Compressibility & Consolidation | Civil Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Compressibility And Consolidation
COEFFICIENT OF COMPRESSIBILITY (av)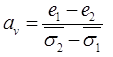
e1 = Void Ratio at effective stress 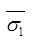
e2 = Void ratio at effective stress 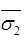
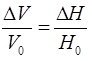
ΔV = Change in volume in m3, or cm3.
V0 = Initial volume in m3 or cm3.
ΔH = Change in depth in ‘m’ or ‘cm’.
H0 = original depth in ‘m’ or ‘cm’.
Remember: Consolidation settlement is a function of effective stress and not the function of total stress.
COEFFICIENT OF COMPRESSION (Cc)
(a)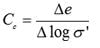
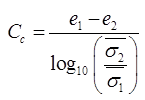
(b) CC = 0.009 (WL- 10) For undisturbed clays of low to medium senstivity WL = liquid limit expressed in percent.
(c) CC = 0.007 ( WL- 7) For remoulded soil of low sensitivity
(d) CC = 0.40 (e0- 0.25) For undisturbed soil of medium sensitivity e0 = Initial void ratio
(e) For remoulded soil of low sensitivity.
CC =1.15(e0- 0.35)
(f) C =0.115 w where, w = Water content
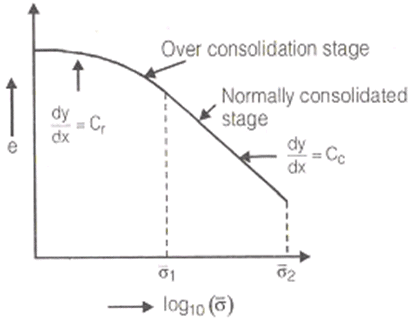
OVER CONSOLIDATION RATIO
O.C.R >1
For over consolidated soil.
O.C.R = 1
For normally consolidated soil.
O.C.R < 1
For under consolidated clay
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION OF 1-D CONSOLIDATION
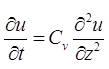
where,
u = Excess pore pressure,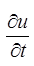 = Rate of change of pore pressure
= Rate of change of pore pressure
CV = Coefficient of consolidation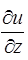 = Rate of change of pore pressure with depth.
= Rate of change of pore pressure with depth.
COEFFICIENT OF VOLUME COMPRESSIBILITY:
where, e0 = Initial void ratio
mv = Coefficient of volume compressibility
COMPRESSION MODULUS:
where, Ec = Compression modulus.
DEGREE OF CONSOLIDATION
(i)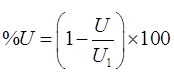
where, % U = % degree of consolidation.
U = Excess pore pressure at any stage.
Ui = 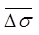 = Initial excess pore pressureat
= Initial excess pore pressureat
At t = 0, U = u1 ⇒ %u= 0%
at t = ∞ , u = 0 ⇒ %u =100%
(ii)
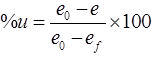
where, ef = Void ratio at 100% consolidation
i.e., of t =∞
e = Void ratio at time ‘t’
e0= Initial void ratio i.e, at t = 0
(iii) 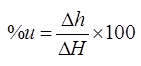
where, ΔH = Final total settlement at the end of completion of primary consolidation i.e., at t =∞
Δh = Settlement occurred at any time ‘t’.
TIME FACTOR
where, Tv = Time factor
CV = Coeff. of consolidation in cm2/sec.
d = Length of drainage path
t = Time in ‘sec’
d= Ho/2 For 2-way drainage d =H0 For one-way drainage.
where, H0 = Depth of soil sample.
(i)
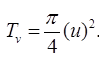 , if u ≤ 60% T50 = 0.196
, if u ≤ 60% T50 = 0.196
(ii) , if u > 60%
METHOD TO FIND 'Cv'
(i) Square Root of Time Fitting method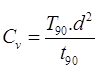
where,T90 = Time factor at 90% consolidation
t90 = Time at 90% consolidation
d = Length of drainage path.
(ii) Logarithm of Time Fitting method
where,T50 = Time factor of 50% consolidation
t50 = Time of 50% consolidation
Remember: Square root of time fitting method is better for soil having higher secondary consolidation.
COMPRESSION RATIO:
(i) Initial compression Ratio
where, Ri = Initial reading of dial gauge.
R0 = Reading of dial gauge at 0% consolidation
Rf = Final reading of dial gauge after secondary consolidation.
(ii) Primary Consolidation Ratio
where, R100 = Reading of dial gauge at 100% primary consolidation.
(iii) Secondary Consolidation Ratio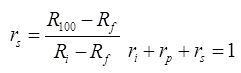
TOTAL SETTLEMENT
S = Si + SP+Ss
where Si = Initial settlement, Sp=Primary Settlement Ss = Secondary settlement
(i) Initial Settlement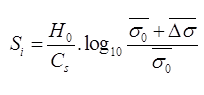
For cohesionless soil.
where,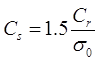
where, Cr = Static one resistance in kN/m2
H0 = Depth of soil sample
for cohesive soil.
where, It = Shape factor or influence factor, A = Area.
Remember: For square footing , A = B2 and It = 1
-for strip footing
(ii) Primary Settlement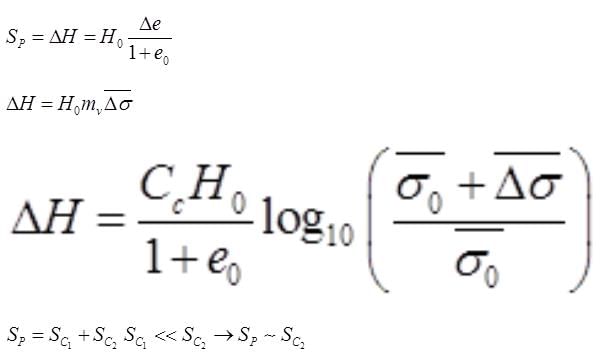
sc1 = Settlement for over consolidated stage
sc1 = Settlement normally consolidated stage
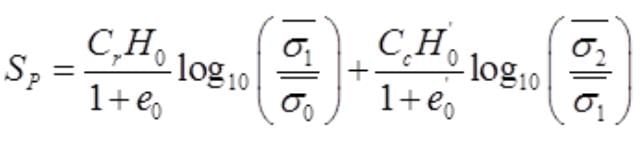
(iii) Secondary Settlement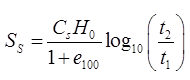
where, H0 ~ H100
H100 = Thickness of soil after 100% primary consolidation.
e100 = Void ratio after 100% primary consolidation.
t2 = Average time after t1 in which secondary consolidation is calculated.
|
2 videos|133 docs|55 tests
|
FAQs on Compressibility & Consolidation - Civil Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is compressibility in civil engineering? |  |
| 2. How is compressibility measured in civil engineering? |  |
| 3. What is consolidation in civil engineering? |  |
| 4. How does consolidation affect civil engineering projects? |  |
| 5. What are the factors affecting compressibility and consolidation in civil engineering? |  |






















