Carburetion & Fuel Injection | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) PDF Download
CARBURETION AND FUEL INJECTION
- In SI engine, carburetor prepares combustible air fuel mixture after atomizing the fuel and mixing it with air. The design of carburetor is complex because the optimum fuel air ratio required by engine varies widely over its operational range.
Variation of mixture Requirement for maximum power, and minimum specific fuel Consumption.
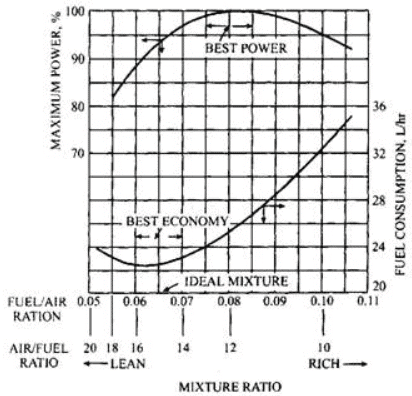
- Mixture requirement for maximum power is 12.5 : 1 air fuel ratio (A/F ratio) i.e. It is accomplished by complete utilization of oxygen present richer than stoichiometric mixture (15 : 1) A/F ratio is required.
- Mixture requirement for minimum specific fuel consumption is 17 : 1 (A/F ratio). For complete combustion of fuel for mixture leaner than stoichiometric (15 : 1) A/F ratio mixture is required.
| Range of Operation | Load | Governing Factor | A / F ratio |
| Iding and lowload | 0 20% of rated power | Dilution of Mixtureby products of combustion | 12.5:1 (rich mixture) |
| Normal Poweror cru sin g range | 20% 75% of rated power | Fuel economy | 16.7:1(Slighly lean) |
| Maximum Power | 75% 100% of rated power | Full utlisation of air | 14:1 (rich mixture) |
Simple of Elementary Carburetor
| Operation | GoverningFactor | A / Fratio |
| Starting And Warmup | LessFuelvapour due tolow temperature | 3:1(Very rich) |
| Acceleration | Inertia of liquid Fuel | rich |
Simple Elementary Carburetor
- To avoid the overflow of the fuel from the nozzle, the end of the main nozzle is slightly kept higher than the level of fuel in the float chamber. This difference of level between the tip of the main nozzle and fuel level in the float chamber is called nozzle lip. You can see the nozzle lip level in the diagram above.
- This carburettor is meant for cruising or normal range at a single speed.
- The drawbacks of this simple carburettor are it provides increasing richness as the engine speed increases.
It provides too lean mixture at low loads to be ignited.
Fuel air ratio in the carburettor when compressibility of air is not considered
If Z(nozzle lip) = 0
F/A ratio considering air as compressible
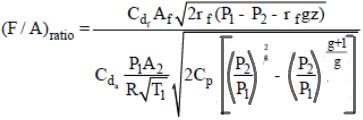
is mass flow rate of fuel and air respectively
Cdf ,Cda is Coefficient of discharge of fuel nozzle and venturi throat
Af ,A2 is cross section area of fuel nozzle and venturi throat
r f ,r a is density of fuel and air
P1,P2 is atmospheric pressure and pressure at throat.
Z is nozzle lip, i.e. Difference in height of nozzle tip and float chamber level
- At high attitude
because of low density of air at high attitude hence
value is very high so mixture becomes too rich.
- Nozzle lip is provided so that there is no spilling of fuel due to vibration or slightly non horizontal position of carburettor thus avoiding wastage of fuel & fire hazard.
- In aircraft carburettor fuel to low density of air at high altitude, to avoid too much richness of mixture; Back suction control, air bleeding etc. are used to reduce the amount of fuel to maintain A/V ratio. This is called as altitude compensation.
- Surging is a leakage problem in carburettors when they are titled or during aerobic in aircraft. With petrol injection system in place of carburettor is used to avoid surging.
FUEL INJECTION
Fuel is directly injected in the combustion chamber at the end of compression stroke in diesel engine.
Requirements of a Diesel Injection System
- The fuel should be introduced into the combustion chamber very precisely
- Fuel should be measured accurately
- Injection of fuel should be in such a way to obtain desired heat release pattern.
- Good atomization should be obtained.
- Spray pattern should be in such a way to have rapid mixing of air and fuel.
- Beginning and end of injection should be sharp.
- The distribution of fuel should be uniform in all the cylinders.
Constituent of Injection System
- Pumping element
- Metering element
- Metering control element
- Distributing control element
- Timing element
- Mixing element
TYPE OF INJECTION SYSTEMS
Air Injection
- The fuel is metered and pumped to the fuel valve by a camshaft driven fuel pump. The fuel valve is opened by a mechanical linkage operated by the camshaft which controls the timing of injection. The fuel valve is also connected with compressor through a high pressure line.
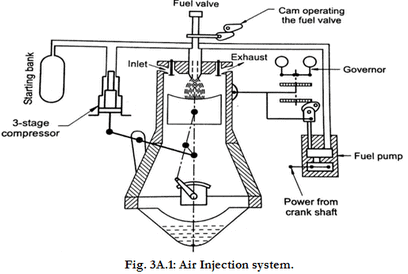
- With this system, good atomization and high mean effective pressure is obtained. Also low power fuel is needed.
- The disadvantage of this system is requirement of multistage compressor and separate mechanical linkages, which increases its weight and cost. Also brake horse power of engine is reduced because of power loss in operating compressor and linkages.
Solid Injection System
In solid injection, the liquid fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber without the aid of compressed air. Hence, it is termed as airless injection mechanical injection or Solid injection.
Solid injection systems may be further classified as follows:
-Common Rail System
-Unit Injection System
-Individual Pump and Nozzle System
-Distributor System
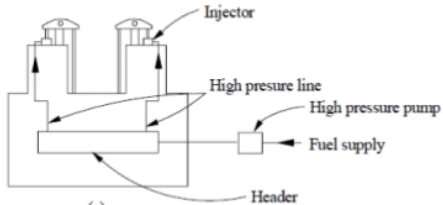
Common Rail System
- A high pressure fuel pump delivers fuel to an accumulator. Whose pressure is kept constant. A common rail or pipe transfer this fuel to separator injector of each cylinder. Here metering and timing is controlled at each cylinder. This system is self governing according to the speed of the engine.
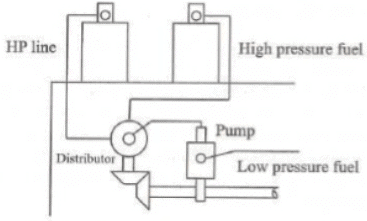
Distributor System
- In this system, the pump which pressurise the fuel also meters and times it. The fuel pump, after metering the required amount of fuel, supplies it to a rotating distributor at correct time to supply it to cylinder. Here distribution is very uniform in the cylinder and cost of the system is very less.
TYPE OF NOZZLES IN INJECTION SYSTEM
Pintle Nozzle
- It causes good atomization and reduced penetration. It is used precombustion chamber & air-cell chambers.
Pintaux Nozzle
- It is a development of pintle nozzle where an auxiliary hole is drilled nozzle body. It provides good cold starting performance.
INJECTION
- The purpose of carburetion and fuel injection is the same i.e. preparation of the combustible charge. But in case of carburetion fuel is atomized by air speed greater than the fuel speed at the fuel nozzle. Whereas in fuel injection. Fuel speed at speed to atomize the fuel.
Basic fuel injection equations
- Volume of fuel injected per cycle = Cd× A × V× t
Here,
Cd = Coefficient of discharge
A = Area of orifice
v = Velocity
t = Time for injection
- Velocity of injection (Vf)
Here,
Pinj = Injection pressure
Pcylinder = Cylinder pressure
rf = Injection density
- Time for one injection
Here
N = Number of rotation Per minute
q = Angle of crank travel over which injection takes place
|
5 videos|103 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Carburetion & Fuel Injection - Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical)
| 1. What is carburetion and fuel injection? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of carburetion over fuel injection? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of fuel injection over carburetion? |  |
| 4. Which is more commonly used in modern engines, carburetion, or fuel injection? |  |
| 5. Can a carbureted engine be converted to fuel injection? |  |