Physical & Chemical Properties of Amines | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Physical Properties |

|
| Chemical Properties |

|
| Distinction between Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Amines |

|
| General Chemical Properties of Aromatic Amines |

|
Physical Properties
Here are some essential physical properties of amines:
- Odour: Lower aliphatic amines have a fishy odor and exist in the gaseous state. Primary amines with 3-4 carbon atoms are liquid at room temperature, while those with more than four carbon atoms are solid.
- Color: Aryl amines, like aniline, are mostly colorless but acquire color due to atmospheric oxidation when exposed.
- Solubility:
- Lower aliphatic amines can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, making them soluble.
- However, as the size of hydrophobic alkyl groups increases, solubility in water decreases.
- Tertiary amines lack free hydrogen atoms, leading to an absence of intermolecular association.
- Intermolecular H-Bonding:
- Both primary and secondary amines exhibit intermolecular associations through hydrogen bonding between hydrogen and nitrogen atoms.
- In primary amines, the intermolecular association is more prominent than in secondary amines, primarily due to the presence of two hydrogen atoms.
- Organic solvents such as benzene, ether, and alcohol can dissolve amines due to their lower polarity compared to alcohols, resulting in strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
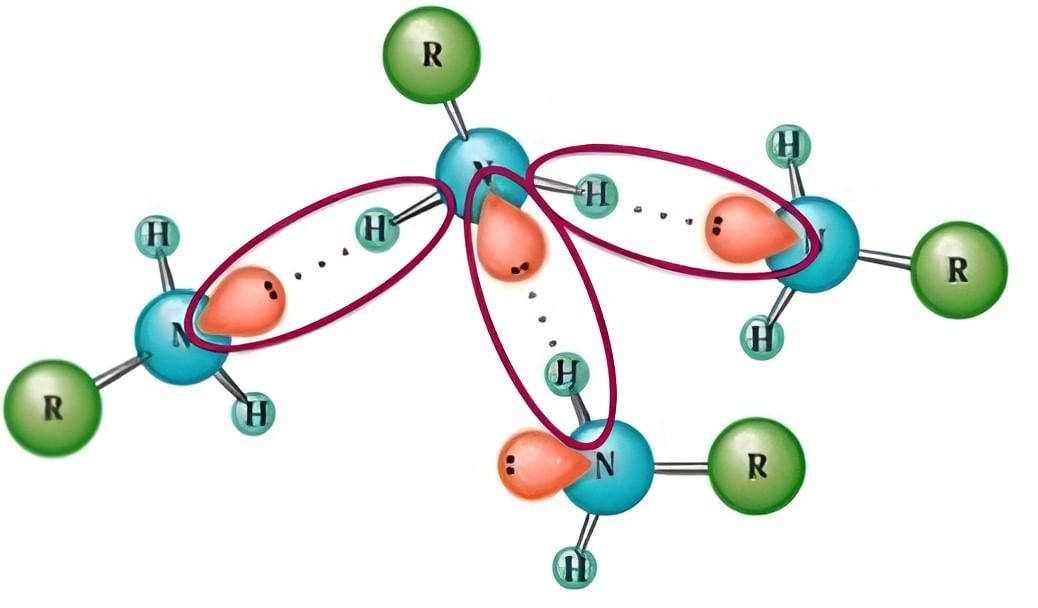 Hydrogen Bonding between Primary Amine Molecules
Hydrogen Bonding between Primary Amine Molecules
Boiling Points: The boiling order of amines is: primary amines > secondary amines > tertiary amine
Chemical Properties
(i) Basic nature
Amines are more basic than ammonia.
The following reactions prove their basic nature.
(a) It forms ethyl ammonium hydroxide when dissolved in water.
Ethyl ammonium hydroxide ionizes to give OH- ions.
C2H5NH3OH C2H5 + NH3 + OH-
(b) It reacts with acids to form salts.
C2H5NH2 + HCl C2H5NH3Cl(Ethyl ammonium chloride) or C2H5NH2.HCl( Ethylamine hydrochloride)
C2H5NH2 + H2SO4 (C2H5NH3)2 SO4 (Ethyl ammonium sulfate)
(c) Its aqueous solution behaves like ammonium hydroxide. The aqueous solution of ethylamine precipitates iron, chromium, and aluminum as hydroxides when salts are treated with it.
(d) Its hydrochloride, like ammonium chloride, forms double salts with PtCl4 and AuCl3.
These double salts decompose on heating to pure metal and this method is used to determine the molecular mass of amines.
(ii) Reaction with Alkyl Halides (Alkylation)
Ethylamine reacts with alkyl halides and forms secondary, tertiary amines, and quaternary ammonium salt.
Reaction of Ethylamine with Alkyl Halides
(iii) Reaction with Acetyl Chloride or Acetic Anhydride
Acetylation takes place when ethylamine combines with acetyl chloride or acetic anhydride.
(iv) Carbylamine Reaction
When you heat aliphatic and aromatic primary amines with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide, they produce foul-smelling substances known as isocyanides or carbylamines.
Nucleophilic RNH2 attacks electrophilic intermediator [:CCl2] dichlorocarbene.
This reaction is also known as Isocyanide Test and used for the detection of primary amines. Secondary and tertiary amines do not show this reaction.
Mechanism-
(v) Reaction with sodium
Hydrogen is evolved when ethylamine is heated with sodium.
2C2H5NH2 + 2Na 2C2H5NHNa (Sodium derivative of ethylamine)+ H2
(vi) Reaction with Grignard's reagent
Ethylamine reacts with Grignard's reagent to form alkanes.
(vii) Hofmann's Mustard Oil Reaction
Carbon disulphide reacts with ethylamine in the presence of HgCl2 to form ethyl isothiocyanate which has a mustard oil-like smell.
C2H5NH2 + CS2 + HgCl2 C2H5N = C = S ( Ethyl isothiocyanate ) + 2HCl
(viii) Reaction with Aldehydes
Ethylamine reacts additively with aldehydes to form α-hydroxyl amines which are changed to Schiff bases with the elimination of water molecules.
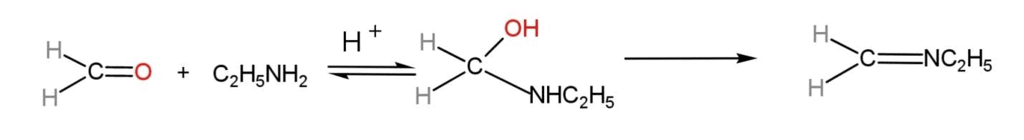 Ethylamine Reaction with Aldehydes
Ethylamine Reaction with Aldehydes
Distinction between Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Amines
Test | Primary amine | Secondary amine | Tertiary amine |
1. Action Test CHCl3 and alcoholic KOH. | Bad-smelling carbyl-amine (Isocyanide is formed) | No action. | No action. |
2. Action of CS2 and HgCl2. (Mustard Oil test | Alkyl isothiocyanate is formed which has a pungent smell like mustard oil. | No action. | No action. |
3. Action of Nitrous acid. | Alcohol is formed with the evolution of nitrogen. | Forms nitrosoamine which gives green colour with phenol and conc. H2SO4 (Liebermann's test.) | Forms nitrite in cold which on hearing gives nitrosoamine which responds to Liebermann's test. |
4. Action of acetyl chloride. | Acetyl derivative is formed | Acetyl derivative is formed | No action. |
5. Action of Hinsberg's reagent | Monoalkyl sulphonamide is formed which is soluble in KOH. | Dialkyl sulphonamide is formed which is insoluble in KOH. | No action. |
6. Action of methyl iodide. | 3 molecules (moles) of CH3I to form quaternary salt with one mole of primary amine. | 2 moles of CH3I to form quaternary salt with one mole of secondary amine. | One mole of CH3I to form quaternary salt with one mole of tertiary amine. |
General Chemical Properties of Aromatic Amines
(i) Reaction with nitrous acid
Primary amines react with nitrous acid to produce diazonium ions as follows.
ArNH2 + HNO2 Ar — N+ ≡ N :
R — NH2 + HNO2 R — N+ ≡ N
However, the diazonium ions of aliphatic amines are very unstable and produce carbocation immediately, which can produce different products.
R — N+ ≡ N R+ (Carbocation)
(ii) Electrophilic Substitution
NH2 — NHR and —NR2 strongly activate the benzene ring toward electrophilic substitution.
b. Sulfonation :
The dipolar ion structure of sulfanilic acid accounts for its (a) high melting point, (b) insolubility in H2O and organic solvents, (c) solubility in aqueous NaOH, (d) insolubility in aqueous HCl.
will not exist as a dipolar ion since -COOH is too weakly acidic to transfer an H to the weakly basic -NH2 attached to the electron-withdrawing benzene ring. When attached to an aliphatic C, the NH2 is sufficiently basic to accept H- from COOH.
(a) Bromination
- Aniline undergoes bromination with bromine water at room temperature, resulting in the formation of a white precipitate of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline. The primary challenge in electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines lies in their exceptionally high reactivity, leading to substitution predominantly at the ortho and para positions.
- To control the activating effect of the amino group (-NH2) and prepare a monosubstituted aniline derivative, it can be protected through acetylation using acetic anhydride.
- Subsequent substitution can then be performed, followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to yield the desired substituted amine.
- Acetylation shields the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom of the anilino group from resonance with the oxygen atom, thereby reducing its availability for donation to the benzene ring via resonance.
- Consequently, the activating effect of the -NHCOCH3 group is diminished compared to that of the amino group.
(b) Nitration
- Direct nitration of aniline results in the formation of tarry oxidation products alongside the nitro derivatives.
- Additionally, under strongly acidic conditions, aniline is protonated to generate the anilinium ion, which exhibits meta-directing behavior. Consequently, significant amounts of meta derivatives are produced alongside ortho and para derivatives.
- However, by first protecting the -NH2 group through acetylation with acetic anhydride, the nitration reaction can be controlled, favoring the formation of the para-nitro derivative as the primary product.
(c) Sulphonation
- Aniline undergoes sulphonation with concentrated sulfuric acid to form anilinium hydrogensulfate.
- Upon heating with sulfuric acid at elevated temperatures (453-473K), the major product obtained is p-aminobenzenesulfonic acid, commonly known as sulphanilic acid.
- Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reactions (alkylation and acetylation) due to salt formation with aluminum chloride, a Lewis acid catalyst.
- This interaction results in the acquisition of a positive charge by the nitrogen atom of aniline, rendering it a strong deactivating group for further reactions.
(iii) The Hinsberg Test
This test can be used to demonstrate whether an amine is primary, secondary, or tertiary. Primary amines react with benzenesulfonyl chloride to form N-substituted benzenesulfonamides. These, in turn, undergo acid-base reactions with the excess potassium hydroxide to form water-soluble potassium salt. Acidification of this solution will cause the water-soluble in the next stage, cause the water-insoluble N-substituted sulfonamide to precipitate.
Secondary amies react with benzene sulfonyl chloride in aqueous potassium hydroxide to form insoluble, N - N-disubstituted sulfonamides that precipitate after the first stage. N3N-
Disubstituted sulfonamides do not dissolve in aqueous potassium hydroxide.
If the amine is a tertiary amine and if it is water-insoluble, no apparent change will take place in the mixture as we shake it with benzene sulfonyl chloride and aqueous KOH. When we acidify the mixture, the tertiary amine dissolves because it forms a water-soluble salt.
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Physical & Chemical Properties of Amines - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the physical properties of amines? |  |
| 2. What are the chemical properties of amines? |  |
| 3. How are primary, secondary, and tertiary amines distinguished from each other? |  |
| 4. What are the general chemical properties of aromatic amines? |  |
| 5. How do the physical and chemical properties of amines relate to their classification as organic compounds? |  |





















