Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Previous Year Questions - Carbon and its compounds
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: Carbon compounds:(i) are good conductors of electricity.
(ii) are bad conductors of electricity.
(iii) have strong forces of attraction between their molecules.
(iv) have weak forces of attraction between their molecules.
The correct statements are: (2024)
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (c)
The correct answer is (c) because carbon compounds generally do not conduct electricity well (bad conductors), and they have weak forces of attraction between their molecules, which means the molecules can move around easily. This explains why carbon compounds often exist as gases or liquids rather than solids.
Q2: (A) (i) Define a homologous series of carbon compounds.
(ii) Why is the melting and boiling points of C4H8 higher than that of C3H6 or C2H4?
(iii) Why do we NOT see any gradation in the chemical properties of homologous series compounds?
(iv) Write the name and structures of (i) aldehyde and (ii) ketone with molecular form C3H6O.
OR
(B) (i) Write the name and structure of an organic compound ‘X’ having two carbon atoms in its molecule and its name is suffixed with ‘-ol’.
(ii) What happens when ‘X’ is heated with excess concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K? Write the chemical equation for the reaction stating the conditions for the reaction. Also, state the role played by concentrated sulphuric acid in the reaction.
(iii) Name and draw the electron dot structure of the hydrocarbon produced in the above reaction. (2024)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (A) (i) A series of carbon compounds in which the same functional group substitutes for hydrogen in a carbon chain / Series of compounds having same functional group and similar chemical properties.
(ii) Because melting point and boiling point increase with molecular mass.
(iii) Because chemical properties of organic compounds are solely determined by their functional group which remains same in a homologous series.
(iv) (i) Aldehyde: Propanal
(ii) Ketone: Propanone
OR
(B) (i) Ethanol Structure: 
(ii) Ethene is formed
( Note: Deduct ½ mark if the conditions required are not mentioned in the equation)
Concentrated Sulphuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent.
(iii) Ethene
Q3: Consider the following statements about homologous series of carbon compounds :
(A) All succeeding members differ by — CH2 unit.
(B) Melting point and boiling point increases with increasing molecular mass.
(C) The difference in molecular masses between two successive members is 16 u.
(D) C2H2 and C3H4 are NOT the successive members of alkyne series.
The correct statements are — (2024)
(a) (A) and (B)
(b) (B) and (C)
(c) (A) and (C)
(d) (C) and (D)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a)
In a homologous series of carbon compounds, like alkanes or alkynes, each member differs from the next by a specific group of atoms (—CH2), which is explained in statement (A). As the size of the molecules increases (more carbon and hydrogen atoms), their melting and boiling points also generally increase, as stated in (B). Thus, both (A) and (B) are correct, making option (a) the right answer.
Q4: (a) (i) Give reason why carbon can neither form C4+ cations nor C4- anions but form covalent compounds.
(ii) What is homologous series of carbon compound? Write the molecular formula of any two consecutive members of homologous series of aldehydes.
(iii) Draw the structure of the molecule of cyclohexane (C6H12).
OR
(b) (i) Name a commercially important carbon compound having functional group —OH and write its molecular formula.
(ii) Write chemical equation to show its reaction with
(1) Sodium metal
(2) Excess cone, sulphuric acid
(3) Ethanoic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst
(4) Acidified potassium dichromate
Also write the name of the product formed in each case. (2024)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) (i) Carbon cannot form C4+ cations because removal of 4 electrons from a carbon atom would require a large amount of energy and it cannot form C4- anion because it would be difficult for the nucleus with 6 protons to hold 10 electrons.
Thus it shares electrons to form covalent compounds.
(ii) A series of compounds in which the same functional group substitutes for hydrogen in a carbon chain / series of compounds having same functional group and similar chemical properties.
CH3CHO, C2H5CHO (any other consecutive members)
(iii) Structure of cyclohexane (C6H12)
OR
(b) (i) Ethanol – C2H5OH
(ii)
NOTE: Name of the product for each reaction is given in bold letters under the reaction.
Q5: The structural formula of Cyclohexane is (CBSE 2024)
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (b)
The correct structural formula for cyclohexane is shown in option (b). Cyclohexane, C6H12 , is a cyclic hydrocarbon with a six-membered ring structure, where each carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms and two hydrogen atoms. This configuration ensures all carbon-carbon bonds are single, fitting the description and structure in option (b).
Q6: Which one of the following hydrocarbons is different from the others? (2024)
(a) C4H10
(b) C7H14
(c) C5H12
(d) C2H6
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (b)
The hydrocarbons C4H10 (butane), C5H12 (pentane), and C2H6 (ethane) are all alkanes, which are saturated hydrocarbons containing only single bonds. However, C7H14 is an alkene, which has at least one double bond. Therefore, option (b) is different from the others.
Q7: More than three million carbon compounds have been discovered in the field of chemistry. The diversity of these compounds is due to the capacity of carbon atoms for bonding with one another as well as with other atoms. Most of the carbon compounds are poor conductors of electricity and have low melting and boiling points.
(a) Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group —Br.
(b) Given below are the formulae of some functional groups :

Write the name of these functional groups.
(c) What would be observed on adding a 5% alkaline potassium permanganate drop by drop to some warm ethanol taken in a test tube? State the role of KMn04 in the reaction and write the chemical equation for the reaction involved.
OR
(c) Write the name of the compound formed when ethanol is heated at 443 K temperature with excess of cone. H2S04. What is the role of cone. H2S04 in the reaction? Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved. (2024)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) CH3Br
C2H5Br
(b) (i) Aldehyde (ii) Ketone
(c) The colour of KMnO4 disappears;
KMnO4 acts as an oxidizing agent.
OR
(c) Ethene Conc. H2SO4 acts as a dehydrating agent.
Q8: The number of single and double bonds present in a molecule of benzene (C6H6) respectively, are: (2024)
(a) 6 and 6
(b) 9 and 3
(c) 3 and 9
(d) 3 and 3
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (b)
Benzene (C6H6) has a unique structure with alternating single and double bonds between its carbon atoms, often represented as a hexagon with a circle in the center. In this structure, there are 3 actual double bonds and the remaining 3 bonds are single bonds, but due to resonance, it’s commonly shown as having 3 double bonds and 3 single bonds. So, the correct answer is (d) 3 and 3. It seems the answer you provided is incorrect.
Q9: The melting and boiling points of carbon compounds are generally low and they are largely non-conductors of electricity. State two conclusions based on these two properties. (2024)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns:
(i) Low melting points and boiling points - Weak intermolecular forces of attraction.
(ii) Non-conductors of electricity - Bonding in these compounds does not give rise to any ions. / Covalent bonds or sharing of electrons do not form any charged particles.
Q10: Case-based/data-based questions with 3 short sub-parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Carbon is a versatile element that forms the basis of all living organisms and many of the things we use. A large variety of compounds is formed because of its tetravalency. Compounds of carbon are formed with oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine and many other elements.
Answer the following questions:
(a) What are hydrocarbons?
(b) List two properties by virtue of which carbon can form a large number of compounds.
(c) (i) Write the formula of the functional group present in
(1) aldehydes, and (2) ketones. Write chemical equation for the reaction that occurs between ethanoic acid and ethanol in the presence of a catalyst.
OR
(c) (ii) What are structural isomers ? Write the structures of two isomers of butane (C4H10). (2024)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) Compounds formed by carbon and hydrogen only.
(b) Tetravalency and Catenation
(c) (i)

(c) (ii) Compounds with identical molecular formula but different structures
Two isomers of butane C4H10
Q11: Distinguish between a saturated and an unsaturated hydrocarbon by flame test. List the products of combustion reaction of a saturated hydrocarbon. (2024)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Carbon dioxide; Water
Carbon dioxide; Water
Q12: Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction? Name the oxidising agent used in this conversion. Write chemical equation for this oxidation reaction. How is this reaction different from the reaction in which ethanol burns in the presence of oxygen? (2024)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns:
(i) Oxygen is added to ethanol to produce ethanoic acid.
(ii) Alkaline potassium permanganate or Acidified potassium dichromate
(iii)
(iv) It is oxidation reaction while other is combustion reaction/ burning of ethanol is exothermic while other is endothermic.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q1: Explain why carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bonds. Explain in brief two main reasons for carbon forming a large number of compounds. Why does carbon form strong bonds with most other elements? (2023) View Answer
View AnswerAns: As carbon has four valence electrons and it can neither loose nor gain four electrons thus, it attains noble gas configuration only by sharing of electrons. Thus, it forms covalent compounds. The existence of large number of compounds is due to some unique properties of carbon which are:
(i) Carbon atoms possess an unique property to link together to form very long chains. This property is referred to as catenation.
A large number of carbon atoms can join together to form straight chains, branched chains and rings as shown below: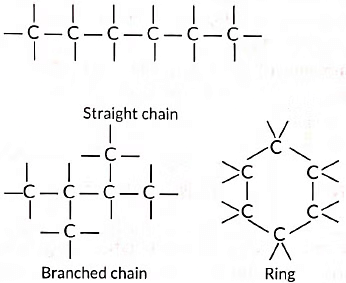
(ii) Due to small size and presence of four valence electrons, a carbon atom can form multiple bonds with some other carbon atoms as well as with other atoms like oxygen, nitrogen etc., This increases the variety of compounds formed by it and hence the number of compounds is tremendously increased. Due to small size, the nucleus of carbon atom can hold its shared pairs of electrons strongly. As a result, the bonds that carbon forms with most of the other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc. are very strong there by making these compounds exceptionally stable.
Due to small size, the nucleus of carbon atom can hold its shared pairs of electrons strongly. As a result, the bonds that carbon forms with most of the other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc. are very strong there by making these compounds exceptionally stable.
Q2: (i) Draw two structural isomers of butane.
(ii) Draw the structures of propanol and propanone.
(iii) Name the third homologue of:
(a) alcohols
(b) aldehydes
(iv) Name the following:
(b) CH3 - CH2CH = CH2
(v) Show the covalent bond formation in nitrogen molecule. (2023)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (i) Structural isomers of butane are the following:

(iii) (a) Three homologue of alcohol are the following:CH3OH, CH3CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2OH
Third homologue of alcohol is CH3CH2CH2OH
(b) Three homologue of aldehyde are the following:
HCHO, CH3CHO, CH3CH,CHO
Third homologue of aldehyde is CH3CH2CHO.
(iv) (a) Benzene (b) But-1-ene
(v) Z = 7, 

Q3: Write the chemical equation for the following:
(i) Combustion of methane
(ii) Oxidation of ethan
(iii) Hydrogenation of ethene
(iv) Esterification reaction
(v) Saponification reaction (2023)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (i) The process in which compounds of carbon react with oxygen to give carbon dioxide, water, heat and light, is known as combustion. Alkanes burn in air and release large amount of heat, therefore can be used as excellent fuels.
(ii) Oxidation is a process in which oxygen is added to a substance.
(iii) Hydrogenation means addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated compound.
(iv) When alcohol is added to carboxylic acid in the presence of acid catalyst then, a fruity smelling ester is formed. This process is called esterification.
(v) Esters react in the presence of an acid or a base to give the alcohol and carboxylic acid. This reaction is known as saponification because it is used in the preparation of soap.
Q4: Consider the structures of the three cyclic carbon compounds (I), (II) and (III) given below and select the correct option from the following: 
(a) (I) and (III) are isomers of hexane and (II) is benzene.
(b) (I) is an isomer of hexane, (II) is benzene and (III) is an isomer of hexene.
(c) (I) is a saturated cyclic hydrocarbon and (II) and (III) are unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons.
(d) (I) is cyclohexane and (II) and (III) are the isomers of benzene. (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (c)
Structure (I) is cyclohexane, a saturated cyclic hydrocarbon with single bonds between all the carbon atoms.
Structure (II) is benzene, an unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon with alternating double bonds, giving it aromatic stability.
Structure (III) is cyclohexene, an unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon with one double bond.
Thus, (I) is a saturated cyclic hydrocarbon, and (II) and (III) are unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons, making (c) the correct answer.
Q5: A saturated organic compound ‘A’ belongs to the homologous series of alcohols. On heating ‘A’ with concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K, it forms an unsaturated compound ‘B’ with molecular mass 28 u. The compound ‘B’ on addition of one mole of hydrogen in the presence of Nickel, changes to a saturated hydrocarbon ‘C’.
(A) Identify A, B and C.
(B) Write the chemical equations showing the conversion of A into B.
(C) What happens when compound C undergoes combustion?
(D) State one industrial application of hydrogenation reaction.
(E) Name the products formed when compound A reacts with sodium. (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (A) Ethanol (C2H5OH) belongs to alcohol's homologous series.
A- Ethanol (C2H5OH)
B- Ethene (C2H4)
C- Ethane (C2H6)
(B) Dehydration occurs when ethanol is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K, resulting in the formation of ethene Concentrated sulphuric acid serves as a dehydrating agent in this reaction. (C) Compound C is ethane. When it undergoes combustion, it forms CO2 and water.
(C) Compound C is ethane. When it undergoes combustion, it forms CO2 and water. (D) Hydrogenation reactions are used in the production of saturated vegetable ghee from unsaturated vegetable oils.
(D) Hydrogenation reactions are used in the production of saturated vegetable ghee from unsaturated vegetable oils.
(E) Sodium ethoxide is formed when ethanol (C2H5OH) reacts with sodium (Na). The reaction is as follows:
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q1: Carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bonding. Why ? (Term II, 2021-22 C) View Answer
View AnswerAns: Carbon can form only covalent compounds because carbon can neither gain nor lose four electrons to acquire stable octet. The only way by which it can acquire the nearest noble gas configuration is by sharing its valence electrons with other C-atoms or atoms of other elements. Hence, carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bonding.
Q2: (a) Write the molecular formula of the following carbon compounds :
(i) Methane
(ii) Propane
(b) Carbon compounds have low melting and boiling points. Why? (Term II, 2021-22)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) (i) Methane (CH4)
(ii) Propane (CH3CH2CH3) or C3H8
(b) Due to weak intermolecular forces of attraction, covalent compounds generally have low melting and boiling points.
Q3: Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points. Why? (2022)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points because the forces of attraction between molecules of covalent compounds are very weak. On applying a small amount of heat these molecular forces break.
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q1: Write the name of an allotrope of carbon. (2021C) View Answer
View AnswerAns: Diamond
Q2: "Carbon prefers to share its valence electrons with other atoms of carbon or with atoms of other elements rather than gaining or losing the valence electrons in order to attain noble gas configuration.” Give reasons to justify this statement. (Term II, 2021)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Carbon has atomic number 6 with four electrons in the valence shell. If it gains four electrons in order to complete its octet, it will lead to the formation of C4- anion. The addition of four electrons in valence shell j will result in strong electronic repulsions between eight I electrons now present in valence shell. Hence, it will be : difficult for the nucleus to hold on to ten electrons. On the other hand, if it loses four electrons, it forms C4+ cation. It would require a large amount of energy to remove four electrons. Hence, carbon prefers to share its valence electrons with other atoms of carbon to attain noble gas configuration. The bond formed is known as covalent bond.
Q3: Draw the electron dot structure of the molecules of (a) Oxygen, and (b) Nitrogen. The atomic numbers of oxygen and nitrogen are 8 and 7 respectively. (Term II, 2021-22 C)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) Formation of oxygen molecule:
(b) Formation of nitrogen molecule:
Q4: Carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bonding. Why? (Term II, 2021-22 C)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Carbon can form only covalent compounds because carbon can neither gain nor lose four electrons to acquire stable octet. The only way by which it can acquire the nearest noble gas configuration is by sharing its valence electrons with other C-atoms or atoms of other elements. Hence, carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bonding.
Q5: State the reason why
(i) carbon compounds have low melting and boiling points.
(ii) carbon compounds do not conduct electricity.
(iii) carbon can form only covalent compounds. (Term II, 2021-22)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (i) Due to weak intermolecular forces of attraction, carbon compounds generally have low melting and boiling points.
(ii) Carbon compounds do not contain ions and hence, are generally poor conductors of electricity.
(iii) Carbon can form only covalent compounds because carbon can neither gain nor lose four electrons to acquire stable octet. The only way by which it can acquire the nearest noble gas configuration is by sharing its valence electrons with other C-atoms or atoms of other elements.
Q6: (a) Draw the electron dot structure for ethyne. (Term II, 2021-22)
(b) List two differences between the properties exhibited by covalent compounds and ionic compounds.
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: 
(b) 
Q7: (a) Write the molecular formula of the following carbon compounds:
(i) Methane
(ii) Propane
(b) Carbon compounds have low melting and boiling points. Why? (Term II, 2021-22)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) (i) Methane (CH4)
(ii) Propane (CH3CH2CH3) or C3H8
(b) Due to weak intermolecular forces of attraction, covalent compounds generally have low melting and boiling points.
Q8: Consider the carbon compounds having following molecular formula:
(i) C3H6
(ii) C3H8
(iii) C4H6
(iv) C6H6
(v) C6H12
(a) State the number of double covalent bonds present in C3H6.
(b) Write the formula of first member of the homologous series to which the carbon compound C4H6 belongs.
(c) Which one of the above compounds forms ring structure of carbon atoms?
(d) Identify, which of the above compounds, is a member of alkane series. (Term II, 2021-22)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) C3H6(or CnH2n, n = 3) i.e, alkene series thus, has one double covalent bond.
(b) C4H6 (or CnH2n-2, n = 4) i.e., alkyne series.
The first member of alkyne series is ethyne (C2H2) HC ≡ CH.
(c) C6H12 can form ring structure of C-atoms.
(d) Alkane series: Cn H2n+2
Only C3H8 is a member of alkane series CH3 — CH2 — CH3
Q9: The molecular formulae of two alkynes, A and B are CxH2 and C3Hy respectively.
(a) Find the values of x and y.
(b) Write the names of A and B. (Term II, 2021-22)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) General formula of alkyne CnH2n - 2
For CxH2, 2n - 2 = 2 ⇒ n = 2 ∴ x = 2.
For C3Hy, n = 3, y = 2n - 2 = 2 x 3 - 2 = 4
Hence, x = 2, y = 4
(b) A is ethyne (C2H2) and B is propyne (C3H4).
Q10: What is a homologous series? Find the difference in molecular mass between the two consecutive members of a homologous series. State how in a homologous series of carbon compounds the following properties vary with increase in molecular mass: (Term II, 2021-22)
(i) Melting and boiling points
(ii) Chemical properties
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: A homologous series is the family of organic compounds having the same functional group, similar chemical properties but the successive (adjacent members of the series differ by a —CH2 unit or 14 mas units.
(i) As the molecular mass increases in a homologous series, melting and boiling points also increases.
(ii) Chemical properties remains same for the members of homologous series because they all have same functional group.
Q11: Draw two different possible structures of a saturated hydrocarbon having four carbon atoms in its molecule. What are these two structures of the hydrocarbon having same molecular formula called? Write the molecular formula and the common name of this compound. Also write the molecular formula of its alkyne. (Term II, 2021-22)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: 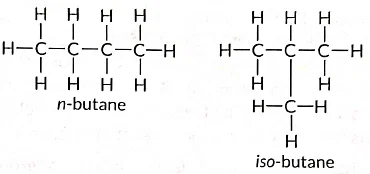
These are called structural isomers as they have the same j molecular formula i.e., C4H10 but different structures. As i the molecular formula is C4H10, common name of this | compound is butane. i The alkyne of four carbon atoms is butyne. Its structure i is as follows:
The molecular formula of butyne is C4H6.
Q12: (i) Write the molecular formula of benzene and draw its structure.
(ii) Write the number of single and double covalent bonds present in a molecule of benzene.
(iii) Which compounds are called alkynes? (Term II, 2021-22)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (i) Molecular formula of benzene is C6H6.
(ii) Number of single bonds = 9
Number of double bonds = 3
(iii) Alkynes are the unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one triple bond between two carbon atoms (—C ≡ C—)
Q13: Consider the following organic compounds:
(i) 
(a) Name the functional group present in these compounds.(b) Write the general formula for the compounds of this functional group.
(c) State the relationship between these compounds and draw the structure of any other compound having similar functional group (Term II, 2021-22)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) Aldehyde (—CHO) group.
(b) CnH2nO
(c) Compound (i) is propanal, and compound (ii) is ethanal. They belong to the same homologous series where each successive compound differs from each other by a—CH2 unit.
Other member of same homologous series:
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q1: How are covalent bonds formed? (2020) View Answer
View AnswerAns: Covalent bonds are formed by sharing of electron pair between two atoms. Covalently bonded molecules are observed to have stronger bonds within the molecule but intermolecular forces are weak.
Q2: Covalent compounds are generally poor conductors of electricity. Why? (2020)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Covalent compounds do not contain ions and hence, are generally poor conductors of electricity.
Q3: Name a cyclic unsaturated carbon compound. (2020)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: A cyclic unsaturated carbon compound is a compound that contains a carbon ring with one or more double or triple bonds between the carbon atoms. An example of a cyclic unsaturated carbon compound is benzene, which has a ring of six carbon atoms with alternating double bonds.
Q4: Carbon, a member of group 14, forms a large number of carbon compounds estimated to be about three million. Why is this property not exhibited by other elements of this group? Explain. (2020)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation. Carbon shows catenation due to its small size and stronger carbon-carbon bond strength. As we move down the group, the element-element bond energies decrease rapidly. For this reason, other elements of this group show little or no catenation property.
Q5: 3 mL of ethanol is taken in a test tube and warmed gently in a water bath. A 5% solution of alkaline potassium permanganate is added first drop by drop to this solution, then in excess.
(i) How is 5% solution of KMnO4 prepared?
(ii) State the role of alkaline potassium permanganate in this reaction. What happens on adding it in excess?
(iii) Write chemical equation of this reaction. (2020)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (i) 5% solution of KMnO4 is prepared by adding 5 g of KMnO4 in 95 g of water.
(ii) Here alkaline KMnO4 acts as an oxidising agent. It oxidises ethanol to ethanoic acid by donating nascent oxygen. If excess of KMnO4 is added the purple colour will persist indicating no more alcohol is left and reaction stops.
(iii) 
Q6: (a) Define isomerism. Draw all possible isomers of butane.
(b) "A compound ‘X’ on combustion gives a yellow flame with lots of smoke.” What inference would you draw from this statement ?
(c) State the role of alkaline KMnO4 in the reaction involving conversion of an alcohol to corresponding carboxylic acid. (2020)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) Isomers are those molecules which have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae i.e., show different properties and the phenomenon is called isomerism. The structures of possible isomers of butane (C4H10) are: (b) The compound 'X’ is an unsaturated compound (alkene or alkyne) which burn in air with a yellow sooty flame (producing black smoke).
(b) The compound 'X’ is an unsaturated compound (alkene or alkyne) which burn in air with a yellow sooty flame (producing black smoke).
(c) Alkaline KMnO4 acts as an oxidising agent which oxidise alcohol (—OH) to corresponding carboxylic acid (—COOH).
Q7: (a) What is a homologous series? Explain with an example.
(b) Define the following terms giving one example of each.
(i) Esterification
(ii) Addition reaction (2020)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) A homologous series is the family of organic compounds having the same functional group, similar chemical properties but the successive (adjacent) members of the series differ by a —CH2 unit or 14 mass units.
For example, alkane series has general formula CnH2n + 2.
First member of homologous series of alkane is methane, i.e., CH4.
Second member of homologous series of alkane is ethane, i.e., C2H6.
Third member of homologous series of alkane is propane i.e., C3H8.
(b) (i) Carboxylic acids react with alcohols in the presence of a little concentrated sulphuric acid to form pleasant smelling esters. This reaction is called esterification reaction.
(ii) Those reactions in which atoms or group of atoms are simply added to a double or triple bond without the elimination of any atom or molecule, are known as addition reactions.
Q8: (a) Carry out following conversions:
(i) Ethanol to ethene
(ii) Ethanol to ethanoic acid
(b) Differentiate between addition reaction and substitution reaction. Give one example of each. (2020)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) (i) When ethanol is heated with cone. H2SO4 at 443 K, ethene is obtained due to dehydration of ethanol.
(ii) When 5 % alkaline KMn04 solution is added drop by drop to warm ethanol then it gets oxidised to ethanoic acid.
(b) Addition reactions: Those reactions in which atoms or group of atoms are simply added to a double or triple bond without the elimination of any atom or molecule, are known as addition reactions.
Substitution reactions: The reactions which involve the displacement or substitution of an atom or a group of atoms in an organic compound by another atom or group of atoms, are known as substitution reactions. Saturated hydrocarbons are fairly unreactive and inert in the presence of most of the reagents. However, in presence of sunlight, hydrocarbons undergo rapid substitution reactions. e.g.,
Q9: (a) A compound 'X' undergoes addition reaction with H2 to form a compound Y having molecular mass 30 g mol-1. ‘X’ decolorises bromine water and burns with a smoky flame. Identify ‘X’ and Y and write chemical equations of the reactions involved.
(b) Write the structural formulae of (i) Butanone, and (ii) Pentanoic acid.
(c) Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent ? Give reason to justify your answer. (2020 C)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) As the molecular mass of Y is 30 g mol-1, it is ethane (C2H6 = 12 x 2 + 6 x 1 = 30).
‘X’ is ethene (CH2 = CH2) which decolourises Br2- water and burns with a smoky flam.


(c) No. we are not able to check if water is hard by using a detergent as detergent works well in hard water as well. This is because calcium and magnesium salts of detergents are soluble in water and hence, detergents can be used for washing even in hard water.
Q10: Assertion(A): Esterification is a process in which a sweet smelling substance is produced.
Reason (R): When esters react with sodium hydroxide an alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid are obtained.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (b)
Assertion (A): Esterification is a process in which a sweet-smelling substance is produced. This is true. Esterification is a chemical reaction between an acid (usually a carboxylic acid) and an alcohol, resulting in the formation of an ester, which typically has a fruity or sweet smell.
Reason (R): When esters react with sodium hydroxide, an alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid are obtained. This is also true. This reaction is known as saponification, where an ester reacts with a strong base to produce an alcohol and the salt of a carboxylic acid.
Since both statements are true, but the reason does not explain the assertion (as esterification and saponification are different processes), the correct answer is (b) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Q11: Assertion(A): Carbon has a strong tendency to either lose or gain electrons to attain noble gas configuration.
Reason (R): Carbon has four electrons in its outermost shell and has the tendency to share electrons with carbon or other elements.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (d)
Assertion (A): Carbon has a strong tendency to either lose or gain electrons to attain noble gas configuration. This is false. Carbon does not lose or gain electrons easily because that would require a lot of energy. Instead, it tends to share electrons.
Reason (R): Carbon has four electrons in its outermost shell and has the tendency to share electrons with carbon or other elements. This is true. Carbon typically forms covalent bonds by sharing electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Since the assertion is false but the reason is true, the correct answer is (d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
Q12: Which oils should be chosen for cooking to remain healthy? (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Oils containing unsaturated fatty acids should be chosen for cooking to remain healthy while animal fats generally contain saturated fats which are harmful for health.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q1: What is a homologous series of carbon compounds? Give an example and list its three characteristics. (2019) View Answer
View AnswerAns: A homologous series is defined as a group of compounds having the same functional group, similar chemical properties in which the successive members differ by a -CH2 group or 14 mass unit.
For example, in alkane homologous series, the general formula is CnH2n+2 i.e.; first three members are CH4. C2H6 and C3H8 where two successive members differ by -CH2 group.
Characteristics of homologous series:
- All compounds in the series can be represented by a general formula, e.g., for alcohol it is CnH2n+1OH, for alkane CnH2n+2, for alkene CnH2n and for alkynes CnH2n-2, where, n = 1, 2, 3.....
- All compounds in the series have similar chemical properties.
- All members of the series, show a gradual change in their physical properties.
- Physical properties generally increase as the molecular mass increases.
Q2: What happens when 5% alkaline potassium permanganate solution is added drop by drop to warm propyl alcohol (propanol) taken in a test tube? Explain with the help of a chemical equation. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: When 5% alkaline potassium permanganate solution is added drop by drop to a solution of warm propyl alcohol or propanol, it gets oxidised to propanoic acid. Here, alkaline potassium permanganate solution is the oxidising agent. Equation of the reaction taking place is:
Q3: The formulae of four organic compounds are given as following:

(A) Which one of these compounds P, Q, R or S is a saturated hydrocarbon?
(B) Identify the organic acid and give its structural formula. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (A) S is a saturated hydrocarbon.
(B) Q is an organic acid.
Structural formula:
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q1: A compound 'X' on heating with excess conc. sulphuric acid at 443 K gives an unsaturated compound 'Y'. 'X' also reacts with sodium metal to evolve a colourless gas 'Z'. Identify 'X', 'Y and 'Z. Write the equation of the chemical reaction of formation of 'Y' and also write the role of sulphuric acid in the reaction. (2018) View Answer
View AnswerAns: As X reacts with conc. H2SO4 to give an alkene so it should be an alcohol as cone. H2SO4 acts as a dehydrating agent. The reaction of X with Na also confirms that it is an alcohol because alcohols react with Na metal to evolve colourless hydrogen gas.
Here, cone H2SO4 acts as a dehydrating agent i.e., helps in the removal of water.
Q2: (a) Why are most carbon compounds poor conductors of electricity?
(b) Write the name and structure of a saturated compound in which the carbon atoms are arranged in a ring. Give the number of single bonds present in this compound. (2018)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) Due to catenation, carbon forms covalent bonds with the constituent elements in the carbon compounds, hence it does not have mobile electrons and carbon compounds do not dissociate themselves into ions and hence, they are poor conductor of electricity.
(b) Structure:
Name: Cyclopentane
Number of single bonds: 15
Q3: (a) Compare soaps and detergents on the basis of their composition and cleansing action in hard water.
(b) What happens when ethanol is treated with sodium metal? State about the behaviour of ethanol in this reaction.
(c) Draw the structure of cyclohexane.
(d) Name the following compound. (2018)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a)
(b) when ethanol is treated with sodium metal observation received are-
Hydrogen gas is evolved and it behaves like an acid.
(c) structure of cyclohexane is below-
(d) Name of the compound is Ethanal and it is an Acetaldehyde
Q4: A gas is evolved when ethanol reacts with sodium. Name the gas evolved and also write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved. (CBSE 2018, 16)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: When ethanol reacts with sodium metal, it forms sodium ethoxide (C2H5O– Na+) and hydrogen gas is released. The reaction is as follows: So, the gas is hydrogen that is evolved during the reaction.
So, the gas is hydrogen that is evolved during the reaction.
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q1: Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group -CI. (Delhi 2017)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: The molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having - Cl functional group are CH3CI and CH3CH2CI.
Q2: Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group -OH. (Delhi 2017)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: The molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having - OH functional group are CH3OH and CH3CH2OH.
Q3: Write the molecular formula of the 2nd and 3rd member of the homologous series whose first member is ethene. (AI 2017)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Homologous series of alkenes have general formula, CnH2n whose first member is ethene.
2nd member of homologous series of alkenes is C3H6 i.e., propene.
3rd member of homologous series of alkenes is C4H8 i.e., butene.
Q4: Write the molecular formula of the 2nd and 3rd member of the homologous series whose first member is methane. (AI 2017)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Methane, CH4 is an alkane. Alkanes have general formula, CnH2n+2.
2nd member of homologous series of alkanes is C2H6 i.e., ethane.
3rd member of homologous series of alkanes is C3H8 i.e., propane.
Q5: Two carbon compounds X and Y have the molecular formula C4H8 and C5H12 respectively. Which one of these is most likely to show addition reaction? Justify your answer. Also give the chemical equation to explain the process of addition reaction in this case. (Delhi 2017)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: All unsaturated hydrocarbons (containing double or triple bonds) have tendency to get converted to saturated hydrocarbons (single bonds) by adding small molecules such as hydrogen (H2), halogens (X2), etc. Such reactions are called addition reactions. Compound with the molecular formula C4H8 belongs to alkene series (CnH2n). Hence, it will undergo addition reaction.
Q6: Soaps and detergents are both types of salts. State the difference between the two. Write the mechanism of the cleansing action of soaps. Why do soaps not form lather (foam) with hard water? Mention any two problems that arise due to the use of detergents instead of soaps. (Delhi 2017, Al 2015)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: The molecules of soap are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. Detergents are generally ammonium or sulphonate salts of long chain carboxylic acids.
Difference between Soap and Detergent
Soaps:
(i) Soaps are sodium salts of long chain carboxylic acids.
(ii) The ionic group in soap is -COO-Na+.
(iii) Soaps are not useful when water is hard.
Detergents
(i) Detergents are the odium salt of long chain benzene sulphonic acids.
(ii) The ionic groups in detergents is SO3-Na+ or SO4-Na+.
(iii) Detergent can be used for washing purpose even when water is hard
Cleansing action of soap can be described as follows:
The soap molecule is generally represented as RCOONa. In solution, it ionises to form RCOO- and Na+. Each soap molecule has a polar head group (carboxylate ion, COO- group) and a long nonpolar hydrocarbon tail (R group from long chain fatty acid). The polar head attracts the polar water molecule and is called hydrophilic end and the nonpolar tail attracts the water-insoluble oily or greasy dirt particles.
Q7: Why are certain compounds called hydrocarbons? Write the general formula for homologous series of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes and also draw the structure of the first member of each series. Write the name of the reaction that converts alkenes into alkanes and also write a chemical equation to show the necessary conditions for the reaction to occur. (AI 2017)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons.
(a) Saturated hydrocarbons: Alkanes (CnH2n+2) are the compounds of carbon that have a single bond.
(b) Unsaturated hydrocarbons: The compounds of carbon having double bonds are alkene (CnH2n) and having triple bonds are alkyne (CnH2n-2). The reaction which converts unsaturated hydrocarbons to saturated hydrocarbons i.e. alkenes to alkane is known as hydrogenation reaction. It is used to obtain ghee from oil.
Q8: A student took four test tubes P, Q, R and S and filled about 8 mL of distilled water in each. After that he dissolved an equal amount of Na2SO4 in P, K2SO4 in Q, CaSO4 in R and MgSO4 in S. On adding an equal amount of soap solution and shaking each test tube well, a good amount of lather will be obtained in the test tubes:
(a) P and Q
(b) P and R
(c) P, Q and S
(d) Q, R and S
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a)
Soap forms lather easily in soft water, while hard water (which contains calcium and magnesium ions) reacts with soap to form scum, preventing the formation of lather.
In this case:
(i) Test tube P contains Na₂SO₄ (sodium sulfate), and Test tube Q contains K₂SO₄ (potassium sulfate). Both sodium and potassium salts do not contribute to water hardness, so they will allow soap to form lather.
(ii) Test tube R contains CaSO₄ (calcium sulfate), and Test tube S contains MgSO₄ (magnesium sulfate). Both calcium and magnesium contribute to water hardness, which prevents lather formation.
Therefore, a good amount of lather will be obtained in test tubes P and Q.
Q9: A student is given equal amount of three samples of water with temporary hardness labelled as ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’. He keeps the three samples at different temperatures – A at room temperature, B at 50 ºC and C at 95 ºC. Which sample will give maximum amount of lather when 10 mL of soap solution is added to each sample and shaken for equal time?
(a) A only
(b) Both A and B
(c) Both B and C
(d) C only (CBSE 2017)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (d)
In this scenario:
- Sample C is kept at 95 ºC, which is close to boiling temperature. At this high temperature, the temporary hardness will be significantly reduced due to the decomposition of bicarbonates, allowing more lather to form when soap is added.
- Samples A (at room temperature) and B (at 50 ºC) will still retain more temporary hardness than sample C, and therefore will produce less lather.
Thus, sample C will give the maximum amount of lather, making the correct answer (d) C only.
Q10: What is a saturated hydrocarbon? Write the formula of any one saturated hydrocarbon. (CBSE 2017)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: A saturated hydrocarbon is a hydrocarbon in which the carbon atoms have only single covalent bonds between them. Formula of any one saturated hydrocarbon is CH4.
Q11: Ethanol reacts with sodium and forms two products. These are:
(a) sodium ethanoate and hydrogen
(b) sodium ethanoate and oxygen
(c) sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
(d) sodium ethoxide and oxygen (CBSE 2017, 16, 14, 11)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (c)
When ethanol (C₂H₅OH) reacts with sodium (Na), it forms sodium ethoxide (C₂H₅ONa) and hydrogen gas (H₂) as products. The reaction is as follows: In this reaction, sodium displaces hydrogen from ethanol, resulting in the formation of sodium ethoxide and the release of hydrogen gas.
In this reaction, sodium displaces hydrogen from ethanol, resulting in the formation of sodium ethoxide and the release of hydrogen gas.
Thus, the correct answer is (c) sodium ethoxide and hydrogen.
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q1: Write the next homologue of each of the following: (Delhi 2016)
(i) C2H4
(ii) C4H6
 View Answer
View AnswerAns. (i) C2H4 belongs to alkene series having general formula, CnH2n.
Thus, next homologue will be C3H2x3 = C3H6
(ii) C4H6 belongs to alkyne series having general formula, CnH2n-2.
Thus, next homologue will be C5H2x5-2 = C5H8
Q2: Name the following compounds: (Delhi 2016)
(a) CH3—CH2—OH
(b) 
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a) CH3 - CH2 - OH: Ethanol (Alcohol)
(b) 
Q3: Select saturated hydrocarbons from the following: (Delhi 2016)
C3H6; C5H10; C4H10; C6H14; C2H4
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes) have general formula, CnH2n+2. Among the given compounds, only C4H10 and C6H14 satisfy the above formula. Thus, these are saturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbons have the general formula CnH2n (alkene) and CnH2n-2 (alkyne).
Q4: Write the name and structure of an alcohol with three carbon atoms in its molecule. (Al 2016)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: An alcohol with three carbon atoms in its molecule is propanol. The structure of propanol is
Q5: Write the name and structure of an alcohol with four carbon atoms in its molecule. (AI 2016)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: An alcohol with four carbon atoms is butanol and its structure is:
Q6: Write the name and structure of an aldehyde with four carbon atoms in its molecule. (AI 2016)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: An aldehyde with four carbon atoms is butanal and its structure is:
Q7: Which element exhibits the property of catenation to maximum extent and why? (Foreign 2016)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation. Carbon shows catenation due to its small size and stronger carbon-carbon bond strength.
Q8: Write the name and molecular formula of the fourth member of alkane series. (Foreign 2016)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: The general formula of the alkane series is CnH2n+2. For fourth member of alkane series, n = 4
∴ C4H2 x 4 + 2 = C4 H10 i.e., butane.
Q9: What is homologous series of carbon compounds? (Foreign 2016)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: A homologous series is the family of organic compounds having the same functional group, similar chemical properties but the successive (adjacent) members of the series differ by a —CH2 unit or 14 mass units.
Q10: When ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid in the presence of cone. H2SO4, a substance with fruity smell is produced. Answer the following:
(i) State the class of compounds to which the fruity smelling compounds belong. Write the chemical equation for the reaction and write the chemical name of the product formed.
(ii) State the role of cone. H2SO4 in this reaction. (Delhi 2016)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (i) When ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid in presence of cone. H2SO4, ethyl ethanoate is formed which belongs to the class of ester compounds, having fruity smell.
(ii) The above reaction is called esterification which occurs in presence of cone. H2SO4 which acts as a dehydrating agent and helps in the removal of water. Cone. H2SO4 also acts as a catalyst to speed up the reaction.
Q11: Write chemical equation of the reaction of ethanoic acid with the following:
(a) Sodium;
(b) Sodium hydroxide;
(c) Ethanol
Write the name of one main product of each reaction. (Al 2016)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium as well as sodium hydroxide to form sodium ethanoate.
Q12: Write three different chemical reactions showing the conversion of ethanoic acid to sodium ethanoate. Write balanced chemical equation in each case. Write the name of the reactants and the products other than ethanoic acid and sodium ethanoate in each case. (Al 2016)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Ethanoic acid reacts with Na2CO3 to form sodium ethanoate and CO2 gas is liberated.
With sodium hydrogen carbonate it forms sodium ethanoate.
With NaOH It forms sodium ethanoate.
Q13: List two tests for experimentally distinguishing between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid and describe how these tests are performed. (Al 2016)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Tests for distinguishing between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid are:
(i) Litmus test: When we place a drop of carboxylic acid on blue litmus paper it turns red while alcohol will not change the colour of blue litmus paper.
(ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate test/sodium carbonate
test: If a pinch of NaHCO3 or Na2CO3 is added to two test tubes containing alcohol and carboxylic acid respectively, then test tube containing carboxylic acid will show the evolution of colourless gas with brisk effervescence while test tube containing alcohol does not show any reaction.
Q14: Why is reaction betweerm when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also? State briefly how the formation of micelles help to clean the clothes having oily spots. (Foreign 2016)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: A micelle is a submicroscopic aggregate of molecules with non-polar groups on the inside and hydrophilic groups on the outside. If ethanol is used in place of water, micelle will not be formed as the solution will not have any polar part.
Q15: Which of the following are correct structural isomers of C4H10?
(a) (I) and (III)
(b) (II) and (IV )
(c) (I) and (II)
(d) (III) and (IV ) (CBSE 2016, 15, 14, 11)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (c)
The molecular formula C₄H₁₀ represents butane and its isomer isobutane (also called 2-methylpropane).
Structures (I) and (II)in the image represent these two structural isomers of C₄H₁₀:
(I) shows a straight chain structure (n-butane).
(II) shows a branched structure (isobutane or 2-methylpropane).
Thus, the correct answer is (c) (I) and (II).
Q15: Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element. It is exhibited by both carbon and silicon. Compare the ability of the catenation of the two elements. Give reasons. (CBSE 2016, 11, 10)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element. It is exhibited by both carbon and silicon. Carbon exhibits catenation much more than silicon. Infact no other element exhibits the property of catenation to the extent seen in carbon compounds. Silicon forms compounds with hydrogen which have chains of upto seven or eight atoms, but these compounds are very reactive. The carbon-carbon bond is very strong and hence, stable. This gives us a large number of compounds with many carbon atoms linked to each other. Carbon has a valency of four and it is capable of bonding with four other atoms of carbon or atoms of some other monovalent elements. The bonds formed by carbon atoms are very strong and do not break easily so carbon compounds are stable
The bonds formed by carbon atoms are very strong and do not break easily so carbon compounds are stable
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q1: Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n. (Delhi 2015)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Homologous series of alkenes have general formula, CnH2n whose first member is ethene.
2nd member of homologous series of alkenes is C3H6 i.e., propene.
Q2: Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n+2. (Delhi 2015)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Alkanes have general formula, CnH2n + 2.
2nd member of homologous series of alkanes is C2H6 i.e., ethane.
Q3: Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n-2. (Delhi 2015)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: General formula, CnH2n-2 belongs to alkyne series. The second member of this series is propyne i.e., (C3H4) or CH3—C≡CH.
Q4: Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of ethane. (Al 2015, Delhi 2014)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: The structural formula of ethane (C2H6) is There are total 7 covalent bonds. Six C — H covalent bonds and one C — C covalent bond.
There are total 7 covalent bonds. Six C — H covalent bonds and one C — C covalent bond.
Q5: Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of butane, C4H10. (AI 2015)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Butane (C4H10) has the following structural formula as:
Total number of covalent bonds is 13 in which there are 10C — H and 3C - C covalent bonds.
Q6: With the help of an example, explain the process of hydrogenation. Mention the essential conditions for the reaction and state the change in physical property with the formation of the product. (Delhi 2015)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: The process of adding hydrogen to an unsaturated compound is called hydrogenation. For example, the hydrogenation of ethene leads to the formation of ethane.
Conditions for Hydrogenation
(i) Presence of an unsaturated compound (i.e. an unsaturated hydrocarbon)
(ii) Presence of a catalyst such as finely divided palladium or nickel
In case of the hydrogenation of vegetable oils, liquid unsaturated fatty acids are converted into solid saturated fatty acids.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Previous Year Questions - Carbon and its compounds
| 1. What are the different types of carbon compounds? |  |
| 2. How does carbon form bonds with other elements? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of carbon in biological systems? |  |
| 4. What are the key properties of carbon compounds? |  |
| 5. What are some common reactions of carbon compounds? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|


















