Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Notes > Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) > Second Law of Thermodynamics
Second Law of Thermodynamics | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) PDF Download
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
- Work is said to be high grade energy and heat is low grade energy. The complete conversion of low grade energy into high grade energy in a cycle is impossible while the complete conversion of high grade energy into low grade energy is possible.
- A heat engine works on a thermodynamic cycle in which there is net heat transfer to the system and a net work transfer from the system.
- Boiler, turbine, condenser and pump, all four together constitute a heat engine.
Thermal Efficiency
Wnet = Qnet (First law of thermodynamics)
- A thermal energy reservoir (TER) is defined as a large body of infinite heat capacity which is capable of absorbing or rejecting an unlimited quantity of heat without any appreciable changes in its thermodynamic properties.
PMM2
- It is a device which produces work while exchanging heat with single reservoir in a cycle.
Q2 = 0 , Wnet = Q1 , hth = 1
Such a heat engine is called as PMM2.
- Second Law of Thermodynamics:
- Kelvin Plank Statement: It is impossible for a heat engine to produce net work in a complete cycle if it exchange heat only with a single reservoir.
- PMM2 is impossible according to Kelvin-Plank statement.
- Clausis statement: it is impossible to transfer heat from lower temperature to higher temperature without any external input.
- Heat always flow from a body at higher temperature to a body at lower temperature but it can not flow in reverse direction on its own. Some work must be done to achieve this.
- Refrigeration plant and heat pump constitute of
- Evaporator
- Compressor
- Condenser
- Expander
(Figure: Schematic diagram of Refrigeration plant and heat pump.)
Coefficient Of Performance(COP) =
(COP) ref =
(COP) H.P =
(COP) H.P = (COP) ref + 1
- The basic cycle in refigerator and heat pump is same. But the main purpose of refrigerator is to maintain temperature which is less than that of surrounding while in heat pump, the main purpose is to maintain temperature which is more that of surrounding.
- PMM–3 : Continual motion of a movable device in complete absence of friction is known as PMM-3.
Carnot Cycle:
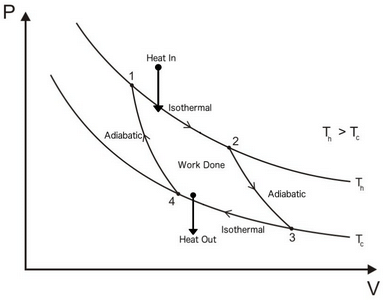
- It is a reversible cycle.
- It is an ideal cycle.
Carnot Theorem: It states that all heat engines operating between a given constant temperature source and given constant temperature sink, none has higher efficiency than a reversible engine.
- The efficiency of all reversible heat engines operating between the same temperature levels is the same.
- Third law of thermodynamics : It is impossible by using any procedure, no matter how idealised the procedure is. to reduce any system to absolute zero of temperature in a finite no. of operations.
- The effect of decreasing T2 to increase thermal efficiency of Carnot cycle is more than the effect of increasing T1 by same amount.
- First law of thermodynamics gave origin to internal energy and second law leads to entropy.
The document Second Law of Thermodynamics | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) is a part of the Mechanical Engineering Course Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical).
All you need of Mechanical Engineering at this link: Mechanical Engineering
|
6 videos|104 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Second Law of Thermodynamics - Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical)
| 1. What is the second law of thermodynamics in mechanical engineering? |  |
Ans. The second law of thermodynamics in mechanical engineering is a fundamental principle that states that the entropy of an isolated system always increases over time or remains constant in ideal cases. It explains the direction of natural processes and sets limits on the efficiency of heat engines.
| 2. How does the second law of thermodynamics relate to mechanical engineering? |  |
Ans. The second law of thermodynamics is essential in mechanical engineering as it helps in understanding the efficiency and performance of various machines, such as heat engines, refrigerators, and turbines. It provides guidelines for designing systems that can convert heat energy into useful work efficiently.
| 3. What are the implications of the second law of thermodynamics in mechanical engineering? |  |
Ans. The second law of thermodynamics has several implications in mechanical engineering. It states that it is impossible to have a perfect heat engine with 100% efficiency. It also implies that heat cannot flow spontaneously from a colder body to a hotter body without external work input. Moreover, it sets limitations on the reversibility of processes and the conversion of heat energy into mechanical work.
| 4. How does the second law of thermodynamics affect the design of mechanical systems? |  |
Ans. The second law of thermodynamics affects the design of mechanical systems by requiring engineers to consider the efficiency, heat transfer mechanisms, and irreversibility of processes. It guides the selection of appropriate materials, insulation, and heat exchange equipment to minimize energy loss and maximize performance. Engineers also need to account for the limitations imposed by the second law when designing energy conversion systems.
| 5. Can the second law of thermodynamics be violated or circumvented in mechanical engineering? |  |
Ans. The second law of thermodynamics is a fundamental principle of nature and cannot be violated or circumvented in mechanical engineering or any other field. While it is possible to increase the efficiency of certain processes or systems, it is not possible to achieve 100% efficiency or create a perpetual motion machine of the second kind. The second law sets a limit on the maximum achievable efficiency of any heat engine, and engineers must work within these constraints.
Related Searches
















