Glossary and Important Information - What is Democracy ? Why Democracy ? | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Glossary |

|
| Important Information |

|
| What is Democracy? |

|
| Features of Democracy |

|
| Why Democracy? |

|
| Broader Meanings of Democracy |

|
Glossary
- Dictatorship: In it all the powers are in the hands of a single individual or a small group of individual and the dictator is not answerable to anybody.
- Democracy: It is a form of government in which the ruling power is vested in the hands of the people and the government is answerable to the people who can change it through constitutional means.
- Communist State: A state-run by the communist Party without allowing other parties to fight elections.
- Coalition: A combination of parties to share power in the government.
- Political Prisoners: Prisoners held in prison or detained for opposing the government.
- Dictator: Head of the state who arbitrarily rules the country.
- Constitution: Rules of laws according to which the government of the state runs.

Important Information
What is Democracy?
- Democracy is a form of government in which the rulers are elected by the people.
- One chief factor common to all democracies is that the government is chosen by the people.
Why define Democracy?
- Defining Democracy is important because: It helps students to demarcate between democratic and non-democratic governments.
- From the non-democratic government, take the example of Myanmar, where rulers were not elected by the people.
- Those who were in charge of the army of the country took over as rulers and people had no say in this decision.
- Dictators like Pinochet (Chile) are not elected by the people. This also applies to monarchies.
A Simple Definition
Democracy is a form of government in which the supreme power is vested in the people and exercised directly by them or by their elected agents under a free electoral system.
Features of Democracy
- The rulers are elected by the people.
- Free and competitive elections are held.
- Each adult irrespective of religion, education, caste, colour, wealth have one vote, one value.
- The elected rulers take decisions within limits set by constitutional law and citizens’ rights.
- Rule of Law
- The rights of the citizens must be protected through Constitution.
- There must be an independent judiciary
Major Decisions by Elected leaders
- In Pakistan, General Pervez Musharraf led a military coup in October 1999 and overthrew a democratically elected government and became President of the country.
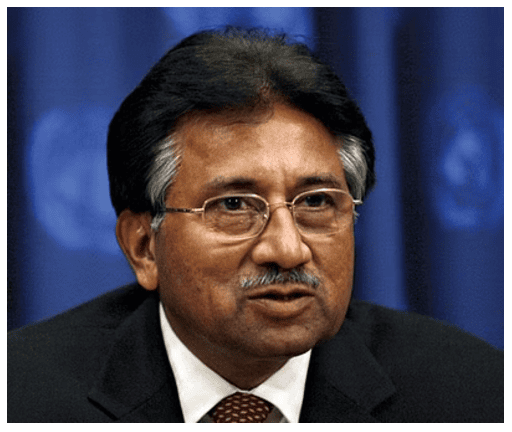

- In 2002, he held a referendum in the country which was based on malpractices and fraud granted him a five-year extension.
- After passing the law, the ‘Legal Framework Order’ which gave the president power to dismiss the national and provincial assemblies, elections were held to the national and provincial assemblies.
- In this case, Pakistan has had elections, elected representatives have some powers.
- But the final power rests with military officers and General Musharraf himself. So, this should not be called a democracy.
- In a democracy, the final decision-making power must rest with those elected by the people.
Free and fair electoral competition
- In China, elections are regularly held after every five years for electing the country’s parliament called the National People’s Congress.
- Before contesting elections, a candidate needs the approval of the Chinese Communist Party.
- The government is always formed by the Communist Party.
- Mexico holds elections after every six years to elect its President.→ But until 2000 every election was won by a party called PRI (Institutional Revolutionary Party). → Opposition parties did contest elections but never managed to win as PRI was known to use many dirty tricks to win elections.
- Both the cases should not be called a democracy.
- Democracy must be based on a free and fair election where those currently in power have a fair chance of losing.
One person, One vote, One value
- There are many instances of denial of equal right to vote.
- In Saudi Arabia, women do not have the right to vote.
- Estonia has made its citizenship rules in such a way that people belonging to the Russian minority find it difficult to get the right to vote.
- In Fiji, the electoral system is such that the vote of an indigenous Fiji has more value than that of an Indian-Fijian.
- In a democracy, each adult citizen must have one vote and each vote must have one value.
Summary Definition
Democracy is a form of government in which:
(i) Rulers elected by the people take all the major decisions.
(ii) Elections offer a choice and fair opportunity to the people to change the current rulers.
(iii) This choice and opportunity are available to all people on an equal basis.
(iv) The exercise of this choice leads to a government limited by basic rules of the constitution and citizens rights.
Rule of Law and Respect for Rights
- Since independence, Zimbabwe ruled by ZANU-PF.
- Its leader, Robert Mugabe has been ruling the country. He is popular but also uses unfair practices in elections.
- Elections have been held regularly and always won by ZANU-PF.
- Opposition party workers are harassed and their meeting disrupted.
- Public protests and demonstrations against the government are declared illegal.
- Television and radio are controlled by the government and give only the ruling party’s version.
- Independent newspapers are there but the government harasses those journalists who go against it.
- The government has ignored some court judgments that went against it and has pressurised judges.
- In this case, the government is not democratic as there is no citizen basic rights, no political opposition, no judiciary.
- A democratic government rule within limits set by constitutional law and citizens’ rights.
Why Democracy?
Debating Merits of Democracy
- Democracy, as a principle, can go beyond the government and can be applied to any sphere of life.
- People use the word democracy not to describe any existing government but to set up an ideal standard that all democracies must aim to become.
- However, if the ideals of democracy are considered then no country in the world is correctly democratic.
Arguments against democracy
- Leaders keep changing in a democracy. This leads to instability.
- Democracy is all about political competition and power play. There is no scope for morality.
- So many people have to be consulted in a democracy that it leads to delays.
- Elected leaders do not know the best interest of the people. It leads to bad decisions.
- Democracy leads to corruption for it is based on electoral competition.
- Ordinary people don’t know what is good for them; they should not decide anything.
Arguments for democracy
- A democratic government is a better government because it is a more accountable form of government.
- Democracy improves the quality of decision-making.
- Democracy provides a method to deal with differences and conflicts.
- Democracy enhances the dignity of citizens.
- Democracy allows us to correct our own mistakes.
Broader Meanings of Democracy
- The most common form that democracy takes in our times is that of a representative democracy where the majority is allowed to take decisions on behalf of all the people.
- The majority of people rule through their elected representatives.
- A democratic decision involves consultation with and consent of all those who are affected by that decision.
- Democracy is a principle that can be applied to any sphere of life.
- Democracy can apply to a government or a family or any other organisation.
Advantages of Democracy
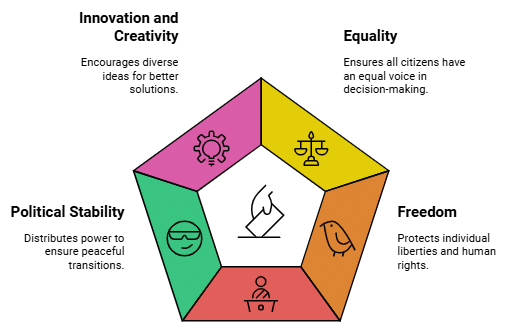
- Equality: Democracy promotes equality among citizens, ensuring that everyone has a voice in decision-making regardless of their background, wealth, or status.
- Freedom: Citizens in a democracy enjoy various freedoms such as freedom of speech, assembly, religion, and press. This fosters individual liberties and protects human rights.
- Accountability: Elected representatives in a democratic system are accountable to the people who elect them. If they fail to fulfill their promises or act against the interests of the public, they can be voted out of office.
- Political Stability: Democracies tend to be more politically stable compared to autocratic regimes because power is distributed among multiple institutions and there are mechanisms in place for peaceful transitions of power.
- Innovation and Creativity: Democracy encourages innovation and creativity as diverse perspectives and ideas are considered in decision-making processes, leading to better problem-solving and policy outcomes.
Disadvantages of Democracy
- Slow Decision-Making: Democratic processes such as debates, negotiations, and consensus-building can sometimes result in slow decision-making, especially in times of crisis when swift action may be needed.
- Majority Tyranny: In a democracy, the majority rule, which can sometimes lead to the oppression or marginalization of minority groups if their rights are not adequately protected.
- Populism: Democracy is susceptible to populism, where leaders may appeal to public emotions and preferences rather than rational policies, leading to short-term solutions and neglect of long-term interests.
- Political Polarization: Democracies may experience political polarization, where society becomes divided along ideological or partisan lines, making it difficult to reach consensus and govern effectively.
- Manipulation and Corruption: Democratic processes, such as elections and lobbying, can be vulnerable to manipulation and corruption by special interest groups, undermining the integrity of the political system.
|
55 videos|637 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Glossary and Important Information - What is Democracy ? Why Democracy ? - Social Studies (SST) Class 9
| 1. What are the main features of democracy? |  |
| 2. Why is democracy considered important? |  |
| 3. How does democracy differ from other forms of government? |  |
| 4. What are some broader meanings of democracy beyond elections? |  |
| 5. How can citizens participate in a democratic system? |  |





















