Born Haber Cycle | Physical Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
BORN HABER CYCLE
Ionisation Energy: The minimum amount of energy required to remove one electron form the outermost shell of an isolated gaseous atom is called ionization energy of the element.
Electron affinity: Amount of energy released when an extra electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom.
Lattice Energy: Amount of energy released when 1 mole of gaseous cation and 1 mole gaseous anion combine to each other and form 1 mole of ionic compound is called lattice energy.
Na (g) + Cl-(g) → NaCl(s) + heat
(Lattice energy)
Example: Calculate the standard enthalpy change for a reaction CO2(g) + H2(g) → CO(g) +H2O (g) given that ΔHf0 for CO2(g), CO(g) and H2O(g) as -393.5, -110.5 and -241.8 KJ/mol respectively.
(a) -31.2 KJ
(b) - 21.2 KJ
(c) -11.2 KJ
(d) 41.2KJ
Ans. (d)
Solution.
ΔHº= SΔHfº(products) - SΔHfº(Reactants)
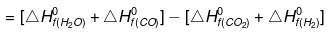
ΔHº = [-241.8 - 110.5] - [-393.5 0]
= - 352.3 393.5 = 41.2 KJ
|
117 videos|226 docs|237 tests
|
FAQs on Born Haber Cycle - Physical Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What is a Born-Haber cycle? |  |
| 2. How is a Born-Haber cycle useful in determining lattice energy? |  |
| 3. What are the key steps involved in a Born-Haber cycle? |  |
| 4. How does a Born-Haber cycle relate to the stability of an ionic compound? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of the Born-Haber cycle? |  |

















