Chemical Properties of Metals | Science Class 10 PDF Download
What are Metals?
Metals are the electropositive element where they tend to donate electrons and form positive ions and become stable.
For example: Na → Na+ + e–
 Some properties of famous metals:
Some properties of famous metals:
- Alkali metals (Li, Na, K, etc) react vigorously with water and oxygen or air.
- Mg reacts with hot water.
- Al, Fe and Zn react with steam.
- Cu, Ag, Pt, Au do not react with water or dilute acids.
Did you know?
Sodium is the most reactive metal.
Reaction of Metals with Oxygen (Burnt in Air)
- → Metals combine with oxygen to form metal oxide.Metal + O2 → Metal oxide
- As the metal burns, a bright flame is produced, the colour of which can be used to identify the metal compound. Fireworks contain small metal filings to produce the bright range of colours you see at displays.

- But all metals do not react with oxygen at the same rate. They show different reactivity towards oxygen. Such as sodium and potassium react so vigorously that they catch fire if kept in the open.
- Examples:
(i) 2Cu + O2 → 2CuO
Copper oxide (black)
(ii) 4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3
Aluminium oxide
(iii) 2Mg + O 2 → 2MgO
The reactivity of different metals are different with O2. - Sodium and potassium react with oxygen of air, burns with a golden yellow colour and form sodium and potassium oxides, which dissolve with water to form alkali called sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide. These turn red litmus blue.
Na2O(s) + H2O (ℓ) → 2NaOH(aq)
K2O(s) + H2O(ℓ) → 2KOH(aq) - Zinc reacts with oxygen only when strongly heated to form zinc oxide,
2Zn(s) + O2(g) → 2ZnO
Since it is less reactive than sodium and potassium. - Copper does not react with oxygen even on strong heating. It reacts very slowly on prolonged heating to form cupric oxide (black oxide).
The reaction is given as:
2Cu(s) + O2(g) → 2CuO(s) - The order of reactivity of these metals towards oxygen is as follows:
Na > K > Mg > Zn > Fe > Cu Reactivity of Metals towards Oxygen
Reactivity of Metals towards Oxygen - At ordinary temperature, the surface of metals like magnesium (Mg), Aluminium (Al), Copper(Cu), Zinc(Zn), lead (Pb) etc. are covered with a thin layer of oxide.
- The protective oxide layer prevents the metals from further oxidation. Silver and gold do not react with oxygen due to this silver and gold are called noble metals.
Do You Know?
- Anodising is a process of forming a thick oxide layer of aluminium. Aluminium develops a thin oxide layer when it is exposed to air.
- This oxide coat of aluminium (Al) makes it resistant to further corrosion. During anodising, the resistance can be improved further by making the oxide layer thicker. In this process, a clean Al article is made the anode and dilute sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is used for electrolyte.
- The oxygen gas evolved at the anode react with Al to make a thicker protective oxide layer. This oxide layer can be dyed easily to give Al articles an attractive finishing.
Nature of Metallic Oxide
Basic Oxides of Metals
Some metallic oxides get dissolved in water and form alkalis. Their aqueous solution turns red litmus blue.
Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq)
K2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq)
Amphoteric Oxides
Metal oxides which react with both acids as well as bases to produce salts and water are called amphoteric oxides.
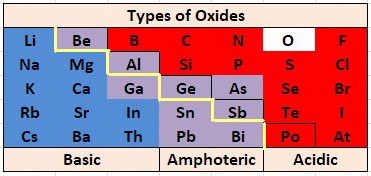
- Generally, metallic oxides are basic in nature except for aluminium and zinc oxides which are amphoteric in nature.
- That means these oxides react with the base as well as acid to form salt and water.
Examples:
(i) Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + H2O
(ii) Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
Sodium Aluminate
Reaction of Metals with Water
- Metal react with water and produce metal oxide and hydrogen gas.
- Metal oxides that are soluble in water dissolve in them to form metal hydroxide. But all metals do not react with water.
Metal + Water → Metal oxide + Hydrogen gas
Metal + Water → Metal Hydroxide
Metal oxide + Water → Metal hydroxide
Some oxide of metals dissolves in water and form alkalis.
Examples:
- 2Na + 2H2O(cold) → 2NaOH + H2 + heat
- Ca + 2H2O(cold) → Ca(OH)2 + H2
The following activity clears this reaction properly:
Activity
Procedure
Aim: To study the reactivity of metals with water & zincObservation
- Take the samples of common metals such as copper, iron, calcium, aluminium, sodium and potassium.
- Put a small amount of the samples separately in beakers that are half-filled with water.
- Sodium and Potassium calcium react with cold water. Sodium and Potassium react violently with cold water, making a hissing sound.
- These reactions are exothermic and evolved hydrogen gas which catches fire and leads to a little explosion.
- Calcium reacts less violently and the piece of calcium starts floating in water because the bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of the metal. Now put the metals which do not react with cold water in a beaker that is half-filled with hot water. Magnesium reacts rapidly with hot water. It also starts floating due to the bubbles of hydrogen sticking to its surface. [The rest samples of metals that do not react with cold and hot water, are made to react with steam].
- To study its reactivity with steam, to set up an experiment as shown in the figure below:
- A lump of wet glass wool is placed at the bottom of a boiling tube.
- Then place the metals samples in the middle of the horizontally kept boiling tube one by one.
- Now start at the bottom of a boiling tube with a help of a burner.
- The water present in glass wool forms steam on heating. This steam then passes over the metal.
- Observe that aluminium reacts with steam and iron does not react under ordinary conditions but it reacts only when steam is passed over a hot iron.
- Copper does not react with water either at ordinary temperature or at a higher temperature.
The following reaction occur in the above activity:
(i) Na and K metals react vigorously with cold water to form NaOH and H2 gas is liberated.
(ii)

This reaction is so violent and exothermic that the H2 gas evolved catches fire.
(iii) Calcium reacts with cold water to form Ca(OH)2 and H2 gas. It is less violent.

(iv) Aluminium does not react either with cold or hot water. But it reacts only with steam to form aluminium oxide and hydrogen gas.
(v) Similarly, Zinc reacts with steam to form zinc oxide and H2 gas.
(vi) Magnesium react with hot boiling water to form MgO and H2 gas.

(vii) Iron metal react when steam is passed over a red hot iron and form iron oxide and H2 gas.
(viii) Copper do not react even under strong conditions. Similarly, gold and silver also do not react with water. The above reactions indicate that sodium and potassium are the most reactive metals while copper is the least reactive.
Result: The reactivity order of these metals with water are
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn >Fe > Cu
Reactivity with water decreases.
(i) It does not react with water.
(ii) It reacts violently with water.
(iii) It reacts less violently with water.
(iv) Bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of calcium.
Reaction of Metals with Acids
The highly reactive metals react with dilute acid to displace hydrogen from acid. The reactivity of different metals is different with the same acid.
Metal + Dilute acid → Salt + Hydrogen
Aqua Regia (Royal Water)
Aqua regia is a Latin word it means "royal water". It is a freshly prepared mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid in the ratio of 3 : 1. It is a highly corrosive, fuming liquid and it used for dissolving gold and platinum.
Examples:
Metal+ dilute acid→ Salt + Hydrogen gas
- 2Na(s) + 2HCl(dilute)→ 2NaCl(aq) + H2(g)
- 2K(s)+ H2SO4(dilute)→ K2SO4(aq)+ H2(g) Only Mg and Mn, react with very dilute nitric acid to liberate hydrogen gas.
- Mg(s) + 2HNO3(dilute)→ Mg(NO3)2(aq) + H2(g)
- Mn(s) + 2HNO3(dilute)→ Mn(NO3)2(aq) + H2(g)
How do Metals react with Solutions of other Metal Salts?
- When a more reactive metal is placed in a salt solution of less reactive metal, then the more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal from its salt solution.
- This reaction is also known as displacement reaction.
- Metal A + Salt of metal B → Salt of metal A + Metal B
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq)→FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq)→Cu(NO3)(aq) + 2Ag(s)
Reaction of Metals with Non-metals
- Reactivity of elements is the tendency to attain a completely filled valence shell.
- Atoms of the metals lose electrons from their valence shell to form cation. Atom of the non-metals gain electrons in the valence shell to form anion.
E.g.: Formation of NaCl
Na → Na+ + e-
2, 8, 1 2, 8
Sodium cation
Cl + e- → Cl-
2, 8, 7 2, 8, 8
Ionic compounds
The compounds formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal are called ionic compounds or electrovalent compounds.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
(i) Physical nature: They are solid and hard, generally brittle.
(ii) Melting and Boiling Point: They have high melting and boiling point.
(iii) Solubility: Generally soluble in water and insoluble in solvents such as kerosene, petrol etc.
(iv) Conduction of electricity: Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten and solution form but not in solid state.
Activity
Aim
To compare the reactivity of the metals.
Procedure
- Take a clean wire of copper and an iron nail, two test tube.
- Now dissolve copper sulphate in water in one test tube and ferrous sulphate in another test tube.
- Place an iron nail in the blue coloured copper sulphate solution with the help of a thread and copper wire in the greenish colour ferrous sulphate solution as shown in the figure as below.
Observation
Conclusion
- The blue colour of copper sulphate has faded and becomes greenish. The green colour of the solution is due to the formation of iron (II) sulphate and copper is displaced.
- A reddish-brown coating is formed on the surface of iron nail. The reaction is represented by the chemical equation.
But the greenish colour of FeSO4 does not change. That means no reaction take place.
- These activities show that iron metal is more reactive than copper.
- Similarly, Reaction of copper with silver nitrate solution :
- When a strip of copper metal is placed in a solution of AgNO3. The solution becomes gradually blue and a shiny coating of silver metal gets deposited on the copper strip.
- The reaction may be written as:

- However, if we place the silver wire in a copper sulphate solution no reaction occurs. This means copper can displace silver from its salt solution but silver cannot displace copper from its solution. i.e. copper is a more reactive metal than silver.
Reaction of Metals with Bases
The base has a bitter taste and a slippery texture. A base dissolved in water is called an alkali. When chemically reacting with acids, such compounds produce salts. Bases are known to turn blue on red litmus paper.
When a base reacts with a metal, hydrogen gas is produced. It burns with a pop sound when a burning candle is brought near the test tube’s mouth.
Base + metal → salt + hydrogen
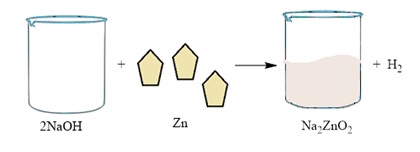
1. 2NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) → Na2ZnO2(aq) + H2(g)
Sodium hydroxide, as it reacts with zinc metal, gives hydrogen gas & sodium zincate.
2. 2NaOH(aq) + 2Al(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaAlO2(aq) + 2H2(g)
Sodium aluminate and hydrogen gas are formed when sodium hydroxide reacts with aluminium metal.
Summary
- The density of metals is usually high.
- Metals are malleable and ductile.
- Metals form an alloy with other metals or non – metals.
- Some metals react with air and corrode. For e.g. Iron.
- Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. Lead is an exception.
- Generally, metals are in a solid-state at room temperature. Except for Mercury. Mercury is in a liquid state.
- Many metals produce metal oxide by burning in the oxygen of the air. Highly reactive metals react violently when they’re burnt in oxygen.
- Metals like sodium and potassium are stored in oil as they react with air in seconds. They’re highly reactive metals.
- Less reactive metals like gold, silver, platinum, etc do not tarnish easily. They stay shiny and lustrous.
- Metals produce metal oxide and hydrogen gas while reacting with water.
- Soluble metal oxides dissolve in water and create metal hydroxide.
- Not all metals react with water. However, highly reactive metals like sodium and potassium react with water violently and an exothermic reaction takes places where the hydrogen immediately catches fire.
- Salt and hydrogen are produced when a metal reacts with an acid.
- Generally, a metal displaces a less reactive metal in a metal salt solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1: What is the composition of molten slag, formed in the extraction of iron in the blast furnace? What is the use of slag?
Ans: Molten slag in the extraction of iron is calcium silicate(CaSiO3). Slag is used for constructions of roads.
Q.2: How do you test ammonia gas?
Ans: Ammonia gas is tested, by showing a drop of conc. HCl by means of a glass rod to it, when dense white fumes of ammonium chloride are formed, which is a proof of ammonia gas.
Q.3: Why do some metals like, Na, K, Ca, Mg not occur in nature as free elements?
Ans: Metals like Na, K, etc (alkali metals) and Ca, Mg etc (alkaline earth metals) are very reactive and hence they react with atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide and also with other non-metals like sulphur present in the earth’s crust to form compounds like oxides, carbonates, sulphides, sulphates and chlorides. So they do not occur in free state, but are found in the form of the above compounds.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Chemical Properties of Metals - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the chemical properties of metals? |  |
| 2. How do metals react with oxygen? |  |
| 3. What happens when metals react with water? |  |
| 4. How do metals react with acids? |  |
| 5. How do metals react with bases? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|






























