Some Important Carbon Compounds – Ethanol And Ethanoic Acid | Science Class 10 PDF Download
In this document for Class 10 Science, specifically covering the chapter "Carbon and Its Compounds," we will explore the captivating realm of carbon compounds. Our focus will be on two compounds, ethanol and ethanoic acid, both of which hold great commercial value amongst many carbon compounds that benefit us in various ways.

What is Ethanol?
Ethanol, which is also called ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH), is part of a group of compounds known as alcohols. Specifically, it is the second member of the series of alcohols.
Preparation of Ethanol
Ethanol is prepared on a commercial scale by fermentation of sugar (molasses). Fermentation is allowed to take place at 298- 303 K in the absence of air. Ethanol (ethyl alcohol) gets oxidised to form ethanoic acid (acetic acid) in the presence of air.
Physical Properties of Ethanol
Here are some important physical properties of ethanol:- Physical state/colour and odour: Pure ethanol is a colourless liquid having a pleasant smell and a burning taste.
 Ethanol is a colurless liquid
Ethanol is a colurless liquid
- Boiling and Freezing points: It is a volatile liquid with a boiling point of 78.1°C, and a freezing point is 118°C.
- Density: Ethanol is lighter than water as its density is 0.79 g ml-1 at 293 K.
- Solubility: Ethanol is miscible with water in all proportions, due to the formation of hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Ethanol containing 5% water is called rectified spirit and containing 0% water is called absolute alcohol. - Conductivity: Ethanol is a covalent compound and does not ionise easily in water, hence it is a neutral compound.
- Action on Litmus: Ethanol is a neutral compound. So, it has no effect on the colour of litmus.
Chemical Properties of Ethanol
- Combustion (or burning):
Ethanol is a highly inflammable liquid and readily burns in air with a blue flame to form water vapour, carbon dioxide and evolving heat. Thus, the combustion of ethanol is an exothermic reaction.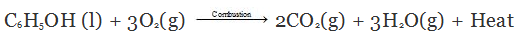
- Reaction with sodium metal:
Ethanol reacts with sodium metal to produce sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas is evolved.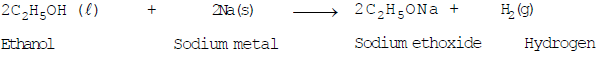
- Reaction with ethanoic acid (Esterification reaction):
The reaction in which alcohol reacts with acetic acid in the presence of conc. H2SO4 to form an ester is called esterification. Esters are sweet-smelling compounds and are used for making perfumes.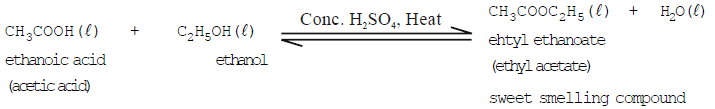
- Reaction with conc. sulphuric acid (Dehydration):
Ethanol when heated with excess of concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K, gets dehydrated to give ethene.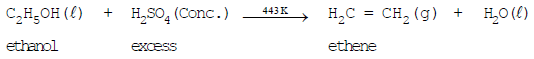
The concentrated sulphuric acid can be regarded as a dehydrating agent which removes water from ethanol.
What are the Uses and Examples of Ethanol?
Ethanol is a highly versatile substance with a wide range of uses. Here are some common examples:- Alcoholic Beverages: Ethanol is the main type of alcohol found in beer, wine, and spirits, which are consumed for social and recreational purposes.
 Ethanol in Paint
Ethanol in Paint - Fuel: Ethanol is used as a biofuel additive in gasoline. It is blended with gasoline to create ethanol fuel, which helps reduce emissions and promote renewable energy sources.
- Disinfectants and Sanitizers: Ethanol is a vital component in many disinfectant products and hand sanitizers. Its antimicrobial properties make it effective in killing germs and bacteria, contributing to hygiene and disease prevention.
Solvents: Ethanol is a versatile solvent used in various industries. It is commonly used in the production of paints, varnishes, perfumes, and pharmaceuticals, serving as a key ingredient in these manufacturing processes.
Extraction of Plant Oils: Ethanol is employed in extracting essential oils from plants. It helps dissolve and extract desired compounds from botanical materials, often utilized in the production of perfumes, flavors, and aromatherapy products.
Preservatives: Ethanol can act as a preservative in certain food and beverage products. It helps extend the shelf life by inhibiting the growth of microorganisms.
These examples represent just a few of the many practical applications of ethanol in our daily lives.
Harmful Effects of Alcohols
- Consumption of small quantities of dilute ethanol causes drunkenness. Even though this practice is condemned, it is a socially widespread practice. However, intake of even a small quantity of pure ethanol (called absolute alcohol) can be lethal. Also, long-term consumption of alcohol leads to many health problems.
- When large quantities of ethanol are consumed, it tends to slow metabolic processes and depress the central nervous system. This results in a lack of coordination, mental confusion, drowsiness, lowering of normal inhibitions and finally stupor (unconscious state of wild).
- Drinking alcohol over a long period damages the liver.
Denatured Alcohol
Ethanol to which certain poisonous and nauseating substances like methyl alcohol, pyridine, copper sulphate etc. have been added is termed denatured alcohol.
Note: To prevent the misuse of ethanol (Alcohol), industrial alcohol is coloured blue so that it can be recognised easily.
Harmful effects of denatured alcohol:
- Methanol is highly poisonous compound for human beings. Methanol when taken, even in small amounts, can cause death.
- Methanol gets oxidised to methanal in the liver, which causes coagulation of protoplasm.
- Methanol also affects the optic nerve and causes blindness.
What is Ethanoic Acid?
Ethanoic acid is commonly called acetic acid and belongs to the homologous series of carboxylic acid and is represented as CH3COOH. 5-8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar and is used for preserving foods like sausage, and pickles.
Physical Properties of Ethanoic Acid
- At ordinary temperatures, ethanoic acid is a colourless liquid with a strong pungent smell and sour taste.
- Its boiling point is 391 K and its density at 273 K is 1.08 (heavier than water).
- It is miscible with water due to the formation of hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
- On cooling at 289.6 K, it turns into ice-like crystals, hence named glacial acetic acid.
- It dissolves sulphur, iodine and many other organic compounds.
- It dimerises when dissolved in benzene.
Chemical Properties of Ethanoic Acid
- Reaction with alcohols (Esterification reaction):
Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of conc. H2SO4 to form ethyl ethanoate which is an ester.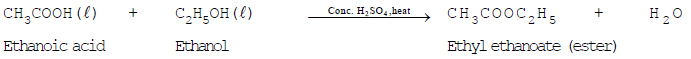
The reaction of carboxylic acid with an alcohol to form an ester is called "esterification reaction".
Note: Ester can be hydrolysed in the presence of an acid or a base to give back the parent carboxylic acid and the alcohol.
Example:
(i) Ethyl ethanoate on acid hydrolysis gives ethanoic acid and ethanol.
CH3COOC2H5(l) + H2O(l) → CH3COOH(aq.) + C2H5OH
(ii) Hydrolysis of ester in the presence of a base (alkali) is called "Saponification reaction".
Note: Alkaline hydrolysis of higher esters is used in the manufacture of soaps.
- Reaction with sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogen carbonate:
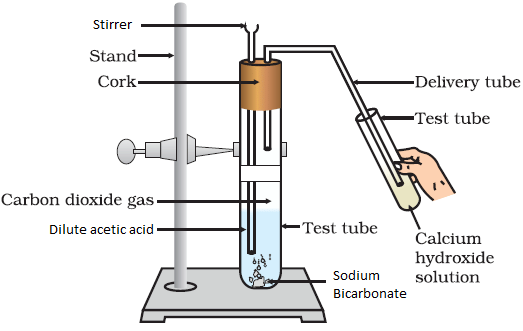 Reaction of Sodium Bicarbonate with Acetic Acid
Reaction of Sodium Bicarbonate with Acetic Acid - Ethanoic acid decomposes sodium hydrogen carbonate and sodium carbonate with a rapid evolution of carbon-dioxide gas.
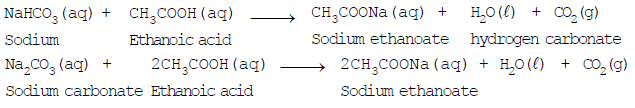
Note: Reactions of ethanoic acid with NaOH, NaHCO3, Na2CO3 and active metals show that the hydrogen present in the carboxyl (COOH) group is acidic in nature.
What are the Uses and Examples of Ethanoic Acid?
Ethanoic acid, also known as acetic acid, has various uses and examples in different industries and everyday life. Here are some common applications:

- Food Industry: Ethanoic acid is widely used in the food industry as a preservative, flavor enhancer, and acidulant. It is commonly found in salad dressings, pickles, condiments, and processed foods.
- Vinegar Production: Ethanoic acid is the main component of vinegar. It gives vinegar its characteristic sour taste and is used in culinary preparations, marinades, and dressings.
- Cleaning and Disinfecting: Ethanoic acid is an effective cleaning agent and disinfectant. It is commonly used for household cleaning tasks, such as removing grease and stains, and as a natural alternative to harsh chemicals.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Ethanoic acid serves as a key ingredient in the production of pharmaceuticals, including medicines, ointments, and topical creams.
- Textile Industry: Ethanoic acid is utilized in textile manufacturing processes, such as dyeing and finishing. It helps improve dye absorption, color fastness, and fabric softness.
- Chemical Synthesis: Ethanoic acid is a versatile compound used as a precursor in the synthesis of various chemicals, such as esters, solvents, and polymers.
- Laboratory Applications: Ethanoic acid is commonly used in laboratories as a reagent, solvent, and pH adjuster for experiments and analysis.
These are just a few examples of the many uses and applications of ethanoic acid in various industries and everyday products.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Some Important Carbon Compounds – Ethanol And Ethanoic Acid - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the chemical formula of ethanol and how is it commonly produced? |  |
| 2. What are the main physical properties of ethanol? |  |
| 3. What are the primary uses of ethanol in everyday life? |  |
| 4. What is the chemical structure of ethanoic acid and how is it related to ethanol? |  |
| 5. What are the common applications of ethanoic acid in industry and household products? |  |






















