Introduction: Control Systems - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
What is Control System?
- A system is an arrangement, set, or collection of things connected or related in such a manner as to form it entirely or whole.
- The word control usually means regulate, direct, or command.
- The control system is that means by which any quantity of interest in a machine, mechanism or other equipment is maintained or altered in accordance with a desired manner.
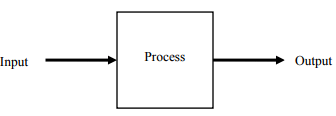 An Example of a Control Action
An Example of a Control Action - Control of a room temperature is achieved by switching ON and OFF of a supply to a heating appliance. Thus power supply to an appliance is switched ON, when the room temperature is felt low and switched OFF, when the desired temperature is reached.
- The above system can be modified, if the duration of application of power is predetermined to achieve the room temperature within desired limits.
- However, a further refinement can be made by measuring the difference between the actual room temperature and the desired room temperature and this difference being the error is used to control the element which in turn controls the output i.e. room temperature.
- The above description indicates that in the former case the output (room temperature) has no control on the input and the control action is purely based on a sort of predetermined calibration only, whereas in the later case the control action is affected by a feedback received from the output to the input.
Open Loop & Closed Loop Systems
Open Loop Systems:- An open-loop control system consists of a controller or control actuator to obtain the desired response.
- It utilizes an actuating device to control the process directly without using device.
- An example of an open-loop control system is an electric toaster.
- In Open Loop Controlling action there is no feedback is present to sense the error in the desired output.
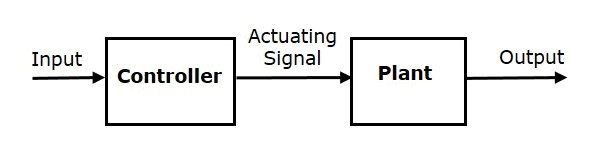 Open Loop System
Open Loop System
Advantages:
(a) Simple and economic
(b) No stability problem
Disadvantages :
(a) Inaccurate
(b) Unreliable
(c) The effect of parameter variation and external noise is more.
Note:
- No performance analysis is required for open loop control system.
- Feedback is not used for improving stability.
- An open loop stable system may become unstable when negative feedback is applied.
- Except oscillators in positive feedback, we have always unstable systems.
Closed Loop System OR Feedback System
- In a closed-loop control system, it consist of an additional measure of the actual output to compare the actual output with the desired output response.
- The measure of the output is called the feedback signal.
- A feedback control system that tends to maintain a relationship of one system variable to another by comparing functions of these variables and using the difference as a
means of control. - Since as the system is become more complex, the interrelationship of many controlled variables may be considered in the control scheme.
- An example of closed-loop control system is a person steering an automobile by looking at the auto’s location on the road and making the appropriate adjustments.
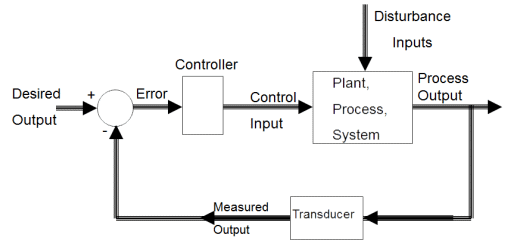 Closed Loop System
Closed Loop System
Examples of closed-loop systems are:
- Electric Iron
- DC motor speed control
- A missile laughing system (direction of missile changes with the location of target)
- Radar tracking system
- Human respiratory system
- Autopilot system
- Economic inflation
Advantages
(a) Accurate and reliable.
(b) Reduces effect of parameter variations.
- Example: RLC network
(c) Bandwidth of the system can be increased.
(d) Reduces effect of non-linearities
Disadvantages
(a) The system is complex and costly.
(b) The system may become unstable.
(c) Gain of the system reduced with negative feedback.
Comparison Between Open Loop & Closed Loop System
Open Loop System- So long as the calibration is good, an open-loop system performance will be accurate.
- Organization is simple and easy to construct.
- Generally stable in operation. If non-linearity is present, system operation degenerates.
Closed Loop System
- Due to feedback due to feedback, the performance of closed. closed-loop systems are accurate.
- Complicated and difficult.
- Stability depends on system components.
- Comparatively, the performance is better than the open-loop system, if non-linearity is present.
Features of Control Systems
- Control systems need to be easy for both clients and managers to understand and handle. If they're too complicated, they might not work properly. So, it's important to design control systems that are easy to use. These systems should meet the needs of the organization and produce meaningful results.
- They should be suitable and appropriate for achieving the goals of the enterprise. These objectives should be smartly defined.
- Control systems should be simple and straightforward. They use efficient techniques to detect sudden changes, helping to achieve desired outcomes quickly.
- Additionally, they should be adaptable and look ahead to the future.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Control Systems
Advantages:
- Control systems can respond faster than humans and are highly reliable.
- They can automate tasks, reducing the need for human intervention, which boosts productivity and cuts labor costs.
- These systems are adaptable to various conditions and can be reprogrammed for different functions.
- Many control systems can be monitored and managed remotely, which is useful for applications like space science and remote infrastructure.
- They optimize complex processes and operations, improving efficiency and achieving goals like increased throughput.
Disadvantages:
- Designing and implementing control systems can be expensive.
- They require regular maintenance and updates to function properly.
- Control systems rely heavily on electricity, needing a continuous power supply; any power failure can disrupt operations.
- They are sensitive to environmental factors such as light, temperature, and pressure.
- Operating and handling control systems requires specialized knowledge, which can be complex.
Applications of Control Systems
Control systems have various applications in different fields:
- Medical Equipment: Used to control medical machines like dialysis machines and X-ray machines.
- Farming and Agriculture: Automates tasks in agricultural processes such as crop harvesting and fertilization.
- Robotics: Controls and automates the movements of robots for various operations.
- Power and Energy Systems: Optimizes power generation, consumption, and distribution, enhancing the efficiency of power plants.
- Environmental Control: Regulates physical or chemical characteristics using HVAC systems.
- Transportation: Controls various aspects of transportation, including traffic control systems and air traffic control.
- Industrial Automation: Optimizes production processes in mills, factories, and other manufacturing industries.
- IoT and Home Automation: Controls and automates systems in homes or buildings, such as air conditioning, heating, and security.
 Applications of Control Systems
Applications of Control Systems
In conclusion, control systems have diverse applications, from supporting production in industries to functioning machines. Different types of control systems can be used based on specific purposes and individual needs, spanning from home appliances to industrial settings.
FAQs on Introduction: Control Systems - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is a control system? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between an open-loop and a closed-loop system? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of a closed-loop system over an open-loop system? |  |
| 4. What are the features of control systems? |  |
| 5. What are the applications of control systems? |  |
















