Crystal Lattices & Unit Cells | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
What is a Crystal?
Crystalline solid consists of a large number of small units, called crystals, each of which possesses a definite geometric shape bounded by plane faces. The crystals of a given substance produced under a definite set of conditions are always of the same shape.
 Different crystalline solids formed from repetition of small units (unit cells)
Different crystalline solids formed from repetition of small units (unit cells)
- In a crystal lattice, each atom, molecule or ions (constituent particle) is represented by a single point.
- These points are called lattice sites or lattice points.
- Lattice sites or points are together joined by a straight line in a crystal lattice.
- When we connect these straight lines we can get a three-dimensional view of the structure. This 3D arrangement is called Crystal Lattice also known as Bravais Lattices.
- Note that lattice points only represent the points at which the constituent atom/ion/molecule is present.

What is a Unit Cell?
The smallest repeating unit of a crystal lattice is called a unit cell. It is the building block of a crystal.
- Any amount of the solid can be constructed by simply putting as many unit cells as required.
- We would be studying certain properties of a solid which depend only on the constituents of the solid and the pattern of arrangement of these constituents.

Characteristics of Unit Cell
The following characteristics define a unit cell:
- A unit cell has three edges a, b, and c, and three angles α, β, and γ between the respective edges.
- The a, b and c may or may not be mutually perpendicular.
- The angle between edge b and c is α, a and c is β and between a and b is γ.
 Parameters of a unit cell.
Parameters of a unit cell.
Types of Unit Cell
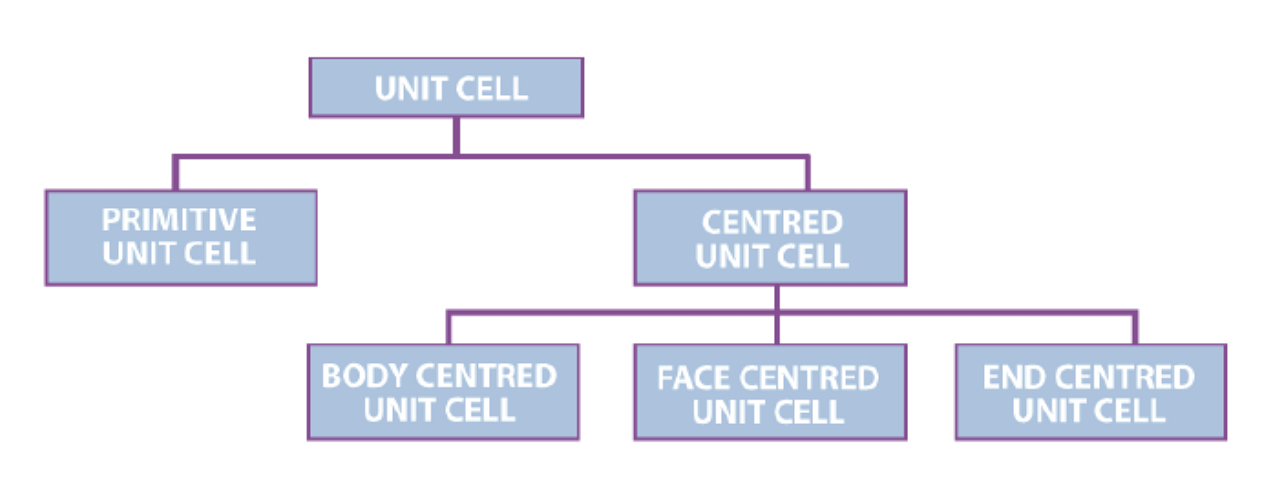
1. Primitive Unit Cells
When the constituent particles occupy only the corner positions, it is known as Primitive Unit Cells. Lattice points only at the corners of the unit cell- Primit
Lattice points only at the corners of the unit cell- Primit
2. Centred Unit Cells
When the constituent particles occupy other positions in addition to those at corners, it is known as Centred Unit Cell.
There are 3 types of Centred Unit Cells:
(i) Body Centred: When the constituent particle at the centre of the body, along with the one’s present at the corners, it is known as Body Centred Unit cell. (ii) Face Centred: When the constituent particle present at the centre of each face, along with the one’s present at the corners is known as the Face Centred Unit cell.
(ii) Face Centred: When the constituent particle present at the centre of each face, along with the one’s present at the corners is known as the Face Centred Unit cell.
(iii) End Centred: When the constituent particle present at the centre of two opposite faces, along with one's present at the corners, it is known as an End Centred Unit cell.
Number of Atoms & Packing Fraction in a Unit Cell
1. Simple Cubic (SC) Unit Cell
- A simple cubic unit cell consists of eight corner atoms. In a simple cubic unit cell, a corner atom touches with another corner atom.
 Simple cubic unit cell of a crystal lattice
Simple cubic unit cell of a crystal lattice - Number of Atoms in a Simple Cubic Unit Cell
A simple cubic unit cell consists of 8 corner atoms. Each and every corner atom is shared by eight adjacent unit cells. Therefore, one corner atom contributes 1/8th of its parts to one unit cell. Since there are eight corner atoms in a unit cell, the total number of atoms is (1/8)* 8=1. Therefore, the number of atoms in a simple cubic unit cell is one. - Atomic Radius
In a simple cubic lattice, a corner atom touches with another corner atom.
Therefore, 2r=a. So, the atomic radius of an atom in a simple cubic unit cell is a/2. - Coordination Number
Consider a corner atom in a simple cubic unit cell. It has four nearest neighbours in its own plane. In a lower plane, it has one more nearest neighbour and in an upper plane, it has one more nearest neighbour. Therefore, the total number of the nearest neighbour is six. - Packing Density
The packing density of a simple cubic unit cell is calculated as follows:
The unit cell Number of atoms
p
Substituting, r=a/2, we get,
The packing density of a simple cubic unit cell is 0.52. It means, 52% of the volume of the unit cell is occupied by atoms and the remaining 48% volume is vacant.
2. Body-Centred Cubic Unit Cell
- A Body-Centered unit cell is a unit cell in which the same atoms are present at all the corners and also at the centre of the unit cell and are not present anywhere else.
- This unit cell is created by placing four atoms that are not touching each other.
 Body-centred cubic unit cell
Body-centred cubic unit cell
- Then we place an atom on top of these four. Again, four spheres eclipsing the first layer are placed on top of this.
- The effective number of atoms in a Body-Centered Cubic Unit Cell is 2 (One from all the corners and one at the centre of the unit cell).
- Moreover, since in BCC the body-centred atom touches the top four and the bottom four atoms, the length of the body diagonal (√3a) is equal to 4r.
 The packing fraction in this case is =
The packing fraction in this case is = 
VF ≈ 0.32
3. Face Centered Cubic (FCC) Unit Cell
- In an fcc unit cell, the same atoms are present at all the corners of the cube and are also present at the centre of each square face and are not present anywhere else.
- The effective number of atoms in fcc is 4 (one from all the corners, 3 from all the face centres since each face-centred atom is shared by two cubes).
 Face centered cubic unit cell
Face centered cubic unit cell
- Since, here each face-centred atom touches the four corner atoms, the face diagonal of the cube
 is equal to 4r.
is equal to 4r.

 .
.
VF ≈ 0.26
4. End Centered Cubic (FCC) Unit Cell
A unit cell with a single constituent particle of atom, molecules, or ions located in the centre of the opposite faces, apart from that present in the corners. Two atoms are present in end centred cubic unit cell.

5. Hexagonal Primitive Unit Cell
Each corner atom would be common to 6 other unit cells, therefore their contribution to one unit cell would be 1/6. Therefore, the total number of atoms present per unit cell effectively is 6.

In the figure, ABCD is the base of the hexagonal unit cell AD=AB=a. The sphere in the next layer has its centre F vertically above E and it touches the three spheres whose centres are A, B, and D.

Hence,
The height of the unit cell (h) = 
The area of the base is equal to the area of six equilateral triangles, =  .
.
The volume of the unit cell =  .
.
Therefore,
VF ≈ 0.26
The Density of Crystal Lattice
The density of crystal lattice is the same as the density of the unit cell which is calculated as:
= 

Here,
Z = no. of atoms present in one unit cell
m = mass of a single atom
Mass of an atom present in the unit cell = m/NA
Bravais Lattices
Bravais (1848) showed from geometrical considerations that there are only seven shapes in which unit cells can exist.
These are
- Cubic
- Orthorhombic
- Rhombohedral
- Hexagonal
- Tetragonal
- Monoclinic
- Triclinic
Moreover, he also showed that there are basically four types of unit cells depending on the manner in which they are arranged in a given shape. These are:
- Primitive Unit cell
- Body-Centred
- Face Centred
- End Centred

He also went on to postulate that out of the possible twenty-eight unit cells (i.e. seven shapes, four types in each shape = 28 possible unit cells), only fourteen actually would exist. These he postulated based only on symmetry considerations. These fourteen unit cells that actually exist are called Bravais Lattices.
Seven Crystal Systems
The seven crystal systems are given below:
A. Cubic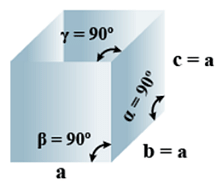
- Bravais Lattices
Primitive, face Centered, Body Centered = 3 - Parameters of Unit Cell
(i) Intercepts: a=b=c
(ii) Crystal angle: α = β = γ = 90o
Example: Pb, Hg, Ag, Au, Diamond, NaCl, ZnS
B. Orthorhombic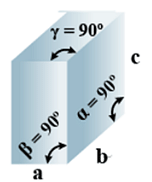
- Bravais Lattices:
Primitive, Face Centered, Body-Centered, End Centered = 4 - Parameters of Unit Cell:
(i) Intercepts: a ≠ b≠ c
(ii) Crystal angle: α = β = γ = 90o
Example: KNO2, K2SO4
C. Tetragonal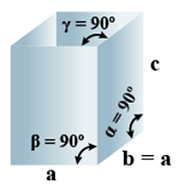
- Bravais Lattices:
Primitive, Body-Centered =2 - Parameters of Unit Cell:
(i) Intercepts: a = b≠ c
(ii) Crystal angle: α = β = γ = 90o
Example: TiO2, SnO2
D. Monoclinic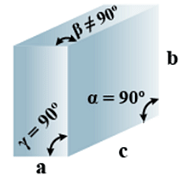
- Bravais Lattices
Primitive, End Centered =2 - Parameters of Unit Cell
(i) Intercepts: a ≠ b≠ c
(ii) Crystal angle: α = γ = 90o
Example: CaSO4.2H2O
E. Triclinic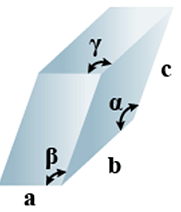
- Bravais Lattices
Primitive = 1 - Parameters of Unit Cell
(i) Intercepts: a ≠ b≠ c
(ii) Crystal angle: α ≠ β ≠ γ
Example: K2Cr2O7, CaSO4 5H2O
F. Hexagonal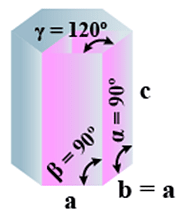
- Bravais Lattices
Primitive = 1 - Parameters of Unit Cell
(i) Intercepts: a = b≠ c
(ii) Crystal angle: α = β = 90o γ =120o
Example: Mg, SiO2, Zn, Cd
G. Rhombohedral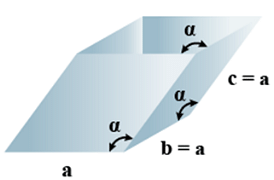
- Bravais Lattices:
Primitive = 1 - Parameters of Unit Cell
(i) Intercepts: a = b= c
(ii) Crystal angle: α = γ = 90o, β≠ 90o
Example: As, Sb, Bi, CaCO3
The table given below can be used to summarize types of lattice formation.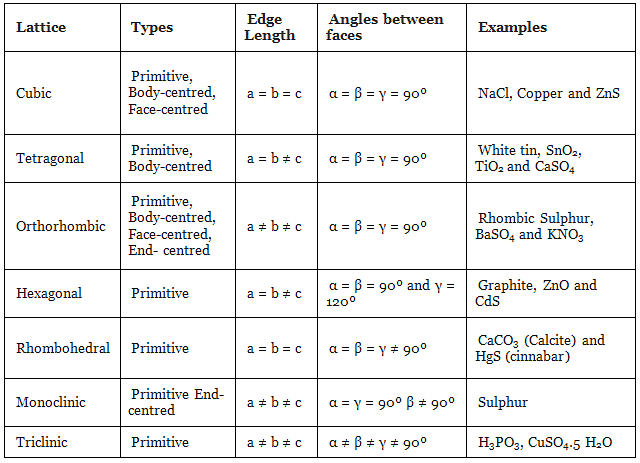
Solved Examples
Q.1: Lithium borohydride crystallizes in an orthorhombic system with 4 molecules per unit cell. The unit cell dimensions are a = 6.8 Å, b = 4.4 Å and C = 7.2 Å. If the molar mass is 21.76 g. Calculate the density of the crystal.
Solution:
Since, Density, 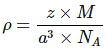 Here z = 4, Av. No = 6.023 x 1023 &
Here z = 4, Av. No = 6.023 x 1023 &
Volume = V = a x b x c
= 6.8 x 108 x 4.4 x 108 x 7.2 x 108 cm3
= 2.154 x 1022 cm3

= 0.6708 gm/cm3
Q.2. An element crystallizes into a structure which may be described by a cubic type of unit cell having one atom in each corner of the cube and two atoms on one of its face diagonals. If the volume of this unit cell is 24 x 10-24 cm3 and density of the element is 7.20 gm/cm3, calculate no. of atoms present in 200 gm of the element.
Ans: Number of atoms contributed in one unit cell = one atom from the eight corners + one atom from the two face diagonals = 1+1 = 2 atoms
Mass of one unit cell = volume × its density
= 24 × 10–24 cm3 × 7.2 gm cm3
= 172.8 × 10–24 gm
∴ 172.8 10–24 gm is the mass of one – unit cell i.e., 2 atoms
∴ 200 gm is the mass = 2 × 200 / 172.8 × 10–24 atoms = 2.3148 × 1024 atoms
Q.3. Calculate the void fraction for the structure formed by A and B atoms such that A form hexagonal closed packed structure and B occupies 2/3 of octahedral voids. Assuming that B atoms exactly fitting into octahedral voids in the HCP formed by A.
Ans: Total volume of A atom = 6 × 4 / 3 πrA3
Total volume of B atoms = 4 × 4/3 πrA3
=4 × 4/3 π(0.414rA)3
Since rB/rA as B is in octahedral void of A
Volume of HCP = 24√2rA3
Packing fraction = 6 × 4/3 πrA3 + 4 × 4/3 π (0.414rA)3 / 24√2rA3 = 0.7756
Void fraction = 1-0.7756 = 0.2244
Q.4: An element with molar mass 2.7×10-2kg mol-1 forms a cubic unit cell with edge length 405 pm. If its density is 2.7×103kg-3, what is the nature of the cubic unit cell?
Ans: d = 2.7×103kg-3
M = 2.7×10 -2 kg mol-1
a= 405 pm = 405 X 10-12
NA= 6.023 X 1023
Using the formula
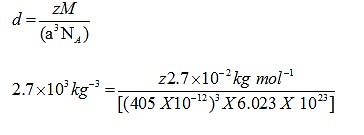
Z=4
Unit cell is fcc unit cell.
Volume of 54 g of the element = 0.054/(2.7 x 103) = 2 X 10-6
Number of unit cell in this volume = volume of 554 g of element/volume of each unit cell = 2 x 10-6/(405 x 10-12)3 = 3.012 x 1022
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|
FAQs on Crystal Lattices & Unit Cells - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is a crystal and how is it formed? |  |
| 2. What is a unit cell in crystallography? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of unit cells? |  |
| 4. How is the packing fraction of a unit cell calculated? |  |
| 5. What are the seven crystal systems and how do they differ? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|






 is equal to 4r.
is equal to 4r.


















