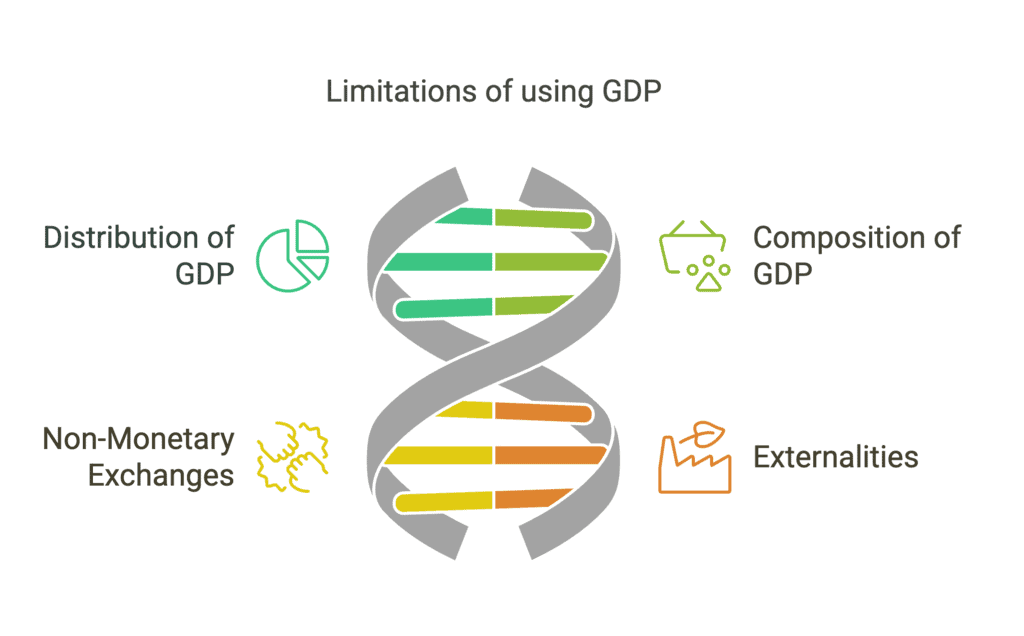
(Q4) Explain any four limitations of using GDP as a measure/index of the welfare of a country.
Ans: Four limitations of using GDP as a measure/index of the welfare of a Country are:
(I) Distribution of GDP
(II) Composition of GDP
(III) Non-Monetary Exchanges
(IV) Externalities.
(Q5) State the various components of the Income Method that are used to calculate national income. (4M)
Ans : COE + OS + MI + NFIA
(Q6) State any four precautions that need to be kept in mind when using the value added method for calculating national income.
(Q7) Giving reason explain how the following should be treated in estimation of national income
(i) Payment of interest by a firm to a bank (6 M)
(ii) Payment of interest by a bank to an individual
(iii) Payment of interest by an individual to a bank
Ans: Yes, Yes, NO (No marks if reason is not given)
(Q8) If the Real GDP is Rs. 500 and the Price Index (base = 100) is 125, calculate the Nominal GDP. (3 M)
Ans: 625
(Q9) If the Nominal GDP is Rs. 600 and the Price Index (base = 100) is 120, calculate the Real GDP.
Ans: 500
(Q10) If the Real GDP is Rs. 400 and the Nominal GDP is Rs. 450, calculate the Price Index (base = 100).
Ans :
(Q11) Calculate the ‘National Income’ and ‘Private Income’ :
Ans: N.I. = (iv + ix) + i + viii + (vi + vii + xii) – ii (11/2M)
= 700 + 100 + 200 + 150 + 20 + 30 + 50 – 10 (1M)
= Rs. 1240 Crore. (1/2M)
Private Income = N.I. – x + iii – xi + v (11/2M)
= 1240 – 250 + 15 – 5 + 10 (1M)
= Rs. 1010 Crore. (1/2M)
(No marks if only the final answer is given
(Q12) Calculate ‘Net National Product at Market Price’ and ‘Personal Income’ : (6 M)
Ans:: Rs 425 Crore, Personal Income = Rs 200 Crore.
(Q13) Calculate ‘Net Domestic Product at Market Price’ and ‘Gross National Disposable Income’: (6 M)
Ans: 550 crore, 575 crore
(Q14) Compute (a) Domestic Income and (b) Net National Disposable Income. (6M)
Ans: 4755, 5450
(Q15) Find (a) National Income and (b) Gross National Disposable Income.(in Crore )
Ans: 250, 315
(Q16) Find (a) Private Income and (b) National Income.
Ans : (a) Private Income (i) + (iv) + (viii) + (ix) (1½m)
= 350 + 10 + 15 + 25(1M)
= Rs 400 crores(½m)
(b) National Income
= Private income + (vii) – (x) + (ii) + (iii)(1½m)
= 400 + 20 - 30 + 25 + 50(1M)
= Rs 465 crores(½m)
(Q17) Suppose in an imaginary economy GDP at Market Price in a particular fiscal year was Rs. 4,000 crores, National Income was Rs. 2,500 crores, Net Factor Income paid by the economy to Rest of the World was Rs.400 crores and the value of Net Indirect Taxes is Rs. 450 Crores. Estimate the value of consumption of fixed capital for the economy from the given data.(4M)
Ans: CFC = 650 (in Rs. crores)
CBSE 2016
Q1 National income is the sum of factor incomes accruing to :
(a) Nationals
(b) Economic territory
(c) Residents
(d) Both residents and non-residents
Ans: (c)
National income is the total income earned by a country's residents from goods and services production in a year. It includes wages, rent, interest, and profits, whether earned domestically or abroad. Non-residents' income is excluded, while residents' foreign earnings (e.g., remittances) are included.
Q2 Depreciation of fixed capital assets refers to : (Choose the correct alternative) (1M)
(a) Normal wear and tear
(b) Foreseen obsolescence
(c) Normal wear and tear and foreseen obsolescence
(d) Unforeseen obsolescence
Ans : (c)
Depreciation refers to the gradual reduction in the value of fixed capital assets due to:
- Normal wear and tear from regular use.
- Foreseen obsolescence, where assets lose value due to technological advancements or changing market conditions.
(Q3) Unforseen obsolescene of fixed capital assets during production is:
(a) Consumption of Fixed Capital
(b) Capital Loss
(c) Income Loss
(d) None
Ans :(b)
Unforeseen obsolescence refers to the sudden loss in value of fixed capital assets due to unexpected factors like natural disasters, accidents, or rapid technological changes. This type of loss is not a part of normal depreciation (Consumption of Fixed Capital) but is classified as a Capital Loss since it affects the asset’s value rather than the firm’s regular income.
(Q4) Define Gross Investment
(Q5) Sale of petrol and diesel cars is rising particularly in big cities. Analyse its impact on gross domestic product and welfare.(4M)
(Q6) The Government incurs expenditure to popularize yoga among the masses. Analyse its
impact on gross domestic product and welfare of the people.(4M)
(Q7) Governments spend on child immunization programmes. Analyse its impact on GDP and the welfare of the people
(Q8) Giving reason explain how the following should be treated in estimation of national income
(a) Payment of Corporate taxes by firm
(b) Purchase of Machinery by factory for own Use
(c) Purchase of Uniforms for nurses by a hospital
Ans: No, Yes, No
(Q 9) Assuming real income to be Rs. 200 crore and price index to be 135, calculate nominal income.
Ans: 270
(Q10) If real income is Rs. 400 and price index is 105, calculate nominal income.
(3M)
Ans: 420
(Q11) If nominal income is Rs. 500 and price index is 125, calculate real income.(3M)
Ans: 400
(Q12) Find the gross value added at market price :(3M) (Rs. Lacs)
(i) Depreciation 20
(ii) Domestic sales 200
(iii) Net change in stocks (-) 10
(iv) Exports 10
(v) Single use producer goods 120
Ans: 80 lakh
(Q13) Find net value added at Factor Cost ( in lakhs)
(a) Durable Use producer goods with a life span of 10 years 10
(b) Single use producer goods 5
(c) Sales 20
(d) Unsold output produced during the year 2
(e) Taxes on production 1
Ans: 15
(Q14) Find net value added at Factor Cost ( in lakhs)
(a) Fixed Capital cost with a life span of 5 years 15
(b) Raw Material 6
(c) Sales 25
(d) Net Change in Stock (-) 2
(e) Taxes on production 1
Ans: 14
(Q15) Find Gross National Product at Market Price and Private Income : (4, 2M)
Ans: 1380, 1110
(Q16) Find Gross National Product at Market Price and Private Income : (4, 2M)
Ans: 640, 550
(Q17) Calculate National Income and Personal Disposable Income : (4, 2M)
Ans: 1030, 730
(Q18) Find net national product at market price and personal disposable income : (4, 2 M)

Ans: 2930, 1550
|
69 videos|380 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Scanner Chapter 3 & 4 - (Macro Economics) - Economics Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the concept of scarcity in macroeconomics? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics? |  |
| 3. How does inflation affect the economy? |  |
| 4. What are the main goals of macroeconomic policy? |  |
| 5. How does fiscal policy influence the economy? |  |

















