Modes of Reproduction used by Single Organism - Class 10 PDF Download
Introduction
- Reproduction is a process by which living organisms produce new individuals of their own kind and maintain their existence generation after generation.
- Reproduction is not essential to maintain the life of an organism but it is essential to maintain life on earth and perpetuation of species from one generation to another.
- Reproduction at its basic level (cellular reproduction) is involved in making similar or dissimilar body designs through the genetic material (DNA) present in the chromosomes of its nucleus.
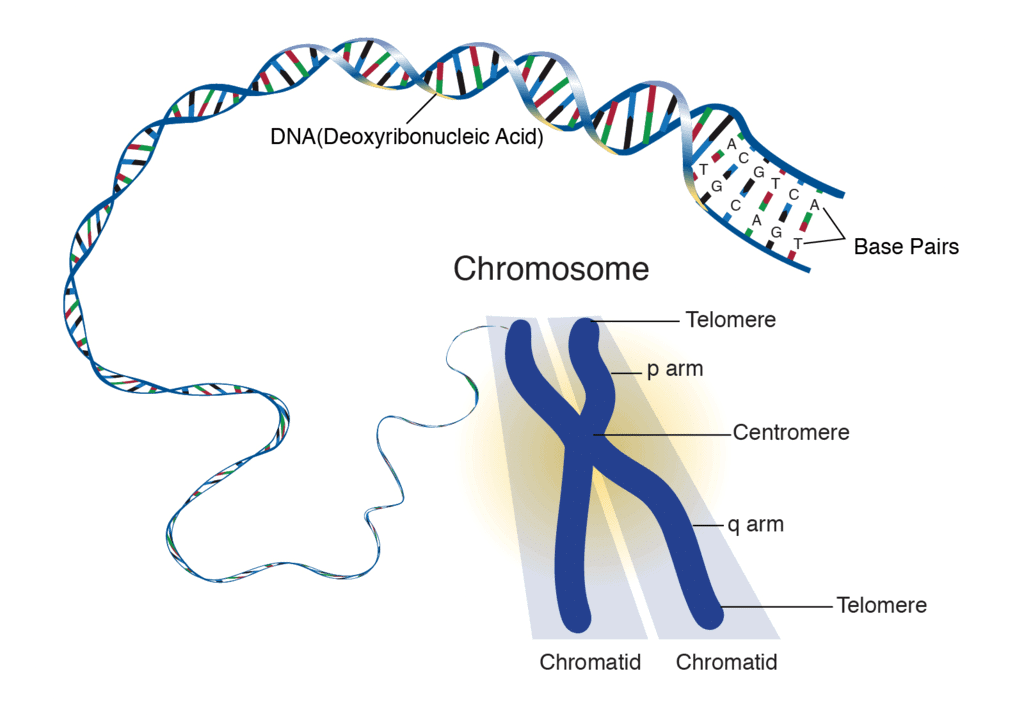 DNA and ChromosomeDNA is the source of information for making proteins:
DNA and ChromosomeDNA is the source of information for making proteins:
- Any change in the information leads to the production of different proteins, which ultimately lead to altered body designs.
- The basic event in reproduction is the production of DNA copies in a reproducing cell. This process is called DNA replication.
- When the cell divides into two, each new cell gets a copy of each DNA or chromosome along with the whole cellular apparatus.
- Complete accuracy in DNA copying leads to two exactly identical cells but any error in duplication can lead to dissimilar cells or variations.
The inbuilt tendency for variations during reproduction forms the basis for evolution:
- Variations during reproduction enable the population of a species to get adapted easily to a particular inhabiting place/niche. Hence, reproduction is linked to the stability of populations of species.
- Stronger variations are useful for the survival of species over time and enable the organisms to tide over any drastic alterations in their habitats.
Importance of Reproduction
(i) Maintenance of the existence: Organisms are maintaining the existence on the earth since their origin, million years ago only because of reproduction.
(ii) Preservation of species: Species are preserved because of reproduction. It is possible because reproducing organisms produce new individuals who are very similar to themselves.
(iii) Role in evolution: Some variations are produced in the new organisms during reproduction which plays an important role in evolution.
Types of Reproduction
There are two main methods of reproduction in living organisms:
- Asexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction
1. Asexual Reproduction
- Production of offsprings by a single parent without the formation and fusion of gametes is called asexual reproduction.
- It is a primitive type of reproduction in which offspring is produced by a cell or any vegetative organ of an organism.
- In this type of reproduction, offsprings are genetically identical to their parents.
➢ Modes of Reproduction used by Single Organism
Modes of asexual reproduction are:
- Fission
- Budding
- Spore Formation
- Fragmentation Regeneration
- Vegetative Propagation
(a) Fission
- It is a kind of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms to create two new individuals.
- It can be of two types:
(i) Binary Fission: One cell splits into two equal halves.
Example: Many bacteria and protozoa like Amoeba, Paramecium and Leishmania. Binary Fission in Amoeba(ii) Multiple Fission: One cell divides into many daughter cells simultaneously.
Binary Fission in Amoeba(ii) Multiple Fission: One cell divides into many daughter cells simultaneously.
Example: Plasmodium (malarial parasite), Amoeba in unfavourable conditions.
(b) Budding
- Process in which an outgrowth (bud) is formed on the body of parent organism which then detaches and becomes a new organism.
Example: Yeast and Hydra.
 Budding in Hydra
Budding in Hydra
(c) Spore Formation
- Spores are the microscopic asexual reproductive bodies with a thick wall. Spores are formed in 'sporangium'.
- Each spore on germination give rise to a new organism.
Example: Rhizopus, Penicillium.
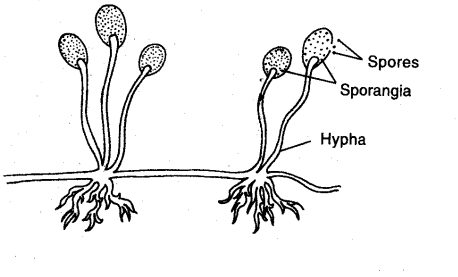 Spore Formation in Rhizopus
Spore Formation in Rhizopus
(d) Fragmentation
- In this process, an organism breaks up into two or more fragments, and each fragment develops into an adult organism.
Example: Spirogyra
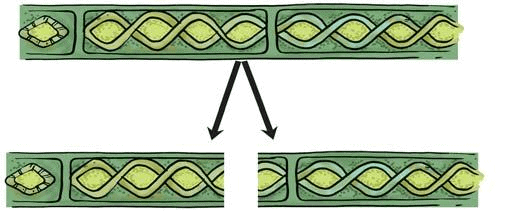 Fragmantation in Spirogyra(e) Regeneration
Fragmantation in Spirogyra(e) Regeneration
- The process of getting back a full organism from the body parts of the parent individual is called regeneration. Regeneration is carried out by specialized cells.
Example: Hydra, Planaria.
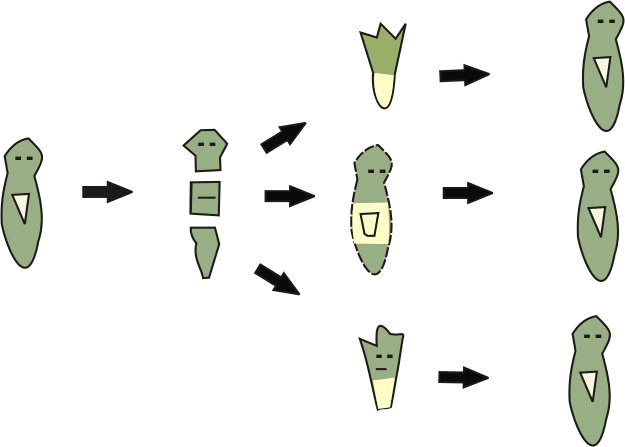 Regeneration in Planaria
Regeneration in Planaria
(f) Vegetative Propagation
- This is an asexual method of reproduction in plants where vegetative parts namely root, stem and leaves give rise to new plants.
FAQs on Modes of Reproduction used by Single Organism - Class 10
| 1. What is the Importance of Reproduction? |  |
| 2. What are the Types of Reproduction? |  |
| 3. What are the Modes of Reproduction used by Single Organism? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between Sexual and Asexual Reproduction? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages and disadvantages of Sexual and Asexual Reproduction? |  |















