Types of Modulus of Elasticity | Physics for JAMB PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity |

|
| Bulk Modulus |

|
| Shear Modulus or Modulus of Rigidity |

|
| Poisson’s Ratio |

|
| Elastic Potential Energy in a Stretched Wire |

|
Depending upon three types of strain, namely, longitudinal, volumetric, and shearing strain, there are three types of Modulus of Elasticity.
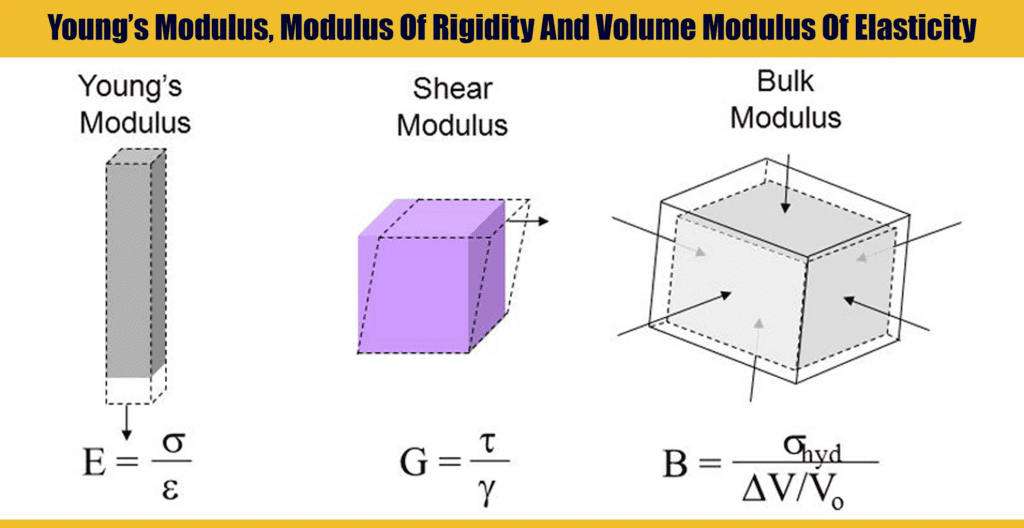 Types of Modulus of Elasticity
Types of Modulus of Elasticity
Young’s Modulus of Elasticity
Let us consider a long bar of cross-sectional area A and length lo, which is clamped at one end. When we apply external force Fl longitudinally along the bar, internal forces in the bar resist distortion, but the bar attains equilibrium in which its length is greater and in which external force is exactly balanced by internal forces. The bar is said to be stressed in this condition.
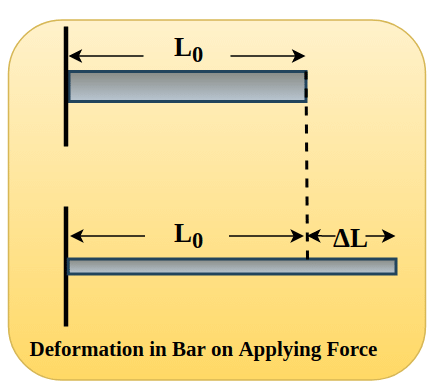 Young's Modulus
Young's Modulus

Bulk Modulus
Let us consider a cube of initial volume V and the area of cross-section A. When a force Fn is applied on the cube from all the directions equally, then there is some decrease in the overall volume of the cube.
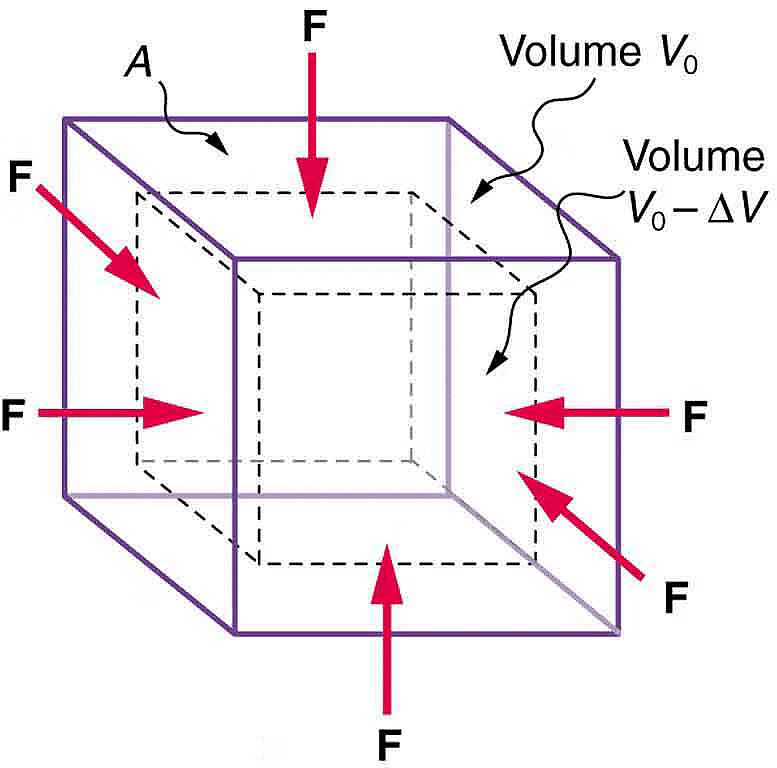 Bulk Modulus
Bulk Modulus
Within the elastic limit, the bulk modulus is defined as the ratio of longitudinal stress and volumetric strain. It is given as:
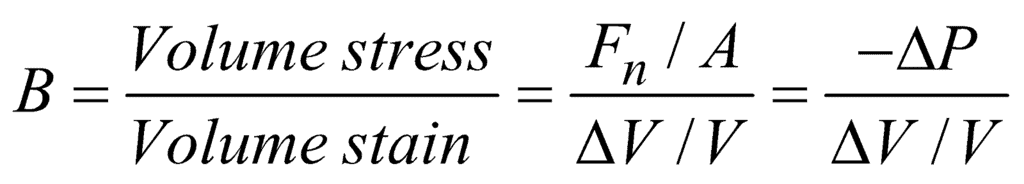
Here Fn = F and the initial volume V=Vo
A negative sign comes to make B positive because, with the increase of pressure, the volume of the body decreases or vice versa.
Shear Modulus or Modulus of Rigidity
It is defined as the ratio of the tangential stress to the shear strain. Shear modulus or modulus of rigidity η is

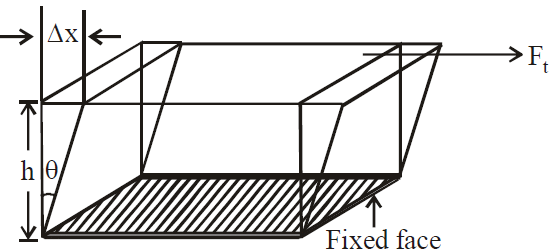 Modulus of Ridigity As we see, there is no change in volume under this deformation, but shape changes.
Modulus of Ridigity As we see, there is no change in volume under this deformation, but shape changes.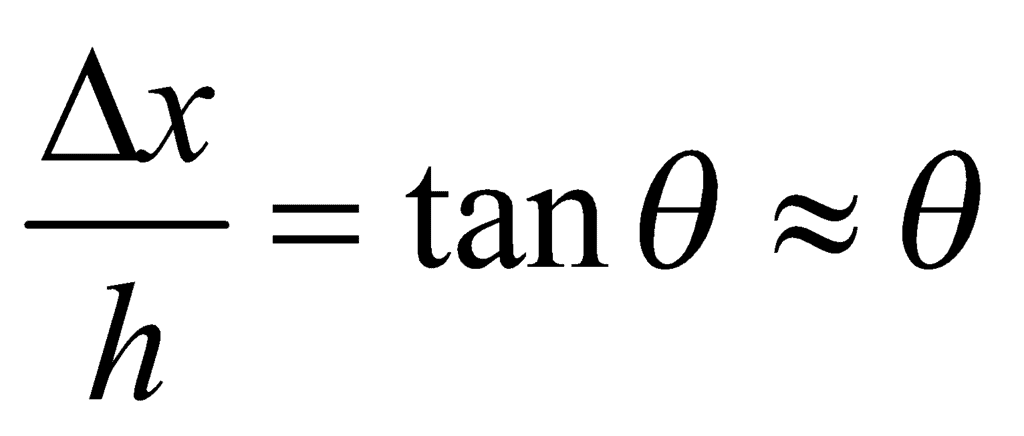 where θ is the shear angle.
where θ is the shear angle.Poisson’s Ratio
The ratio of change in diameter (ΔD) to the original diameter (D) is called lateral strain. The ratio of change in length (Δl) to the original length (l) is called longitudinal strain. The ratio of lateral strain to longitudinal strain is called Poisson’s ratio.
For most of the substances, the value of σ lies between 0.2 to 0.4 When a body is perfectly incompressible, the value of σ is maximum and equals 0.5.
Relations between Elastic Moduli
For isotropic materials (i.e., materials having the same properties in all directions), only two of the three elastic constants are independent. For example, Young’s modulus can be expressed in terms of the bulk and shear moduli.
Q1: As shown in the figure, in an experiment to determine Young's modulus of a wire, the extension-load curve is plotted. The curve is a straight line passing through the origin and makes an angle of 45º with the load axis. The length of wire is 62.8 cm and its diameter is 4 mm. The Young's modulus is found to be x * 104 Nm-2.
The value of x is .
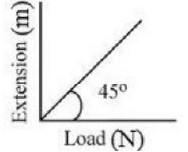
Ans: 5
Sol:
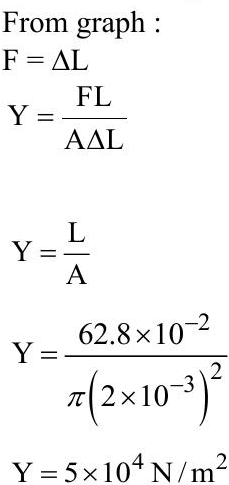
Q2: Choose the correct relationship between Poisson ratio (σ), bulk modulus (K) and modulus of rigidity (η) of a given solid object:
(a) 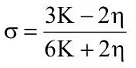
(b) 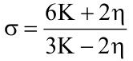
(c) 
(d) 
Ans: (a)
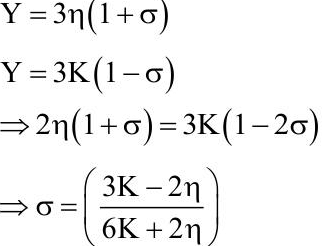
Q3: A force is applied to a steel wire ‘A’, rigidly clamped at one end. As a result elongation in the wire is 0.2 mm. If same force is applied to another steel wire ‘B’ of double the length and a diameter 2.4 times that of the wire ‘A’, the elongation in the wire ‘B’ will be (wires having uniform circular cross sections)
(a) 6.06 x 10-2 mm
(b) 2.77 x 10-2 mm
(c) 3.0 x 10-2 mm
(d) 6.9 x 10-2 mm
Ans: 
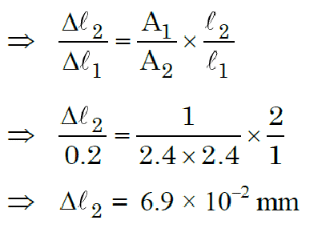
Q4: A thin rod having a length of 1 m and area of cross-section 3 x l0-6m2 is suspended vertically from one end. The rod is cooled from 210°C to 160°C. After cooling, a mass M is attached at the lower end of the rod such that the length of rod again becomes 1 m. Young's modulus and coefficient of linear expansion of the rod are 2 x l011Nm-2 and 2 x lO-5K-1, respectively. The value of M is ______ kg. (Take g = 10 ms-2)
Ans: 60
Sol: If Δl is decease in length of rod due to decease in temperature

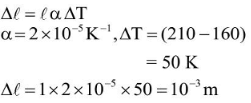
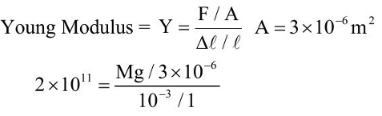
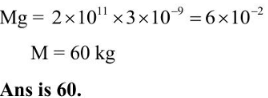
Q5: The Young's modulus of a steel wire of length 6 m and cross-sectional area 3 mm2, is 2 x 1111N/m2. The wire is suspended from its support on a given planet. A block of mass 4 kg is attached to the free end of the wire. The acceleration due to gravity on the planet is 1/4 of its value on the earth. The elongation of wire is (Take g on the earth = 10 m/s2):
(a) 1 cm
(b) 1 mm
(c) 0.1 mm
(d) 0.1 cm
Ans:
Sol: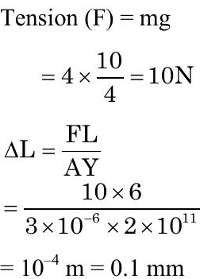
Elastic Potential Energy in a Stretched Wire
The ultimate tensile strength of a material is the stress required to break a wire or a rod by pulling on it. The breaking stress of the material is the maximum stress that a material can withstand. Beyond this point, breakage occurs.
When a wire of original length L is stretched by a length 1 by the applied I inn of force F at one end, then
Work done to stretch wire
Work done per unit volume of wire is given as:
According to the formula given by
Where F is the force needed to stretch the wire of length L and area of cross-section A, is the increase in the length of the wire.
The work done by this force in stretching the wire is stored in the wire as potential energy.
Integrating both sides, we get
which equals the elastic potential energy U.
Now the potential energy per unit volume is
Hence, the elastic potential energy of a wire (energy density) is equal to half the product of its stress and strain.
|
263 videos|277 docs|238 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Modulus of Elasticity - Physics for JAMB
| 1. What is Young's Modulus of Elasticity? |  |
| 2. What is Bulk Modulus? |  |
| 3. What is Shear Modulus or Modulus of Rigidity? |  |
| 4. What is Poisson's Ratio? |  |
| 5. What is Elastic Potential Energy in a Stretched Wire? |  |
















