Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 9 > Glossary and Important Information - Constitutional Design
Glossary and Important Information - Constitutional Design | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Glossary |

|
| Important Information |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Democratic Constitution in South Africa |

|
| Towards a New Constitution |

|
| Why do we need a Constitution? |

|
| Institutional Design |

|
Glossary
- Constitution:The foundational legal document governing a country's government, encompassing basic laws, defining organ functions, jurisdiction, and citizens' fundamental rights.
- Cabinet Mission: In February 1946, the British government sent the cabinet mission to India. It proposed the formation of a federation, with a union government and three types of states and also proposed the formation of a Constituent Assembly and an interim government.
- Objective Resolution: On December 13, 1946, Jawaharlal Nehru moved a resolution in the Constituents Assembly proposing the main objectives or aims of the new constitution to be made for free India. It is known as the Objective Resolution.
- Drafting Committee: A committee set up to draft a constitution.
- Amendment:The term means to change or modify. It is used in connection with changes made in the constitution of a country. The procedure of amendment of the Indian constitution is given in Article 368 of the constitution itself.
- Democracy: A form of government that is chosen by the people to work for their welfare and can be changed by them.
- Preamble: It is an introduction to the constitution that explains the aims and objectives of the constitution.
- Republic: A country in which the head of the state is elected and not hereditary.
- Secularism: It implies religious freedom. The state does not have any official religion of its own. Everyone has the right to preach, practice & profess any religion.
- Universal Adult suffrage: It refers to the right to vote for all the adult citizens of a country without any discrimination on the basis of caste, creed, color, sex, or education. It is based on the principle of one person one vote.
- Apartheid: A system of reaggregation of whites from blacks on the basis of race. Each group had to live in separate areas, and go to separate schools and non-whites had no voting rights.
- Constituent Assembly: An assembly of people’s representatives that writes a constitution for a country.
- Philosophy: The most fundamental principles underlying one’s thoughts and actions.
- Treason: The offense of attempting to overthrow the government of the state to which the offender owes allegiance.
- Tryst: A meeting or meeting place that has been agreed upon.
Important Information
Introduction
In a democracy, rulers and citizens are bound by fundamental rules, collectively known as the constitution. The Constitution dictates citizen rights, government powers, and operational protocols. It serves as the supreme law determining relationships among citizens, governments, and operational guidelines.
Democratic Constitution in South Africa
Apartheid Definition: Policy of discrimination based on race in South Africa.
Features of Apartheid
- Racial classification and separation.
- Separate living areas, schools, universities, and facilities.
- Criminal offense for interracial marriage.
- Restrictions on movement.
- Non-whites were denied voting rights and governance participation.
End of Apartheid
- African National Congress (ANC) was formed in 1910 for a non-racial democratic South Africa.
- Intensified movement in the 1950s, ANC was banned in the 1960s.
- UN condemnation and international sanctions in the 1980s.
- Negotiations for a new constitution in the 1990s.
- In elections in April 1994, the ANC won, forming a non-racial democratic government.
Towards a New Constitution
- Formation of a common constitution by oppressive and freedom-struggling parties.
- South African constitution provides extensive rights and inclusivity.
- Upholds the principle that nobody should be excluded from problem-solving.

Nelson Mandela - Gandhi of South Africa
- Nelson Mandela, an efficient leader of ANC, played a crucial role against apartheid.
- Imprisoned in 1964, released in 1990.
- First democratic elections in 1999, Mandela elected President.
- Symbolizes the transformation from an isolated regime to a model of democracy.
Why do we need a Constitution?
A constitution is a set of written rules accepted by citizens, determining relationships and governance.Functions of a constitution
- Generates trust and coordination among diverse people.
- Specifies government composition and decision-making powers.
- Sets limits on government powers and outlines citizen rights.
- Expresses people's aspirations for a good society.
Making of the Indian Constitution
- Challenges during the making of the Indian Constitution.
- Born through partition in 1947, with challenges of merging princely states.
- Constitution drafted under the Cabinet Mission Plan of 1946.
- Institutional design influenced by colonial rule, French Revolution ideals, and global democratic practices.
- Inspired by Motilal Nehru's constitution (1928) and Karachi session resolution (1931).

Guiding Values of the Indian Constitution
Values embedded in the Preamble:
We, the People of India.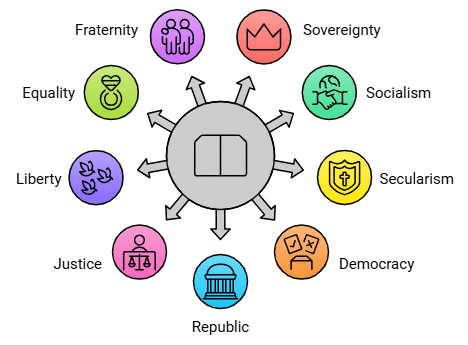
- Sovereign.
- Socialist.
- Secular.
- Democratic.
- Republic.
- Justice.
- Liberty.
- Equality.
- Fraternity.
Reflects the dreams of leaders like Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. Ambedkar.
Institutional Design
- The constitution is not static but designed to accommodate changes.
- Provisions for constitutional amendments (104 to date) reflect changing aspirations and societal dynamics.
- Three categories of amendments based on majority requirements.
The document Glossary and Important Information - Constitutional Design | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 is a part of the Class 9 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 9.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Glossary and Important Information - Constitutional Design - Social Studies (SST) Class 9
| 1. What is the significance of a democratic constitution in South Africa? |  |
Ans. A democratic constitution in South Africa is significant because it establishes the fundamental principles and framework for governance, ensuring that all citizens have equal rights and protections under the law. It promotes democracy, accountability, and human rights, serving as a foundation for a fair and just society.
| 2. Why do we need a constitution in a democratic society? |  |
Ans. A constitution is essential in a democratic society as it outlines the rules and procedures for governance, protects individual rights, and limits the powers of government. It serves as a safeguard against tyranny and ensures that all citizens can participate in the democratic process.
| 3. What are the key elements of institutional design in the context of South Africa's constitution? |  |
Ans. Key elements of institutional design in South Africa's constitution include the separation of powers among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, the establishment of independent institutions, checks and balances to prevent abuse of power, and mechanisms for accountability and transparency in government.
| 4. How did South Africa transition towards a new constitution after apartheid? |  |
Ans. South Africa transitioned towards a new constitution after apartheid through a negotiated process that involved multiple stakeholders, including political parties, civil society, and communities. This led to the creation of a democratic framework that prioritized human rights and inclusivity, culminating in the adoption of the Constitution in 1996.
| 5. What challenges does South Africa face in implementing its constitution effectively? |  |
Ans. South Africa faces several challenges in implementing its constitution effectively, including socio-economic inequalities, corruption, and political instability. Additionally, there are ongoing struggles to ensure that all citizens have access to justice and that their rights are upheld, particularly for marginalized groups.
Related Searches





















