Economic Growth & Development: Economics | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
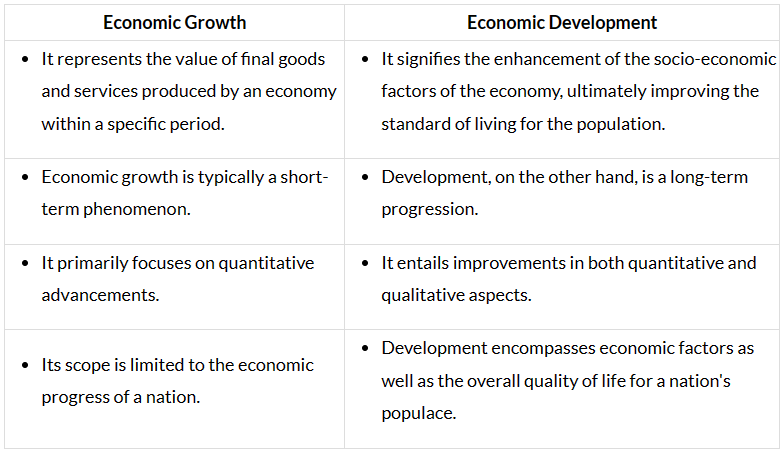
Economic growth pertains to the increase in a nation's income or output of goods and services compared to a previous period. Conversely, economic development entails sustained, long-term growth and augmented income for a country. Developed nations can address crucial aspects like healthcare and gender equality. Economic growth signifies the continuous rise in a country's real national and per capita income. On the other hand, economic development involves the persistent improvement of the material well-being of society. It's crucial to understand that economic development is a broader concept compared to economic growth.
Recent Update on Economic Growth
The Economic Survey 2024-25 and international agencies project India’s real GDP growth for FY26 at 6.3%–6.8%, slightly higher than the 6.4% estimated for FY25, driven by robust domestic demand and policy reforms. Despite global trade challenges, industrial activity (PMI at 58.4 in April 2025) and investment momentum (FDI inflows of $55.6 billion in FY25) sustain growth. The digital economy (10% of GDP) and green energy initiatives (200 GW renewable capacity) further bolster India’s trajectory, aligning with Atmanirbhar Bharat goals.
What is Economic Growth?
Economic growth is the total value of final goods and services produced within an economy during a specific period. It is measured in real terms to adjust for inflation and provide an accurate representation of the economy's performance. Typically, it is expressed as a percentage increase in Gross Domestic Product (GDP). In 2025, India uses the 2021-22 base year for GDP calculations, incorporating digital transactions and GST data for accuracy.

Factors Affecting Economic Growth
Economic growth can be influenced by various factors, including:
- Investment in Physical Capital: Spending on machinery, equipment, and infrastructure enhances productivity. For example, India’s PLI schemes for semiconductors and EVs in 2025 drive manufacturing growth.
- Technological Progress: Advances in technology lead to increased efficiency and innovation. The adoption of UPI (120 billion transactions in 2024) and AI in banking and agriculture exemplifies this in India.
- Human Capital Development: Investing in education and healthcare improves workforce skills. India’s Budget 2025-26 allocates ₹2 lakh crore for skilling to boost productivity.
- Political Stability and Good Governance: Stable policies attract investment. India’s predictable reforms (e.g., labor codes 2019-20) create a conducive business climate.
- Natural Resources: Sustainable management of resources like minerals supports growth. India’s green energy push (40% non-fossil energy in 2025) balances resource use.
What is Economic Development?
Economic development refers to the enhancement of a nation’s economy over time, focusing on augmenting wealth and improving living standards. It encompasses factors such as income growth, enhanced employment, better healthcare, and superior education. The ultimate goal is a robust and prosperous economy benefiting society. In India, schemes like Ayushman Bharat (36.36 crore cards by Jan 2025) exemplify development.

Factors Governing Economic Development
Various elements influence economic development:
- Human Resources: Skilled human capital drives progress. India’s NEP 2020 enhances workforce capabilities.
- Education: Higher literacy rates boost efficiency. India’s literacy rate reached ~80% in 2024, supporting development.
- Infrastructure Development: Improved infrastructure elevates living standards. India’s National Infrastructure Pipeline (₹150 lakh crore by 2025) is a key driver.
- Natural Resources: Sustainable use of resources like minerals fuels growth. India’s net-zero 2070 target integrates resource management.
- Capital Formation: High savings and investment rates propel development. India’s gross capital formation is ~35% of GDP in 2025.
- Digital Economy: Platforms like ONDC and fintech innovations enhance economic inclusion and efficiency.
Difference between Economic Growth and Economic Development
The difference between economic growth and economic development is presented below for better comprehension:
Features of Economic Development
The key aspects of economic development are outlined below:
- Enhances living standards through advancements in social indicators like healthcare and education. India’s PM-JAY saved ₹1.25 lakh crore in healthcare costs by 2025.
- Decreases poverty levels and enhances quality of life. India’s MPI dropped to ~11% in 2024.
- Brings structural transformations, including infrastructure improvements. India’s Gati Shakti integrates transport networks.
- An ongoing process evolving over time, supported by policies like Vision 2047.
- Elevates per capita income, boosting national income. India’s per capita income is ~$2,700 in 2025.
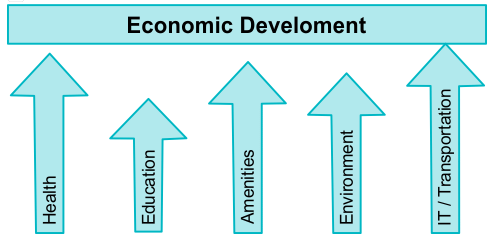
Five Pillars of Economic Development
The Five pillars of Economic Development are crucial for understanding the process of economic growth and sustainability. These pillars form the foundation for a country's economic progress and well-being. In 2025, India emphasizes digital infrastructure and green energy as emerging pillars.
Measurements of Economic Development
- Economic development is a multifaceted concept that goes beyond mere economic growth.
- It encompasses qualitative improvements in various aspects of people’s lives.
- Several indicators are used to measure economic development, providing a comprehensive view of a country’s progress. In India, HDI (rank 125, 2023) and MPI (11% poverty, 2024) are key metrics.
Green GDP
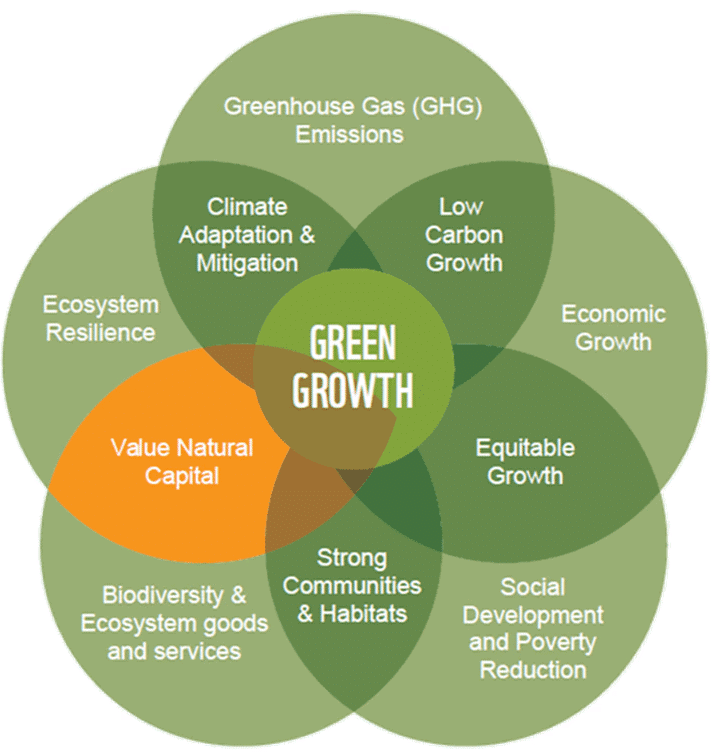
- Green GDP adjusts traditional GDP by accounting for environmental degradation, critical for sustainable development in 2025.
- Subtracts costs of environmental damage from GDP, reflecting true economic health. India’s Budget 2025-26 allocates ₹3 lakh crore for green initiatives.
- Originated to promote sustainability. India’s net-zero 2070 target integrates Green GDP principles.
Gender Inequality Index
The Gender Inequality Index (GII) evaluates gender disparities across three dimensions. India’s GII score improved to 0.437 in 2023, reflecting progress in empowerment.

- Reproductive health: Assesses maternal mortality and adolescent birth rates. India’s MMR dropped to 97 per 100,000 by 2024.
- Empowerment: Gauged by women’s parliamentary seats (14% in 2025) and secondary education rates (80% for females).
- GII highlights gender discrepancies, guiding policies like Beti Bachao Beti Padhao.
Gender Development Index
The Gender Development Index (GDI) quantifies gender inequalities in human development. India’s GDI improved in 2023, reflecting better health and education outcomes.
- Health: Life expectancy at birth (females: 71 years, males: 68 years in 2025).
- Education: Expected years of schooling (females: 12.2 years, males: 12.8 years).
- Economic resources: Estimated earned income (females: $2,200, males: $4,000 in 2025).
Human Capital Index
- The Human Capital Index captures education, employment, and workforce dynamics. India’s HCI score rose to 0.64 in 2024, reflecting skilling initiatives.
- Gauges outcomes on a 0–100 scale across five age groups. India’s NEP 2020 enhances learning outcomes.
Measurement of Economic Growth
The measurement of economic growth is crucial for understanding a country’s economy. The primary metric is real GDP, adjusted for inflation using the 2021-22 base year in India.
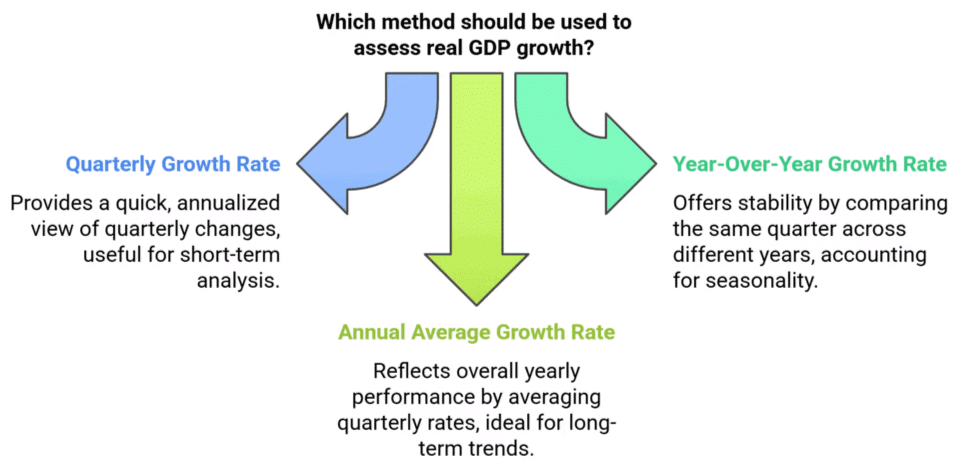
Methods of Assessing Real GDP
- Quarterly Growth at an Annual Rate: Calculates GDP change quarter-to-quarter, extrapolated annually. E.g., a 0.3% quarterly increase equals a 1.2% annual rate.
- Four-Quarter or Year-Over-Year Growth Rate: Compares GDP across consecutive years’ quarters, factoring in seasonality. India’s Q2 FY25 growth was 5.4%.
- Annual Average Growth Rate: Averages four quarters’ growth. For FY25, India’s rates (e.g., 6.5%, 5.4%, 6.7%, 6.8%) yield ~6.4%.
Major Principles of Economic Development and Growth
Economic growth and development are influenced by key principles:
- Natural resources: Land, minerals, and renewable energy drive growth. India’s PM Suryaghar Yojana leverages solar resources.
- Capital formation: Savings and investment, per Adam Smith, yield returns. India’s capital formation is ~35% of GDP in 2025.
- Human resources: Neo-classical models emphasize skilled labor. India’s skilling programs enhance productivity.
- Population growth: Positive in underpopulated areas, but Malthusian risks persist. India’s population (~1.44 billion in 2025) requires balanced growth.
- Digital transformation: Platforms like UPI and AI drive modern growth, unique to 2025’s economy.
Importance of Economic Growth and Economic Development
Economic growth and development shape a nation’s prosperity:
- Enhances Prosperity: Improves living standards via better goods and services. India’s per capita income rose to $2,700 in 2025.
- Job Creation: Reduces unemployment. India’s job market grew 41% YoY in Feb 2025, driven by graduate hiring.
- Government Revenue: Higher revenue funds public services. India’s fiscal deficit target is 4.5% for FY26.
- Technological Innovation: Drives progress. India’s Digital India fosters fintech and AI adoption.
- Poverty Reduction: Expands opportunities. India’s MPI fell to 11% in 2024, aided by PMJDY.
- Sustainable Development: Enhances well-being via healthcare and education. Ayushman Bharat supports this.
- Diversified Growth: Balances sectors. India’s PLI schemes diversify manufacturing.
- Social Issues: Addresses poverty, inequality. Beti Bachao Beti Padhao tackles gender disparities.
- Global Evaluation: International organizations use growth data. India’s G20 presidency 2023 showcased its progress.
Issues in India's Growth, Development, and Employment
Major challenges in 2025 include:
- Illiteracy: Despite literacy at ~80%, gaps in quality education persist, addressed by NEP 2020.
- Poverty: ~11% of the population remains below the MPI line (2024), mitigated by PM Garib Kalyan Yojana.
- Growth Slowdown: Q2 FY25 growth at 5.4% reflects global trade challenges, countered by PLI schemes.
- Inadequate Secondary Sector: Manufacturing lags (28.2% of GVA), but Make in India boosts output.
- Agriculture Monsoon Dependency: ~55% of agriculture relies on monsoons, addressed by PM Fasal Bima Yojana.
- Unemployment: Rural unemployment and gig economy skilling gaps persist, tackled by ₹2 lakh crore skilling budget.
- Digital Divide: Uneven digital access hampers inclusion, mitigated by Digital India.
Recent Developments in India’s Economic Growth and Development (2025)
India’s economic landscape in 2025 reflects dynamic growth and development, driven by policy reforms and global trends. Below are key updates for UPSC preparation:
- Digital Economy: Contributes ~10% to GDP, with UPI handling 120 billion transactions in 2024 (50% of global volume). ONDC and Data Protection Act 2023 enhance inclusion and regulation.
- Climate Economics: Renewable capacity at 200 GW (40% of energy). Budget 2025-26 allocates ₹3 lakh crore for green energy, supporting net-zero 2070 and PM Suryaghar Yojana.
- Policy Reforms: PLI schemes for semiconductors, EVs, and labor codes (2019-20) drive manufacturing and job creation. NITI Aayog’s Vision 2047 replaces Five-Year Plans.
- Global Trade: FDI inflows rose 17.9% to $55.6 billion (FY25), but net FDI fell to $479 million due to volatility. India-UAE FTA boosts exports toward $1 trillion by 2030.
- Inclusion: Ayushman Bharat issued 36.36 crore cards, saving ₹1.25 lakh crore. Financial Inclusion Index at 64.2 (2024) via PMJDY.
- Sectoral Growth: Foodgrain production at 330.9 MT (FY25). Services PMI at 59.1, manufacturing PMI at 58.4 (April 2025).
Note: Sourced from Economic Survey 2024-25, Budget 2025-26, and RBI Bulletins. Use for prelims (e.g., MCQs on GDP, schemes) and mains (e.g., essays on sustainable growth).
Conclusion
- Economic development is a comprehensive concept that includes economic growth. Both are essential for understanding an economy. While growth drives income, development ensures well-being.
- India’s Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat schemes exemplify efforts to foster growth and development, aligning with Vision 2047 for a developed nation.
Powered by Froala Editor
|
108 videos|431 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on Economic Growth & Development: Economics - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the difference between economic growth and economic development? |  |
| 2. What are the five pillars of economic development? |  |
| 3. How is economic growth measured? |  |
| 4. What are the major principles of economic development and growth? |  |
| 5. Why are economic growth and economic development important? |  |

















