Doc: Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are usually called by simple names, like acetic acid (CH3COOH). In IUPAC naming, they get a different name by changing the ending to "oic acid." Here are the rules:
1. Replace the "e" at the end of the alkane name with "oic acid."
2. If there's only one carboxyl group, the carbon with it is always numbered as one. For example, CH3COOH becomes ethanoic acid.
3. If there's more than one carboxyl group, count all the carbon atoms and use Greek numeral prefixes like "di-", "tri-", etc. to show how many carboxyl groups there are.
4. Put together the alkyl chain name, numeral prefixes, and "oic acid" to name the carboxylic acid. Use Arabic numerals to show where the carboxyl groups are.
5. If a carboxyl group is a substituent on a carbon chain, you can call it "carboxylic acid" or "carboxy." For example, 2-furoic acid can be called 2-carboxyfuran.
Table – 1 : IUPAC Nomenclature of Acid derivatives :-
| S.No. | Compound | IUPAC Name |
| 1 | Methanoic acid | |
| 2 | Ethanoic acid | |
| 3 | 2- Cyclohexylpropanoic acid | |
| 4 | 3- Oxo-2- propylbutanoic acid | |
| 5 | 4- Aminobutanoic acid | |
| 6 | 3- Phenylpentanoic acid | |
| 7 | 3- Methylbutanoic adic | |
| 8 | Ethanoylchloride | |
| 9 | Propanoylchloride | |
| 10 | 3- Bromobutanoylbromide | |
| 11 | Cyclopentancarbonyl chloride | |
| 12 | Ethanoid anyhydride | |
| 13 | Trifluoroethanoic anhydride | |
| 14 | 1,2- Benzenedicarboxylic anhydride |
| 15 | Ethanoic methanoic anhydride | |
| 16 | Trifluoroethanoic propanoic anhydride | |
| 17 | Cyclopropane carbonitrile | |
| 18 | 3- Cyanopentanoic acid | |
| 19 | Ethyl-o-cyanobenzoate | |
| 20 | 2- Formylcyclohexane carboxamide | |
| 21 | 2- Hydroxyutane nitrile |
Dicarboxylic Acids
If the substituent is a second carboxyl group, we have a dicarboxylic acid. For example :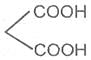
Oxalic acid or Ethanedioic acid
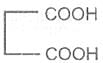
Malonic acid -1, 3- dioic acid
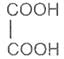
Succinic acid -1, 4- dioic acid
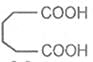
Glutaric acid
Pentane-1, 5-dioic acid
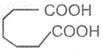
Adipic acid
Hexane-1, 6-dioic acid
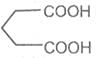
Pimelic acid
Heptane-1, 7- dioc acid
HOOCCH2COOH
Malonic acid
Propanedioic acid
HOOCCH2CH2COOH
Succinic acid
Butanedioic acid
HOOCCH2CH2CH2CH2COOH
Adipic acid
Hexanedioic acid
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Doc: Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the nomenclature of carboxylic acids? |  |
| 2. How are carboxylic acids named? |  |
| 3. Are there any common names for carboxylic acids? |  |
| 4. How do you determine the priority of substituents in carboxylic acids? |  |
| 5. Can carboxylic acids have multiple functional groups? |  |






















