Definite Integral As Limit Of A Sum And Estimate Of Definite Integrals | Mathematics (Maths) Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
Definite Integral As Limit Of A Sum

Remark :
The symbol
was introduced by Leibnitz and is called integral sign. It is an elongated S and was chosen because an integral is a limit of sums. In the notation
is called the integrand and a and b are called the limits of integration; a is the lower limit and b is the upper limit. The symbol dx has no official meaning by itself;
is all one symbol. The procedure of calculating an integral is called integration.
Estimate Of Definite Integration & General Inequality
STATEMENT : If f is continuous on the interval [a, b], there is atleast one number c between a and b such that 
Proof : Suppose M and m are the largest and smallest values of f, respectively, on [a, b]. This means m ≤ f(x) ≤ M when a ≤ x ≤ b



Because f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] and because the number I =  lies between m and M, the intermediate value theorem syas there exists a number c between a and b for which f(c) = I ; that is,
lies between m and M, the intermediate value theorem syas there exists a number c between a and b for which f(c) = I ; that is, 
The mean value theorem for integrals does not specify how to determine c. It simply guarantees the existence of atleast one number c in the interval.
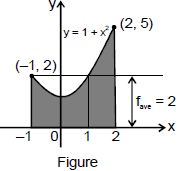
Since f(x) = 1 + x2 is continuous on the interval [–1, 2], the Mean Value Theorem for Integrals says there is a number c in [–1, 2] such that
In this particular case we can find c explicitly. From previous Example we know that fave = 2, so the value of c satisfies f(c) =  = 2
= 2

Thus, in this case there happen to be two numbers c = ± 1 in the interval [–1, 2] that work in the mean value theorem for Integrals.
Walli's Formula & Reduction Formula

Solved Examples
Ex.1 Evaluate  using limit of sum.
using limit of sum.
Sol.







This integral can't be interpreated as an area because f takes on both positive and negative values. But is can be interpreated as the difference of areas A1 – A2, where A1 and A2 are shown in Figure
Ex.2 Prove that,  Hence or otherwise evaluate
Hence or otherwise evaluate 
Sol.
Consider sin nθ + sin (n - 2) θ = 2 sin (n - 1) θ cos θ ⇒ sin nθ sec θ = 2 sin (n-1) θ - sin (n - 2) θ sec θ
Hence 

 ,
,






Ex.3 Prove that 
Sol.
L.H.S. = 


 (From Walli's formula)
(From Walli's formula)
Ex.4 If un =  then show that u1, u2, u3 ,...... constitute an arithmetic progression. Hence or otherwise find the value of un.
then show that u1, u2, u3 ,...... constitute an arithmetic progression. Hence or otherwise find the value of un.
Sol.
un + 1 – 2un + un – 1 = (un + 1 – un) – (un – un – 1)





∴ un – 1 + un + 1 = 2un i.e., un – 1, un, un + 1 form an A.P.
⇒ u1, u2, u3,.........constitute an A.P.
Ex.5 Evaluate 
Sol.






Integrating by parts taking unity as the second function, we have


Ex.6 Show that  Hence or otherwise evaluate
Hence or otherwise evaluate 
Sol.



adding (1) and (2) then




Put a tan x = t ⇒ a sec2x dx = dt when x = 0 ⇒ t = 0 ; x = p/2 ⇒ t = ∝



Differentiating both side w.r.t. 'a', we get 
again differentiating both sides w.r.t. 'a' we get 
Put a = √5 on both sides, we get

Ex.7 Let f be an injective functions such that f(x) f(y) + 2 = f(x) + f(y) + f(xy) for all non negative real x and y with f(0) = 1 and f '(1) = 2 find f(x) and show that  f(x) dx – x (f(x) + 2) is a constant.
f(x) dx – x (f(x) + 2) is a constant.
Sol. We have f(x) f(y) + 2 = f(x) + f(y) + f(xy) ......(1)
Putting x = 1 and y = 1 then f(1) f(1) + 2 = 3f(1)
we get f(1) = 1, 2 & f(1)  1 (
1 (  f(0) = 1 & function is injective) then f(1) = 2
f(0) = 1 & function is injective) then f(1) = 2
Replacing y by 1/x in (1) then f(x) f(1/x) + 2 = f(x) + f(1/x) + f(1) ⇒ f(x) f(1/x) = f(x) + f(1/x) [ f(1) = 2)
Hence f(x) is of the type f(x) = 1 ± xn ⇒ f(1) = 1 ± 1 = 2 (given)
∴ f(x) = 1 + xn and f '(x) = nxn – 1 ⇒ f '(1) = n = 2 ∴ f(x) = 1 + x2
∴ 

Ex.8 Evaluate 
Sol.
Let I =  Make |sin x| – |cos x| = 0 ∴ |tan x| = 1
Make |sin x| – |cos x| = 0 ∴ |tan x| = 1
∴ tan x = ± 1  and both these values lie in the interval [0, π].
and both these values lie in the interval [0, π].
We find for 0 < x < π/4, |sin x| – |cos x| < 0
 |sin x| – |cos x| > 0
|sin x| – |cos x| > 0




Ex.9 Evaluate  , (where [ * ] is the greatest integer function)
, (where [ * ] is the greatest integer function)
Sol. Let I = 
Let f(x) = x2 + x + 1 ⇒ f '(x) = 2x - 1 for x > 1/2, f '(x) > 0 and x < 12, f '(x) , 0
Values of f(x) at x = 1/2 and 2 are 3/4 and 3 integers between them an 1, 2 then x2 - x + 1 = 1, 2
we get x = 1,  and values of f(x) at x = 0 and 1/2 are 1 and 3/4 no integer between them
and values of f(x) at x = 0 and 1/2 are 1 and 3/4 no integer between them




Alternative Method : It is clear from the figure


Ex.10 If 
Sol.


Integrating by parts taking x2 as 1 st function, we we get = 
 [By Prop.]
[By Prop.]

Adding (1) and (2) we get






Ex.11 Prove that 
Sol.
 Intergrating by parts taking x as a first function, we have
Intergrating by parts taking x as a first function, we have







Ex.12 Evaluate 
Sol.
Let g(t) = |t – 1| – |t| + |t + 1| = 

= 
Ex.13 For all positive integer k, prove that 
Hence prove that 
Sol. We have 2 sinx [cos x + cos 3x + ...+ cos (2k–1)x ]
= 2 sinx cosx + 2 sinx cos 3x + ....+ 2 sinx cos(2k – 1)x
= sin 2x + sin 4x – sin 2x + sin 6x – sin 4x + ....... + sin 2kx – sin (2k – 2) x
= sin 2kx
⇒ 2[cos x + cos 3x + ........ + cos (2k – 1) x ] = sin2kx/sinx

 [2 cos2x + 2 cos 3x cos x + ....... + 2 cos (2k – 1 ) x cosx ] dx
[2 cos2x + 2 cos 3x cos x + ....... + 2 cos (2k – 1 ) x cosx ] dx
 [cosx + cos 3x + ....... + cos (2k – 1 ) x ]cosx dx
[cosx + cos 3x + ....... + cos (2k – 1 ) x ]cosx dx
= 
Ex.14 Let f(x) is periodic function such that  Find the function f(x) if (1) = 1 .
Find the function f(x) if (1) = 1 .
Sol.

from (2) and (3) 
Differentiating bot sides w.r.t.x, we get









then f(x) = 1/x3 But given f(x) is a periodic function Hence f(x) = 1
Ex.15 Assume then prove that
then prove that
Sol.










Ex.16 Use induction to prove that , 
Sol.



Now sinkx = sin[(k + 1) x – x ] = sin(k + 1) x cos – cos(k + 1)x sin x
Hence sin (k + 1 ) x cosx = sinkx + cos(k + 1) x sin x
Subistuting P(k + 1) = 

Now I. B. P. to get the result
|
204 videos|290 docs|139 tests
|
FAQs on Definite Integral As Limit Of A Sum And Estimate Of Definite Integrals - Mathematics (Maths) Class 12 - JEE
| 1. What is the concept of definite integral as a limit of a sum? |  |
| 2. How can we estimate definite integrals? |  |
| 3. Can definite integrals be used to find the value of a function at a specific point? |  |
| 4. What is a general inequality related to definite integrals? |  |
| 5. How are definite integrals used in real-world applications? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|


















