DNA & Sex Determination | Science Class 10 PDF Download
How do Traits get Expressed?
1. DNA as the Information Source:DNA contains instructions for making proteins. A gene is a section of DNA that provides information for a specific protein.
2. Role of Proteins in Traits:Proteins influence characteristics by controlling biochemical processes. Example:Plant height depends on plant hormones.
- Enzymes involved in hormone production determine the amount of hormone.
- Efficient enzymes → More hormone → Tall plant.
- Less efficient enzymes → Less hormone → Short plant.
3. Genetic Contribution from Parents:Both parents contribute equally to the DNA of the progeny in sexual reproduction. Each parent provides a copy of the same gene. This means offspring have two sets of genes, one from each parent.
4. Formation of Germ Cells:Germ cells (sperm/egg) must contain only one set of genes instead of two. Genes are stored in chromosomes, which are independent DNA pieces. Each germ cell gets one chromosome from each pair (either maternal or paternal).
5. Restoration of Chromosome Number:When two germ cells combine during fertilization, the normal chromosome number is restored. This ensures genetic stability across generations. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
Mendel’s Experiments & Inheritance
- Mendel’s laws apply to all sexually reproducing organisms.
- Even asexually reproducing organisms follow similar inheritance patterns.
Blood Groups
There are four distinct blood groups in humans:A, B, O, and AB. Blood group O is known as theuniversal donor because individuals with this blood type can donate blood to anyone. Conversely, blood group AB is called the universal recipient, as people with this blood type can receive blood from any donor.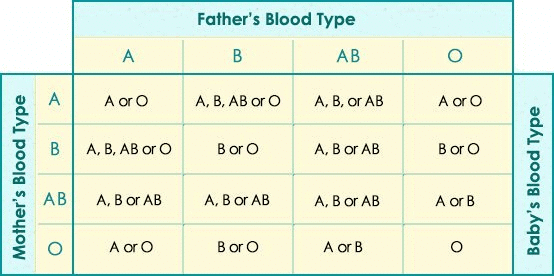 Blood Group
Blood Group
Sex Determination
Inheritance of Sex Chromosomes: In humans, sex is determined by the chromosomes inherited from the parents. Each parent contributes one sex chromosome to the child.
Mechanism of Sex Determination: The combination of the sex chromosomes from each parent determines the sex of the child:
- XX: If the child inherits an X chromosome from the father and an X chromosome from the mother, the child will be female.
- XY: If the child inherits a Y chromosome from the father and an X chromosome from the mother, the child will be male.
Role of the Father: The father plays a crucial role in determining the sex of the child by contributing either an X or a Y chromosome.
Genetic Basis of Sex Determination: The sex chromosomes (XX in females and XY in males) are part of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Out of these, 22 pairs are autosomes, which are the same in both males and females. The 23rd pair is the sex chromosomes, which are different in males and females and determine the sex of the individual.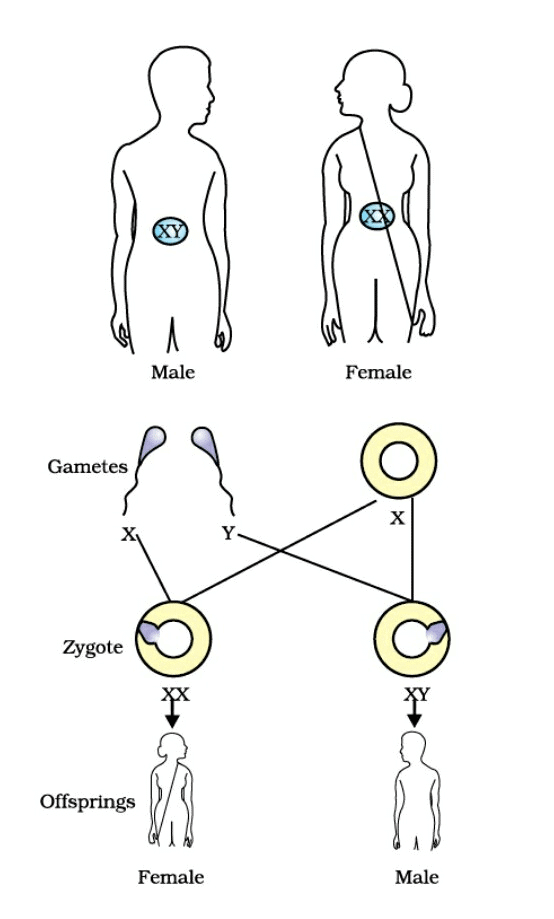 Sex Determination in Human Beings
Sex Determination in Human Beings
Points to Remember
- The word "Genetics" comes from "gene," which means "to grow."
- Bateson introduced the term "Genetics."
- Genetics is the study of heredity and variations.
- Gregor Johann Mendel is known as the Father of Genetics.
- Bateson is called the Father of Modern Genetics.
- Thomas Hunt Morgan is regarded as the Father of Experimental Genetics.
- The term "Heredity" was coined by Spencer.
- Bateson also introduced terms like Genetics, Allele, Homozygous, Heterozygous, F1 Generation, and F2 Generation.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on DNA & Sex Determination - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the basic principles of Mendel's experiments on inheritance? |  |
| 2. How do dominant and recessive traits influence an organism's phenotype? |  |
| 3. What role does DNA play in determining traits and inheritance? |  |
| 4. How does sex determination occur in animals? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of traits studied by Mendel in his experiments? |  |






















