Important Points: Structure of the Atom | Science Class 9 PDF Download
Introduction
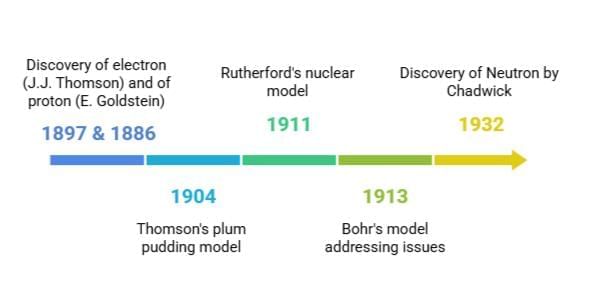
The history of atomic models shows how our understanding of atoms has changed over time. It began with Dalton’s idea that atoms are indivisible. Later, scientists like Goldstein, Thomson, and Chadwick made discoveries that changed this view. Thomson suggested the plum pudding model, and Rutherford proposed the nuclear model. Bohr improved on these ideas by explaining how electrons are arranged. Concepts like electron arrangement, valency, atomic number, and mass number became important. The discovery of isotopes and isobars added more to our knowledge and found uses in areas such as nuclear energy and medicine.
Discovery of the Electron
The electron was discovered by J.J. Thomson in 1897. He performed experiments with cathode rays and found that these rays were made of negatively charged particles. These particles were later named electrons.
Discovery of the Proton
The proton was discovered by E. Goldstein in 1886. He observed rays in a discharge tube moving in the opposite direction to cathode rays. These were called canal rays and were made of positively charged particles, now known as protons.
Thomson's Model
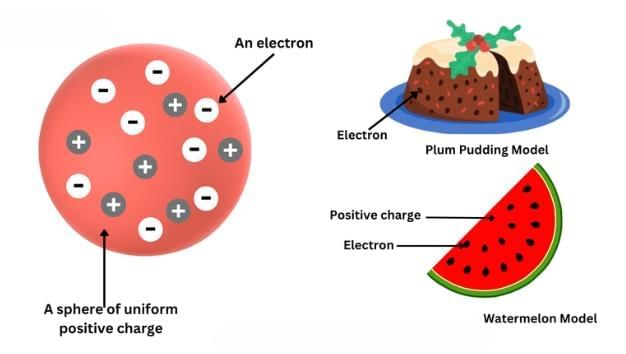
- Proposed that an atom consists of a positively charged sphere in which electrons are embedded like seeds in a watermelon.
- The total positive and negative charges are equal, making the atom electrically neutral.
- Known as the plum pudding or watermelon model.
 Thomson's Model
Thomson's Model
Rutherford's Model
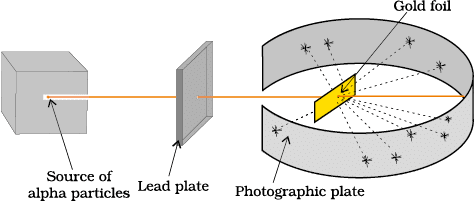
Conducted the gold foil experiment with fast-moving α-particles.
Observations:
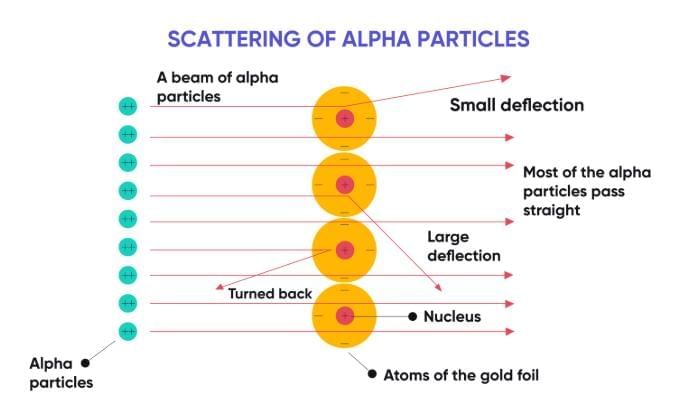
1. Most particles passed straight through.
2. Some were deflected at small angles.
3. A very few rebounded back.
Conclusions:
1. An atom has a tiny, dense, positively charged centre called the nucleus.
2. Most of the atom is empty space.
3. Electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular orbits.
Drawback: Could not explain why revolving electrons do not lose energy and collapse into the nucleus.
Bohr's Model
Bohr improved upon Rutherford’s model.Postulates:
1. Electrons revolve in fixed orbits (energy levels) without radiating energy.
2. Energy is absorbed or emitted when electrons jump between these levels.
Limitations: It violates the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle and does not work well for atoms with more than one electron.
Discovery of Neutron
In 1932, James Chadwick discovered the neutron, a neutral subatomic particle with mass nearly equal to a proton.
Neutrons are present in the nucleus (except in the most common hydrogen isotope, ¹H)
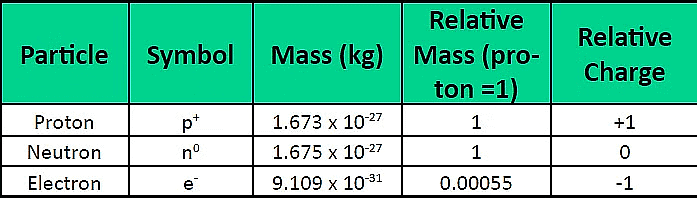 Atomic Structure
Atomic Structure
Electron Distribution Rules (Bohr–Bury Rules)
The distribution of electrons within different orbits of an atom was proposed by Bohr and Bury. The following rules guide the assignment of electron numbers to various energy levels or shells:
1. Maximum electrons in a shell = 2n² (where n is shell number).
K (n=1): 2 electrons, L (n=2): 8 electrons, M (n=3): 18 electrons, N (n=4): 32 electrons
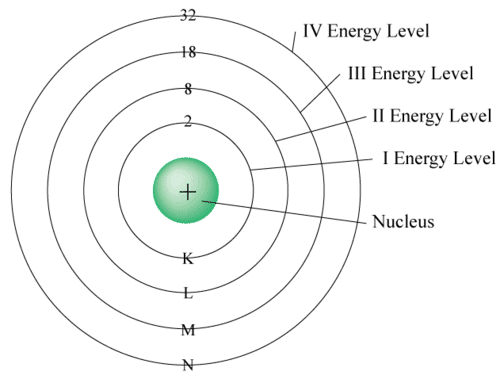
2. The outermost shell can hold up to 8 electrons.
3. Electrons are filled in shells step-by-step, starting from the innermost.
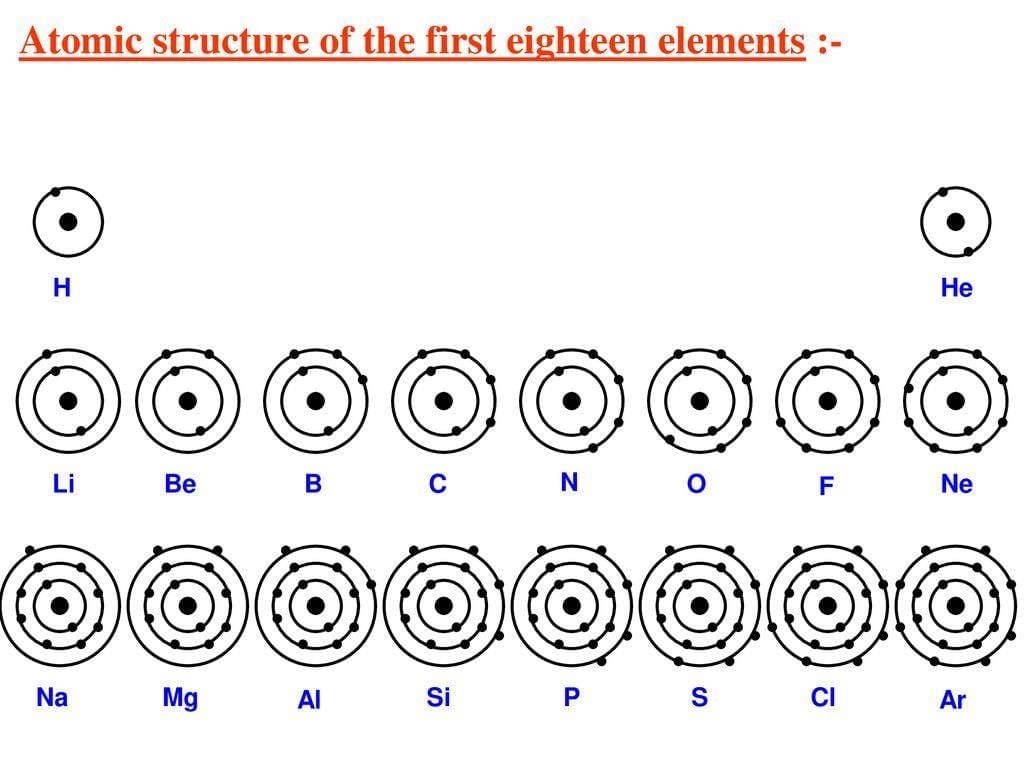
Valency
- Valency is the combining capacity of an atom.
- It is determined by the number of electrons an atom loses, gains, or shares to achieve a stable configuration (usually an octet).
- Atoms with completely filled outermost shells, like noble gases, have a valency of zero.
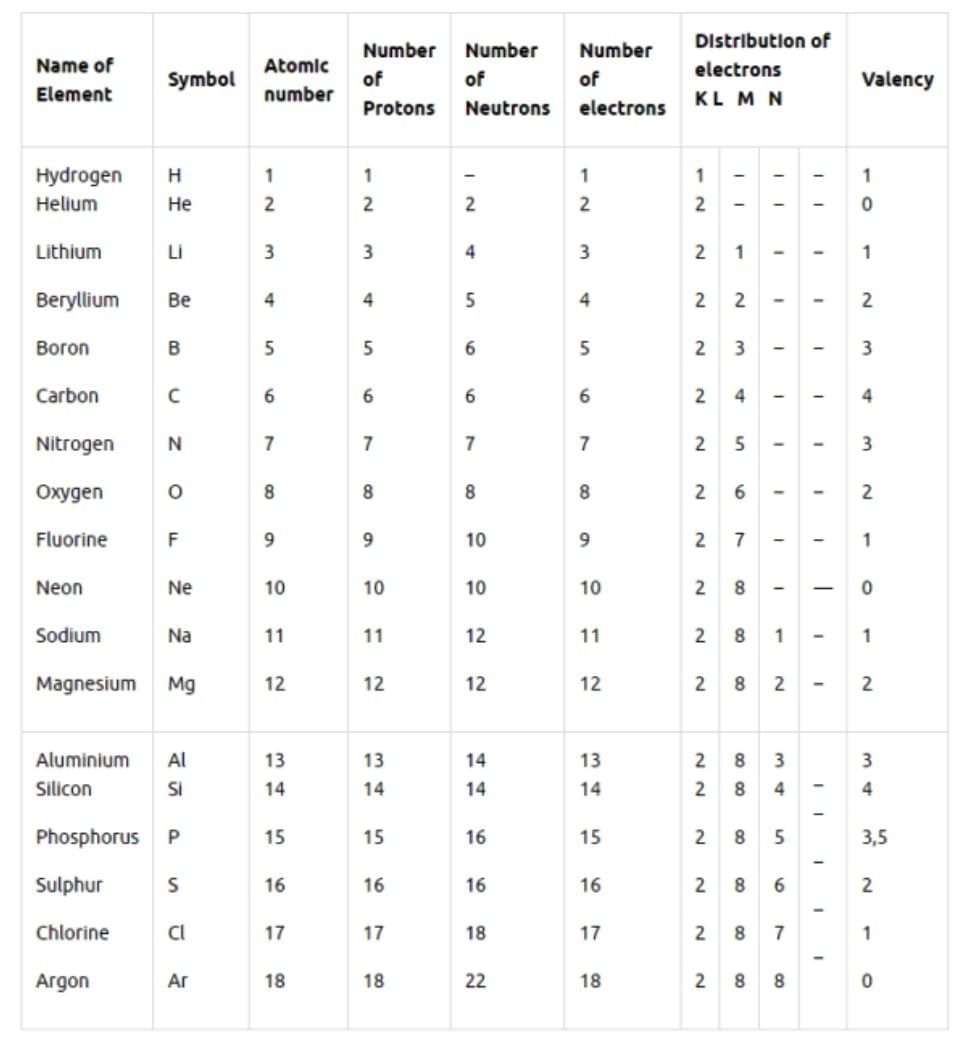
Atomic Number (Z)
- Number of protons in an atom’s nucleus.
- Defines the element.
- Also equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
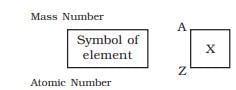
Mass Number (A)
- The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
- Mass Number (A) = Atomic Number (Z) + number of neutrons.
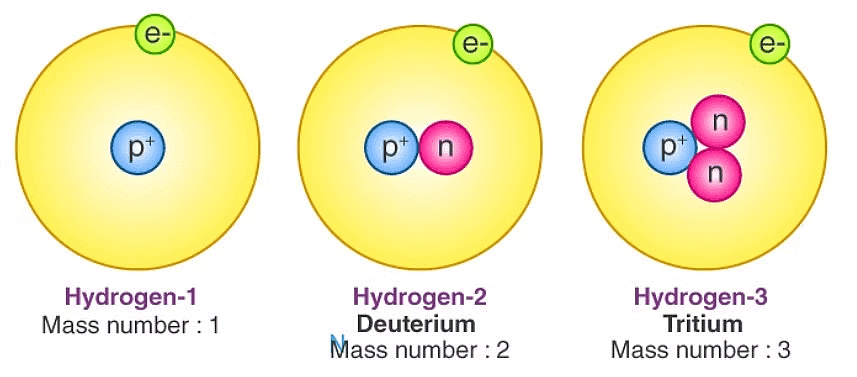
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Have identical chemical properties but differ in physical properties.
Examples:
1. Hydrogen: ¹H (Protium), ²H (Deuterium), ³H (Tritium)
2. Chlorine: ³⁵Cl and ³⁷Cl
Applications:
1. Uranium isotope in nuclear reactors
2. Cobalt isotope in cancer treatment
3. Iodine isotope in goitre treatment
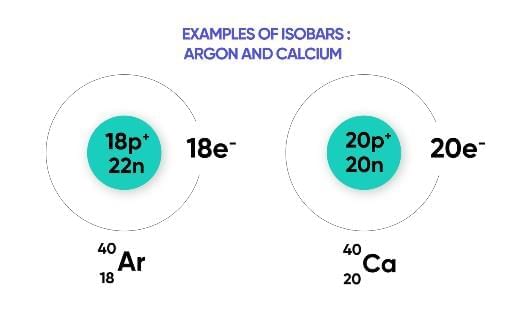
Isobars
Atoms of different elements with the same mass number but different atomic numbers.
Example: Argon (Z=18) and Calcium (Z=20) both have mass number 40.
Practice Questions
Ques. Is it possible for the atom of an element to have one electron, one proton and no neutron? If so, name the element.
Ans. Yes, it is true for the hydrogen atom, which is represented as 1H1 . It has one electron, one proton and no neutron.
Ques. What do you understand by the ground state of an atom?
Ans. The state of an atom where all the electrons in the atom are in their lowest energy levels is called the ground state.
Ques. Who identified the sub-atomic particle electron?
Ans. J.J. Thomson discovered the sub-atomic particle electron and proved that it existed without ever being able to see or isolate one.
Ques. Who discovered the nucleus of the atom?
Ans. Rutherford and his co-workers performed alpha-particle scattering experiments which led to the discovery of the atomic nucleus of atom.
|
84 videos|541 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Important Points: Structure of the Atom - Science Class 9
| 1. What is the historical perspective of atomic theory? |  |
| 2. What are the rules for electron distribution in an atom? |  |
| 3. What is valency and how is it determined? |  |
| 4. What are isotopes and how do they differ from each other? |  |
| 5. What are isobars and what distinguishes them from isotopes? |  |

















