Centrifugal Force | Additional Study Material for JEE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Centrifugal Force |

|
| Simple Pendulum |

|
| Circular Motion in Horizontal Plane |

|
| Motion in a Vertical Circle |

|
Centrifugal Force
When a body is rotating in a circular path and the centripetal force vanishes, the body would leave the circular path. To an observer A who is not sharing the motion along the circular path, the body appears to fly off tangentially at the point of release. To another observer B, who is sharing the motion along the circular path (i.e., the observer B is also rotating with the body which is released, it appears to B, as if it has been thrown off along the radius away from the centre by some force. This inertial force is called centrifugal force.)
Its magnitude is equal to that of the centripetal force = mv2/r . Centrifugal force is a fictitious force which has to be applied as a concept only in a rotating frame of reference to apply Newton's law of motion in that frame)
FBD of ball w.r.t non-inertial frame rotating with the ball.
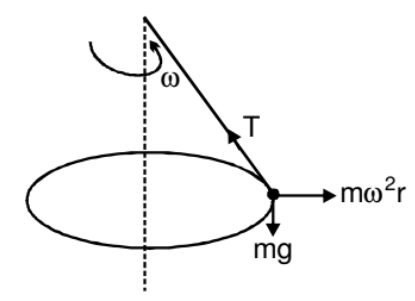
Suppose we are working from a frame of reference that is rotating at a constant, angular velocity ω with respect to an inertial frame. If we analyse the dynamics of a particle of mass m kept at a distance r from the axis of rotation, we have to assume that a force mrω2 act radially outward on the particle. Only then we can apply Newton's laws of motion in the rotating frame. This radially outward pseudo force is called the centrifugal force.
Simple Pendulum
A simple pendulum is constructed by attaching a bob of mass m to a string of length L fixed at its upper end. The bob oscillates in a vertical circle. It is found that the speed of the bob is v when the string makes an angle θ with the vertical.
The force acting on the bob are (figure)
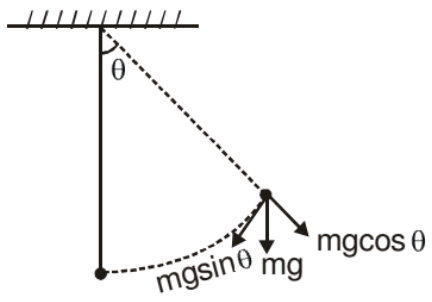
(i) Tension T
(ii) Weight mg
As the bob moves in a vertical circle with centre at O, the radial acceleration is v2/L towards O. Taking the components along this radius and applying Newton's second law, we get
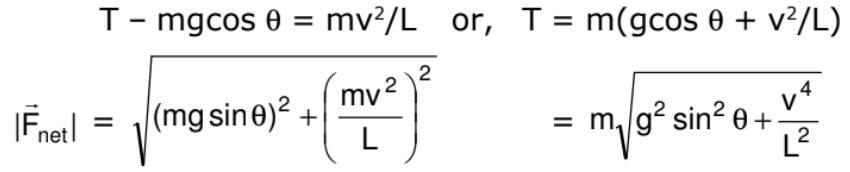
Circular Motion in Horizontal Plane
A ball of mass m attached to a light and inextensible string rotates in a horizontal circle of radius r with an angular speed w about the vertical. If we draw the force diagram of the ball.
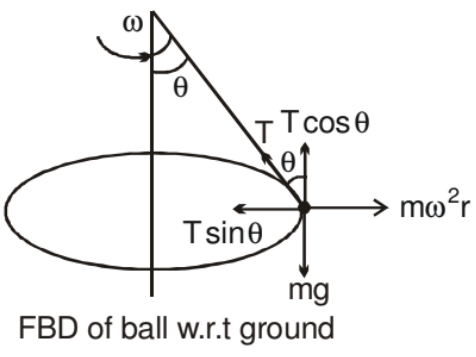
We can easily see that the component of tension force along the centre gives the centripetal force and component of tension along vertical balances the gravitation force. Such a system is called a conical pendulum.
Motion in a Vertical Circle
Suppose a particle of mass m is attached to an inextensible light string of length R. The particle is moving in a vertical circle of radius R about a fixed point O. It is imparted a velocity u in horizontal direction at lowest point A. Let v be its velocity at point B of the circle as shown.
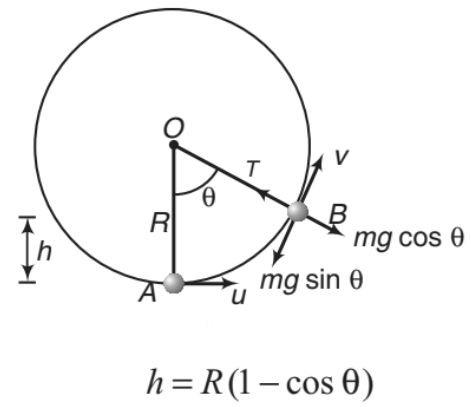
h = R(1 - cosθ) ......(i)
From conservation of mechanical energy
1/2 m(u2- v2) = mgh
or v2 = u2 - 2gh .....(ii)
The necessary centripetal force is provided by the resultant of tension T and mg cosθ
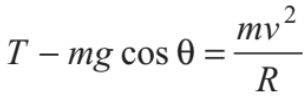 ......(iii)
......(iii)
Now, following three conditions arise depending on the value of u.
➢ Condition of Looping the Loop (u ≥ √5gR)
The particle will complete the circle if the string does not slack even at the highest point (θ = π). Thus, tension in the string should be greater than or equal to zero (T ≥ 0) at θ = π. In critical case substituting T = 0 and θ = π in above equation, we get
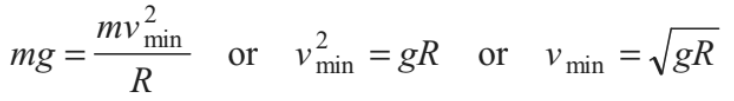 (at highest point)
(at highest point)
Substituting θ = π in Eq.(i), h=2R
Therefore, we have
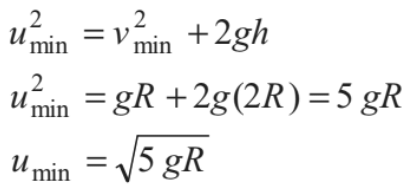
Thus, if u ≥ √5gR , the particle will complete the circle. At u = √5gR, velocity at highest point is v = √gR and tension in the string is zero.
Substituting θ = 0° and u = √5gR in Eq. (iii), we get T = 6mg or in the critical condition tension in the string at lowest position is 6mg. This is shown in Figure.
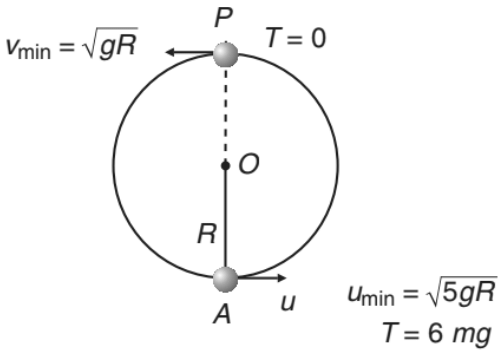
If u < √5gR , following two cases are possible.
➢ Condition of Leaving the Circle (√2gR < u < √5gR)
If u < √5gR the tension in the string will become zero before reaching the highest point. From Eq. (iii), tension in the string becomes zero (T=0)
where,
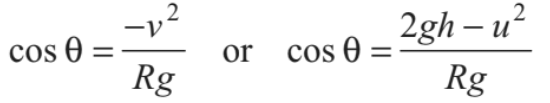
Substituting this value of cos θ in Eq. (i), we get
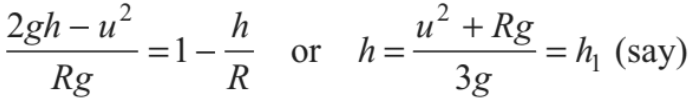 .......(iv)
.......(iv)
or we can say that at height h1 tension in the string becomes zero. Further, if u < √5gR , velocity of the particle becomes zero when
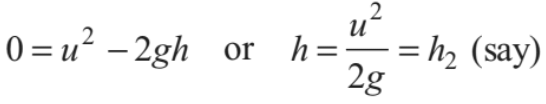 .......(v)
.......(v)
i.e. at height h2 velocity of particle becomes zero.
Now, the particle will leave the circle if tension in the string becomes zero but velocity is not zero or T = 0 but v ≠ 0. This is possible only when
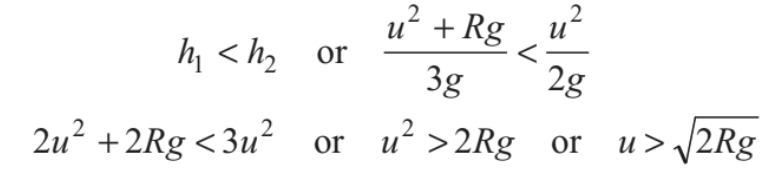
Therefore, if √2gR < u < √5gR the particle leaves the circle.
From Eq. (iv), we can see that h R > if u2 > 2gR . Thus, the particle will leave the circle when h >R or 90 < θ <180 ° . This situation is shown in the Fig.
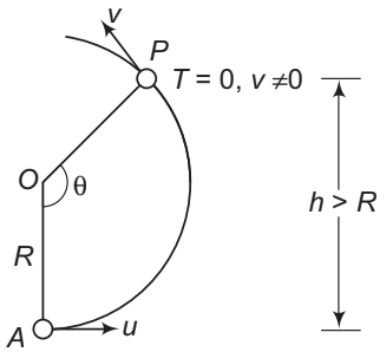
Note: After leaving the circle, the particle will follow a parabolic path as the particle
comes under gravity.
➢ Condition of Oscillation (0 < u < √2gR)
The particle will oscillate, if velocity of the particle becomes zero but tension in the string is not zero. or v = 0, but T ≠ 0. This is possible when
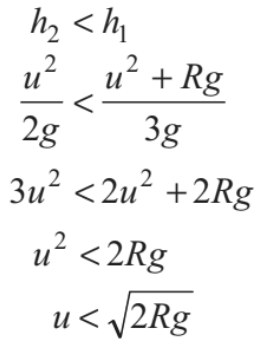
Moreover, if h1=h2, u = √2gR and tension and velocity both becomes zero simultaneously.
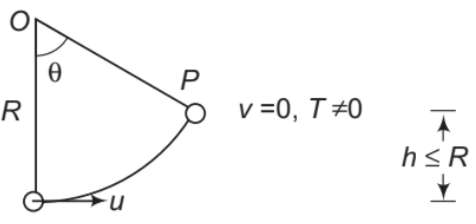
Further, from Eq. (iv), we can see that h ≤ R if u ≤ √2gR Thus, for 0< u ≤ √2gR
particle oscillates in lower half of the circle (0°<θ ≤ 90°).
This situation is shown in the figure.
Note: The above three conditions have been derived for a particle moving in a vertical circle attached to a string.The same conditions apply, if a particle moves inside a smooth spherical shell of radius R. The only difference is that the tension is replaced by the normal reaction N.
|
22 videos|163 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Centrifugal Force - Additional Study Material for JEE
| 1. What is centrifugal force? |  |
| 2. How does a simple pendulum work? |  |
| 3. What is circular motion in the horizontal plane? |  |
| 4. How is motion in a vertical circle different from simple circular motion? |  |
| 5. What is the role of centrifugal force in a vertical circle? |  |















