Types of Force | Science Class 9 PDF Download
Force
From our day to day experience, we all are familiar with the concept of 'Force'. While opening a door, lifting a bucket or a bag, kicking a football or throwing a stone, we have to act differently and in many ways. We are either pushing or pulling the object. The no non-living object moves on its own. We have to apply the effort in the form of push or pull. This pull or push is called force. Thus a force is an external agency that displaces or tends to displace a body from its position of rest. The direction in which the object is pushed or pulled is called the direction of the force. Force has both magnitude and direction. It is a vector quantity.
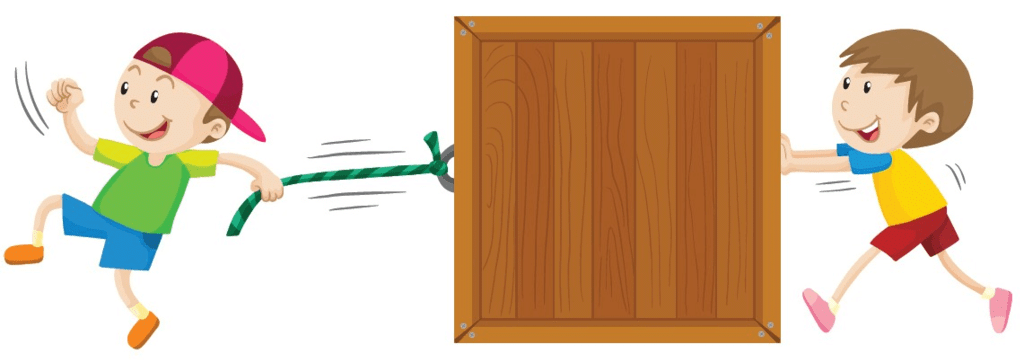 Force is a Push or a Pull
Force is a Push or a Pull
Force is the 'push' or 'pull' which can make a body move, stop a moving body, change the direction and speed of a moving body. Force cannot be seen but the effect of force on an object can be seen or felt.
Definition of Force
A force is a physical quantity related to actions like pushing, hitting, or pulling. It can make an object at rest move, change the direction of a moving object, alter the size and shape of an object, or change how fast an object is moving. The natural tendency of objects to resist changes in their state of rest or uniform motion is known as inertia. The mass of an object indicates its inertia. The SI unit for force is kg m s², known as a newton and represented by the symbol N.
Effect of Force
A force produces the following effects:-- It can move or try to move an object.
- It can stop or try to stop a moving object.
- It can change or try to change the direction of an object's motion.
- It can speed up or slow down an object.
- A force can also change the shape and size of objects.
Force can Move or Tend to Move an Object
- When a force is applied to a stationary object, it can either move it or alter its motion.
- The movement of the object occurs in the direction of the applied force.
- Examples include:
- A football being kicked starts moving.
- A train engine pushes railway cars to set them in motion.
- A horse pulls a cart by applying force.
- Pushing, hitting, and pulling are all methods to set objects in motion.
- A force can also change the speed of an object, making it move faster or slower, or alter its direction.
- Sometimes, when you push against a wall, it doesn’t move because the force you apply is balanced by the wall's strength and the ground pushing back.

Force can Stop or Tend to Stop an Object
When a force is applied on a moving body, it can either stop the body or tend to stop it. For this a force is applied opposite to the direction of motion of the body. Some examples of this are:
(i) When a football in motion has to be stopped a force is applied opposite to the direction of motion of the football.
(ii) A railway locomotive applies brakes on the railway wagons to stop them.
(iii) A rolling body comes to rest due to frictional force. This force acts opposite to the direction of motion of the body.
(iv) At times when you push a car in motion, you are unable to stop it. The force applied by use tends to stop the moving car.
Force can Change or Tend to Change the Direction of Motion of an Object
(i) When a football in motion kicked perpendicular to its motion it's direction of motion changes.
(ii) A perpendicular force is required to make a particle move in a circular path. This force is called centripetal force. This force continuously changes the direction of motion of the body.
(iii) A cricketer applies a tangential force to change the direction of the cricket ball.
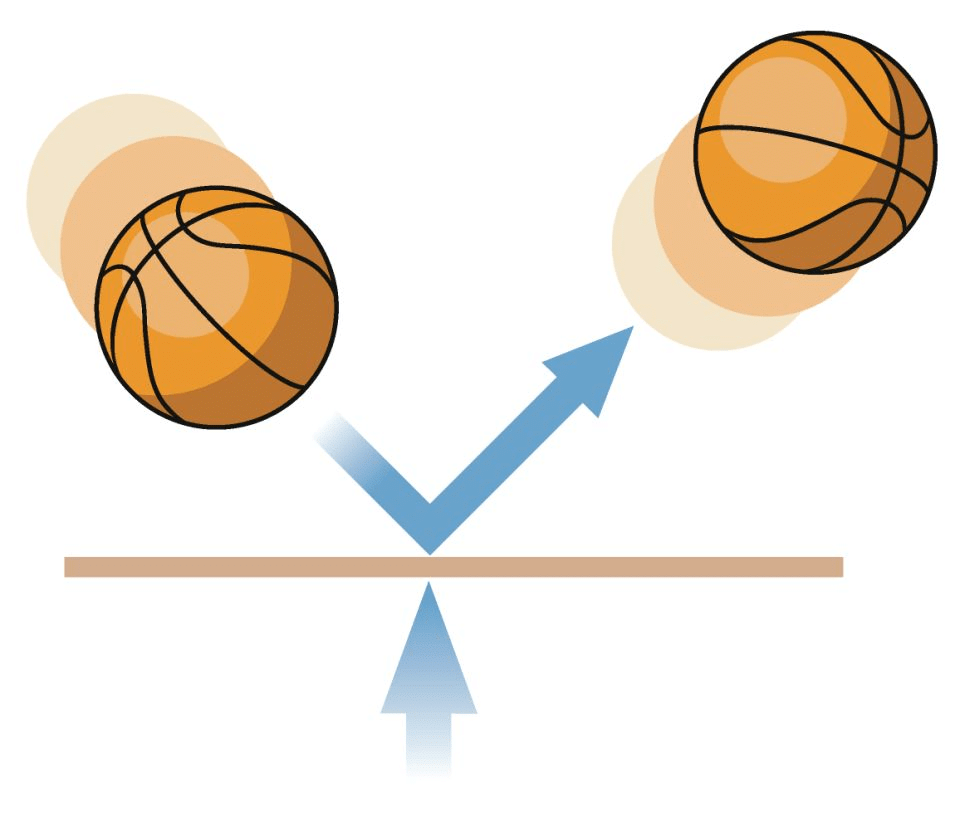
Force can Increase or Decrease the Speed of an Object
- When a force acts on a moving object, whether in the same direction or opposite, it can change the object's speed.
- A force can alter the magnitude of velocity, meaning it can make the object move either faster or slower, or change its direction.
- Examples include:
- When a football is kicked in the direction it’s moving, its speed increases.
- Applying brakes on a car reduces its speed.
- Pushing down on the pedals of a bicycle makes it go faster.
- A freely falling object speeds up towards the Earth due to the force of gravity.
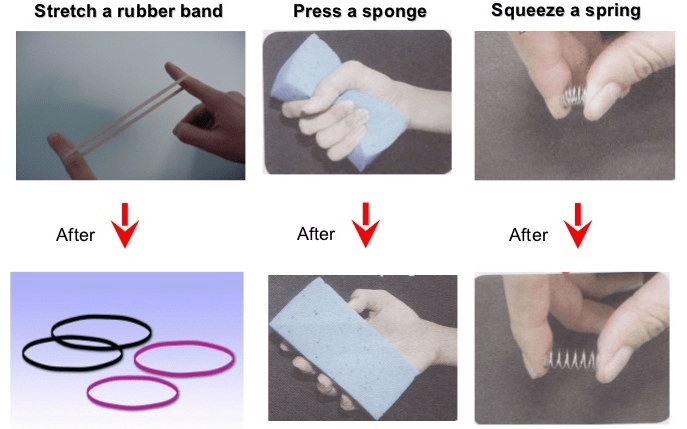
Effect on Shape
A force can also change the shape and size of objects. For example:
- A spring stretches when a force is applied.
- A spherical rubber ball becomes oblong when pressure is applied to it.
Concept of Force
The concept of force gives us the quantitative description of the interaction between two bodies or between a body and the environment.
When you push or pull a car stuck in mud, you exert a force on it. This force may or may not be able to move the car.
Thus force is an agent (often termed as a pull or a push), which
- Can move or tend to move an object.
- Can stop or tend to stop an object in motion.
- Can change or tend to change the direction of motion of an object.
- Can increase or decrease the speed of an object.
- From all these cases we can conclude that force is actually producing acceleration.
Thus, force is an agent whose action can produce acceleration in a body.
A force can also change the shape of an object on which it is acting. For example when you squeeze a soft rubber ball it will be deformed to some extent.
In other words a force can be defined as an agent which, can change or tend to change the dimension of an object or produces or tends to produce acceleration in an object.
Broadly speaking forces are classified as being of two types:
(i) Contact Force: The force which acts on a body either directly or through some connector are called contact forces.
Examples: Biological force, muscular force, mechanical force and frictional force are the examples of contact force.
- Muscular Force: This force produced by the muscles of living beings is called muscular force or biological force.
- Mechanical Force: The force generated by machines is called mechanical force.
- Friction Force: A force which acts at the surface of contact, when one body moves or tends to move upon another body is called the force of friction.
The force of friction has the following properties :
(i) It is produced only when one body is made to move upon another body.
(ii) It always opposes the motion of the body and tries to stop the body.
(iii) It wears off the surface of contact of two bodies.
It is the force of friction which makes it difficult for us to move heavy objects such as large boxes; carts laden with different kinds of substances, etc. Again, it is the force of friction which wears off the tires of our bicycles, cars, trucks, etc.
(ii) Non-contact Force or Field Force: The force which does not make direct contact with a body and acts through space, without any connector is called non-contact force.
Examples:
1. The force of gravity of the earth is a non-contact force that attracts all bodies towards the earth.
2. The electrostatics force can pull tiny bits of dry paper is a non-contact force.
3. A magnet can attract common pins of steel from a distance and hence the magnetic force is non-contact force.
- Gravitational Force:
Here G is a universal gravitational constant & m1 m2 are masses, and r is a distance between two bodies.
- Electrostatics Force:
Here K is a Coulomb's constant & q1 q2 are charges, and r is a distance between two charges.
- Magnetic Force: The strange property of some substances to attract iron or steel objects towards itself is called magnetic property. The substance which has the above property is called a magnet.
As the objects of iron or steel move towards the magnet, therefore we can say that they are acted upon by the force of the magnet.
Resultant Force
If a single force acting on a body produces the same acceleration as produced by a number of forces, that single force is called the resultant of these individual force.
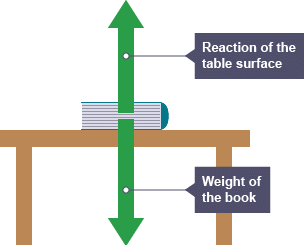
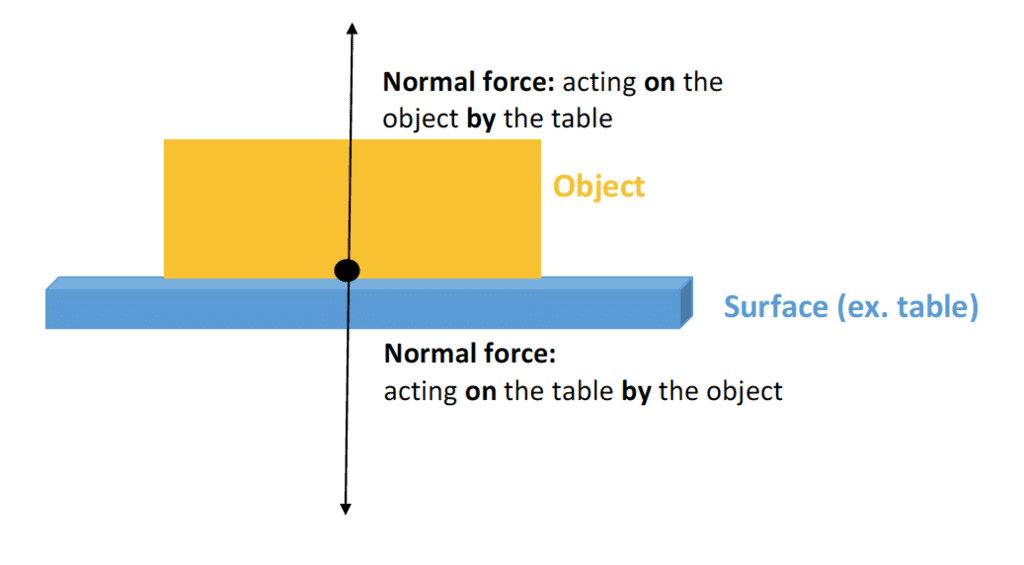
Normal Force
The force exerted perpendicular to the surface of an object that is in contact with it is referred to as normal force.
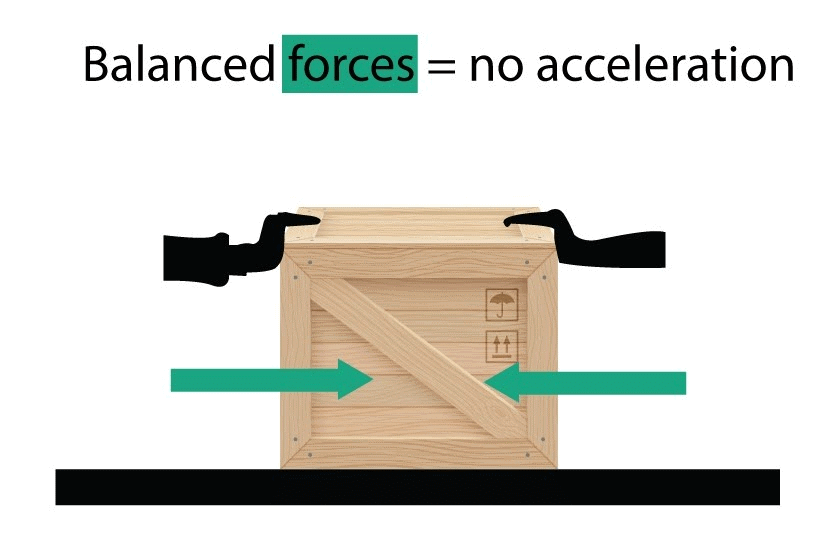
Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
If a group of forces acting on an object does not cause any change in its motion, these forces are called balanced. However, if they cause the object to accelerate, they are considered unbalanced. An unbalanced force will set an object in motion.
Definition of Balanced Forces
When two forces of equal strength push or pull on an object in opposite directions at the same time, the object remains either at rest or moves in a straight line at a constant speed. These forces are known as balanced forces, and they do not alter the object's state of rest or motion.Examples:
1. When we push against a wall, it does not move, meaning it stays still. The force we apply goes forwards, while the wall pushes back with an equal force in the opposite direction. These two opposing forces cancel each other out, making them balanced forces.
2. If a block is pulled equally from both sides, it will remain stationary.
3. When we attempt to push a heavy box on a rough surface, it doesn't move because the friction force is equal to the pushing force. If children push the box with more force, the pushing force exceeds the friction force, resulting in an unbalanced force, and the box begins to move.
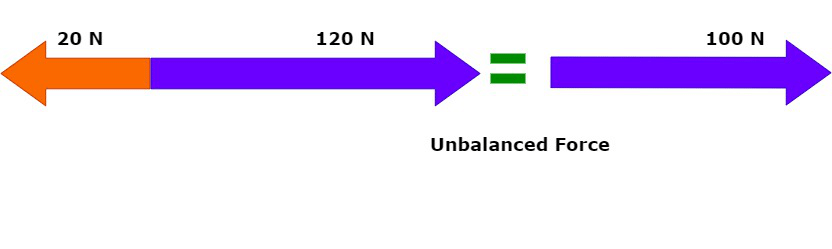
Definition of Unbalanced Forces
When two forces of different strengths push against an object in opposite directions at the same time, the object will move in the direction of the stronger force. This means the forces are not balanced, and the unbalanced force causes the object to move.
Examples:
1. If children push a box on a rough floor with a weak force, the box doesn't move because friction works against the push.
2. A bicycle slows down when the rider stops pedalling due to friction acting against the direction of motion.
A force is a physical quantity related to actions like pushing, hitting, or pulling. It can make an object at rest move, change the direction of a moving object, alter the size and shape of an object, or change how fast an object is moving. The natural tendency of objects to resist changes in their state of rest or uniform motion is known as inertia. The mass of an object indicates its inertia. The SI unit for force is kg m s², known as a newton and represented by the symbol N.
|
84 videos|543 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Force - Science Class 9
| 1. What is force? |  |
| 2. What are balanced forces? |  |
| 3. What are unbalanced forces? |  |
| 4. Can multiple forces act on an object at the same time? |  |
| 5. How can forces be represented? |  |

















