Plastids | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
PLASTIDS
- The term "Plastid" first used by Haeckel .
- Schimper coined the term chloroplastid for green plastids. Meyer called them Autoplast
- Chloroplast name proposed by Erera.
 Plastids
Plastids
TYPES OF PLASTIDS
(1) Chromoplasts :– These are plastids, which contain different types of pigments (carotenes, Xanthophylls etc.). Chlorophylls either absent or occur in very less amount. Chromoplasts occurs mainly in pericarp and petals. Red colour of chillies and red tomatoes is due to the red pigment "Lycopene" of chromoplasts,. Lycopene is a type of carotene. Yellowish - orange colours of fruits are due to a-carotene, b-carotene and g–carotene.b– carotene is precursor of vitamin-A. Richest source ofb-carotene are carrot roots.
- Chromoplasts also occurs in petals but colour of petals are mainly due to water soluble pigments occur in cell sap. e.g. Anthocyanin - (Blue or violet or red pigment) Anthochlor (yellow pigment).
(2) Chloroplasts :– Green plastids with chlorophylls and other photosynthetic pigments.
(3) Leucoplasts :– These store food in different forms like starch (Amyloplasts), Fat and oil (Elaioplasts) and protein (Aleuroplasts). Pigments and lamellar structure absents in Leucoplasts. Generally occurs in non green and underground plant cells.
- All types of plastids have common origin from proplastids, sac like non-lamellar structures.
- Different types of plastids may transform from one form to another. Because genetic meteral is similar. But chromoplasts never transform to chloroplasts.
- Etioplasts :– These are plastids without pigments, stored food and lamellar structures. These plastids occur in etiolated plants due to the absence of light.
- Chromatophores :– These are clusters of pigment granules in cytoplasm of photosynthetic bacteria.
- In Blue-green algae pigments are located on membranous lamellar structures, scattered in Cytoplasm. These structures are known as Chlorosomes or Lamellisomes or Carboxysomes.
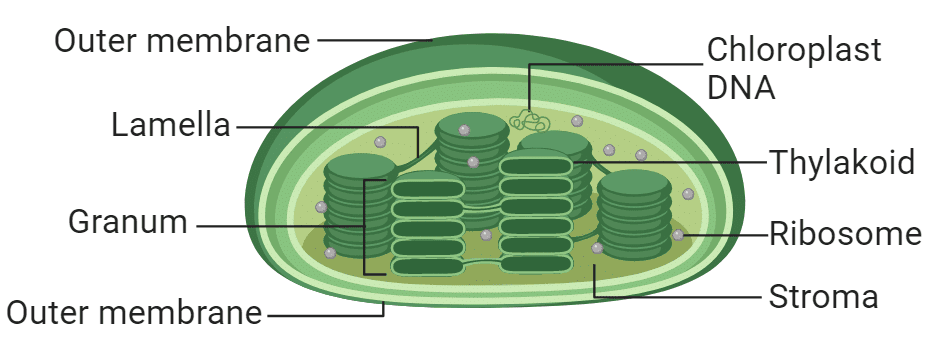
STRUCTURE OF CHLOROPLAST
Shape of chloroplasts | Plant types |
Discoidal or oval | higher plants |
Girdle shaped | Ulothrix |
Cup shaped | Chlamydomonas |
Reticulate | Spirogyra |
Stellate | Zygnema |
- Chloroplast is a double membrane bound cell organelle, and is the largest organelle of cell. (4-6mm x 1-3mm). (largest component is nucleus)
- Internally chloroplast contains stroma (Matrix) and thylakoids or lamellae. Matrix part of chloroplast contains circular or rarely linear DNA, RNA, 70-s Ribosomes, starch grains, enzymes of calvin cycle or dark reaction. Rubisco is the most abundant enzyme on the earth. It made 16 % protein of the chloroplast
- The number of chloroplast in cell of higher plants 20-40.(One in chlamydomonas)
- Thylakoids (Term by Menke 1962) are membrane lined flattend sacs, which forms stacks called granum (Plu. grana). Each chloroplast contains about 20-100 granum. Fret channel or stromal thylakoids is connection between two granum. Photosynthetic pigments (chlorophylls) are located in the thylakoid membranes.
- A photosynthetic functional unit, which consists of about 230 to 400 molecules of various pigments (Chl-a, Chl-b, carotenes, xanthophylls etc.) is called as Quantasomes (By Park & Biggins 1964).
- Chloroplasts has their own genetic system & complete protein synthesis machinary (ds-DNA, RNA, Ribosomes, enzymes, Amino Acids), thus chloroplasts are called as semiautonomous organelle of the cell.
- DNA of chloroplast was discovered by Ris & Plaut. (Upto 14% DNA of cell) * Chloroplast have more genes as compare to mitochondria. (100 or more genes) FUNCTIONS
(1) Photosynthesis : The chloroplasts trap the light energy of sun and transform it into the chemical energy in the form glucose.
(2) Balancing of O2 & CO2 in nature.
(3) Chloroplasts can be changed into chromoplasts during ripening of fruits.
(4) Chloroplasts impart in cytoplasmic inheritance.
(5) Chloroplasts impart the pleasing greenary to the earth.
(6) Chloroplasts store vitamin K, E, Rubisco protein and Fe etc.
BIOGENESIS
(1) From Proplastid
(2) From Division of pre-existing plastids.
(3) Origin from Endosymbiotic origin by a cyanobacterium
|
26 videos|312 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Plastids - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What are plastids? |  |
| 2. What is the role of plastids in photosynthesis? |  |
| 3. How do plastids store food and pigments? |  |
| 4. Can plastids be found in animal cells? |  |
| 5. What other functions do plastids serve apart from photosynthesis? |  |

















