Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanism | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Introduction
In an organic reaction, an organic molecule (called the substrate) reacts with an attacking reagent, forming intermediates and ultimately yielding products. The substrate is the reactant that contributes carbon to form new bonds, while the other reactant is the reagent. When both reactants contribute carbon, the molecule of primary focus is designated as the substrate.
These reactions involve breaking a covalent bond—either between two carbons or between carbon and another atom—and forming a new one. Describing each step, including electron movement, energy changes, and reaction rates, provides the reaction mechanism. Understanding this mechanism is key to predicting organic compound reactivity and designing synthesis strategies. In the following sections, we’ll explore principles underlying these processes.

Fission of a Covalent Bond
Heterolytic fission and homolytic fission are two common ways in which chemical bonds break. Most organic compounds consist of covalent bonds, where two atoms share a pair of electrons. During a chemical reaction, these bonds may break, and new bonds are formed. This process of bond breaking is called bond fission. Bond fission typically occurs in one of two ways:
1. Homolytic Fission
2. Heterolytic Fission
Homolytic Fission
- The term homo means equal, and lytic or lysis refers to breaking.
- Homolytic fission is a process where, during the breaking of a covalent bond, the shared pair of electrons is equally divided between the two atoms.
- Each atom retains one electron from the shared pair, resulting in the formation of free radicals.
- This process is also known as homolysis or homolytic cleavage.
- When a neutral molecule undergoes homolytic fission, the bond splits and produces free radicals, each having one unpaired electron.

Conditions Favoring Homolytic Fission
- Several factors can promote the breaking of a covalent bond through homolytic fission:
- The bond between the two atoms must be non-polar, meaning there should be little to no difference in their electronegativities.
- External factors such as heat, electricity, peroxides, or radicals can also encourage the formation of free radicals.
Free Radicals
- A free radical is an atom or group of atoms that has an unpaired electron.
- In other words, free radicals are species with odd electrons in their outer shell.
- They are produced when a neutral molecule undergoes homolytic fission, where each of the bonded atoms keeps one electron from the shared pair, resulting in the formation of free radicals.
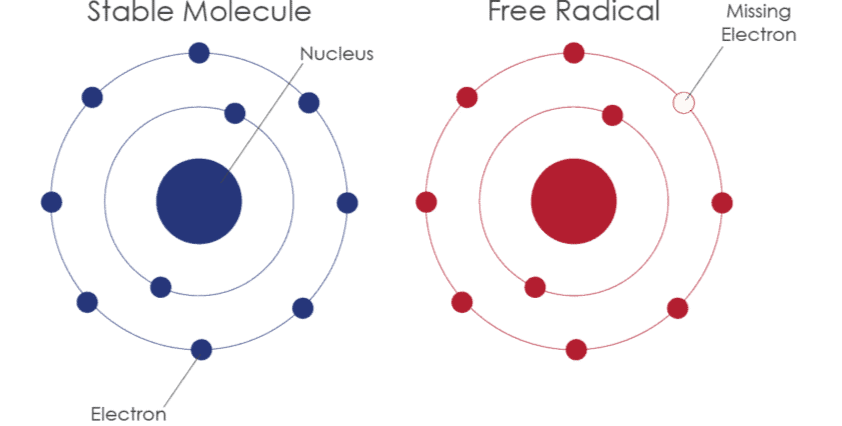
Structure of Free Radicals
Some key features of free radicals include:
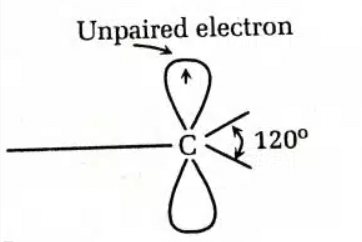
- sp² hybridization of the carbon atom
- Planar geometry of the carbon atom with bond angles of 120°
- High reactivity (they are less stable)
- Paramagnetic behavior, due to the unpaired electron
- They can act as either oxidizing or reducing agents, as they have a tendency to accept or donate electrons.
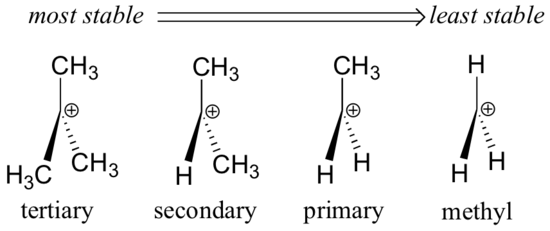
Stability of Free Radicals
The stability of free radicals is ranked as follows:
Methyl free radical < Primary free radical < Secondary free radical < Tertiary free radical.
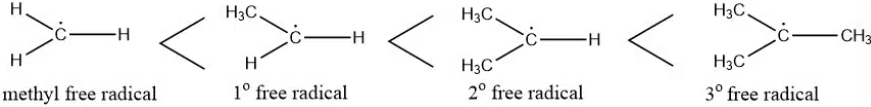
- A free radical’s stability increases with the number of hyperconjugation structures, meaning the more hyperconjugation possibilities, the more stable the radical.
- This makes tertiary radicals more stable than secondary ones, and secondary radicals more stable than primary ones.
- Additionally, resonance effects can further stabilize free radicals.
Heterolytic Fission
- The term "hetero" means different or unequal.
- The words "lytic" or "lysis" relate to the act of breaking.
- Heterolytic fission is a process where a covalent bond is broken and one atom takes both of the shared electrons.
- This leads to the creation of charged particles: a positively charged carbocation and a negatively charged carbanion.
- This process can also be called heterolysis or heterolytic cleavage.
- During this process, when a neutral molecule breaks apart, the atom with the higher electronegativity (the ability to attract electrons) keeps the shared electrons.
- As a result, this leads to the formation of both carbocations and carbanions.

Conditions Favoring Heterolytic Fission
- Several factors promote the breaking of a covalent bond through heterolytic fission:
- The two atoms involved in the bond must have a large difference in electronegativity, meaning the bond should be polar.
- External factors like low temperature and the presence of a polar solvent can also favor heterolytic cleavage.
Carbocation
A carbocation is a positively charged ion where a carbon atom has three bonds but only two electrons in its valence shell, resulting in a formal positive charge. It is an unstable species that often forms as an intermediate in organic reactions.
Properties of Carbocation
1. It is positively charged species.
2. It has a sextet of electrons i.e. diamagnetic.
3. It is formed by heterolysis.
4. It is generally formed due to polar solvent.
Structure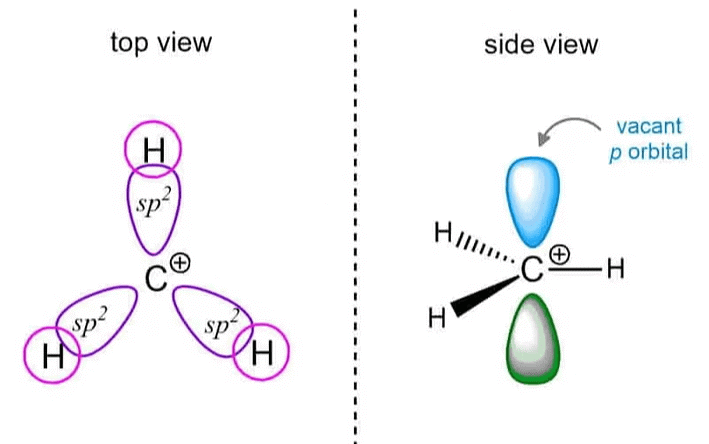
- A carbocation is a positively charged ion where the carbon atom forms three bonds but has only two electrons in its valence shell.
- The carbon atom typically adopts a trigonal planar geometry with bond angles around 120°.
- The carbon atom has an empty p-orbital, leading to a deficiency in electron density and making it highly reactive.
- Carbocations can be classified based on the number of alkyl groups attached to the positively charged carbon: Primary (one alkyl group), Secondary (two alkyl groups), Tertiary (three alkyl groups)
- Tertiary carbocations are the most stable due to inductive and hyperconjugation effects.
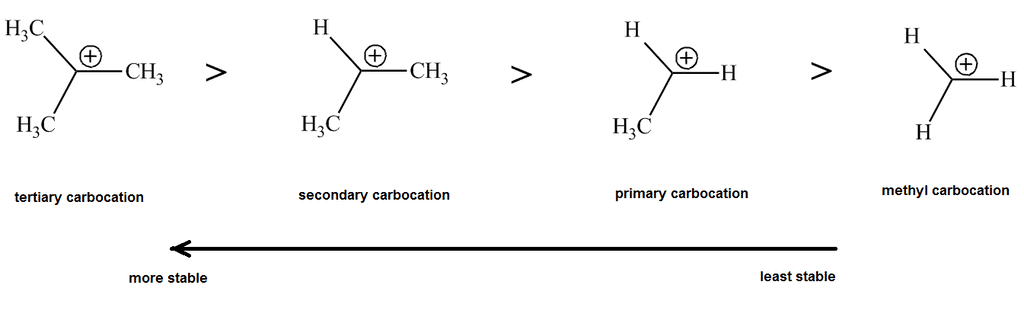
Stability
The stability of a carbocation is influenced by:
- Electron-donating groups (like alkyl groups) stabilize the carbocation.
- Hyperconjugation and resonance can further stabilize the positive charge.
- Tertiary carbocations are more stable than secondary and primary due to better stabilization from alkyl groups.
- In short, more stabilization from these factors increases carbocation stability.
Carbanion
A carbanion is a negatively charged ion where a carbon atom has three bonds and carries a formal negative charge. It is an unstable species that results from the gain of an electron by the carbon atom.
Structure
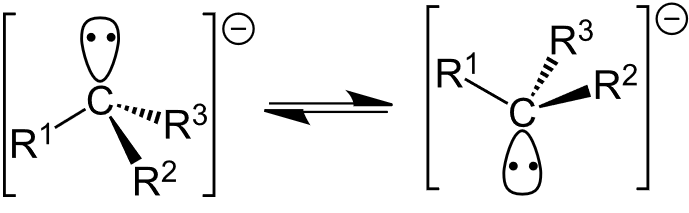
- The carbon atom in a carbanion typically adopts a trigonal pyramidal geometry, with bond angles around 107°.
- The negative charge resides on the carbon atom, often occupying an sp³ hybrid orbital, which makes the carbanion highly reactive.
- Carbanions are generally unstable and are stabilized by electron-withdrawing groups or resonance (if delocalization occurs).
- Carbanions are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the number of alkyl groups attached to the negatively charged carbon, with tertiary carbanions being more stable than primary ones.
Stability
The stability of a carbanion is influenced by several factors:
- Inductive effects: Electron-withdrawing groups stabilize the carbanion by pulling electron density away.
- Resonance: Delocalization of the negative charge through resonance increases stability.
- Hybridization: Carbanions with sp² or sp hybridization are more stable than sp³ ones.
- Substituent size: Larger carbanions are more stable due to charge dispersion.
- Electron-donating groups: Alkyl groups decrease stability by increasing electron density.
- In general, tertiary carbanions are more stable than primary or secondary ones.

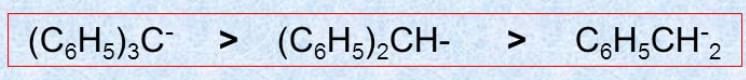
Substrate and Reagent
In organic reactions, ions are typically not involved; instead, molecules react. One molecule is designated as the substrate, and the other as the reagent. The substrate is the molecule whose carbon forms a new bond, while the reagent is the other reactant. When a carbon-carbon bond forms, the choice of substrate and reagent is arbitrary and depends on the molecule being observed.
Example: 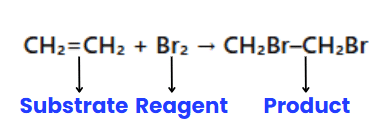
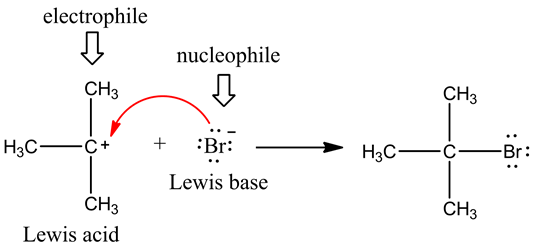
Electrophile
All electron-deficient atom or group of atoms are known as Electrophiles, the electrophile attacks at the electron-rich centre.
It Include:
1. All positively charged species are electrophiles.
H , NO2 , Br , Cl , etc.
2. The compound in which the octet of central atom is not complete
BF3, AlCl3, ZnCl2, etc.
3. All the compounds in which the central atom can expand its octet
SnCl4, SiCl4, etc.
4. All polarising functional group are Electrophiles as well as Nucleophiles
Nucleophile
All electron rich compounds are nucleophiles and attack at the electron deficient centre.
It Include:
- All negatively charged species. Example: -H-, Cl-, NO2-, Br-, CH3- etc.
- The compound in which the central atom has lone pair of electron. Example: NH3, H2O,
,
etc.
- All organometallic compounds are nucleophiles R - Mgx, RLi, R2Cd.
- The compound having p e- density, CH2 = CH2, etc.
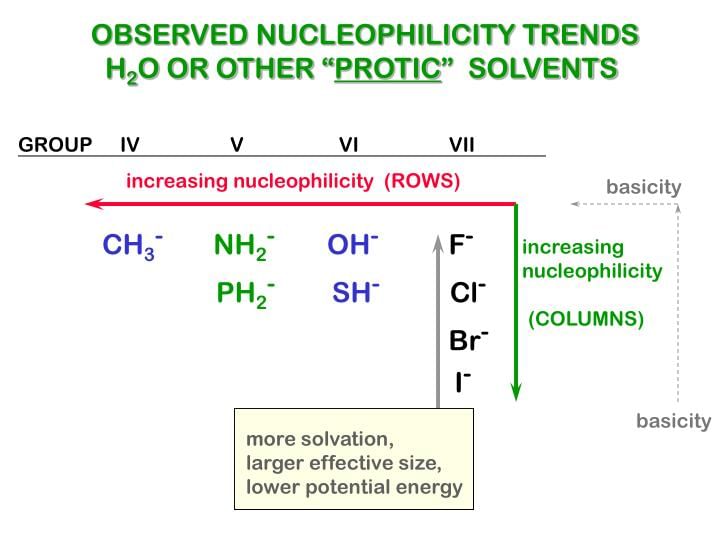
Nucleophilicity
The power of nucleophile is known as nucleophilicity .
- The nucleophilicity of negative charge is greater than the nucleophilicity of lone pair
- Example:
- If lone pair or -ve charge is present on the different atoms then less electronegativity, more will be the nucleophilicity.
- Example:
,
,
,
- If -ve charge or lone pair of electron is present on the same atom then the less stable -ve charge will be the better nucleophile
- Example:
Electron Displacement Effects
The displacement of electrons within the same molecule is known as electronic displacement. These effects affect the stability of a species or compound and it also affects the acidic & basic strength.
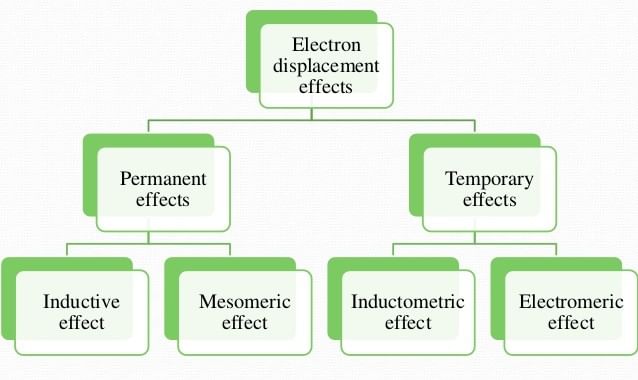
Electronic Displacement Effect is divided into two parts:
1. Permanent effect
- Inductive effect
- Mesomeric (resonance) effect
- Hyperconjugation
2. Temporary effect
- Electromeric effect
- Inductomeric effect
Inductive effect
It is an effect in which permanent polarization arises due to partial displacement of s-electrons along the carbon chain or partial displacement of sigma-bonded electrons toward more electronegative atoms in the carbon chain.
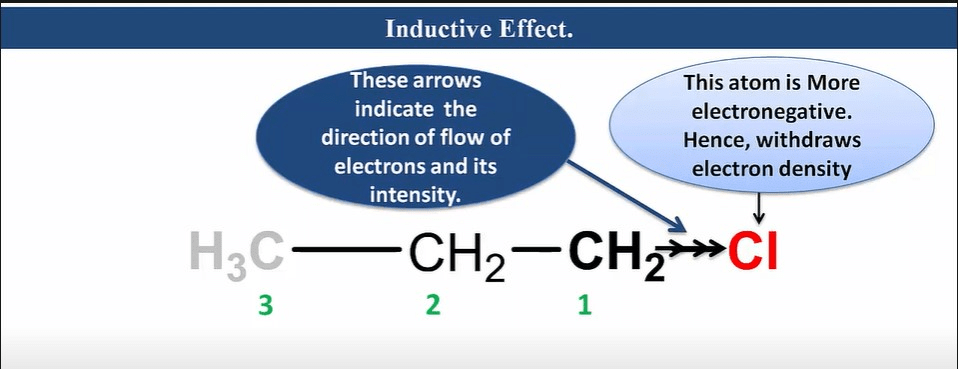
Characteristic of Inductive Effect
- It is a permanent effect.
- It is caused due to electronegativity difference.
- It operates via an s-bonded electron.
- It is a distance-dependent effect.
- As distance increases, its effect decreases.
- It can be neglected after the third carbon.
- It has a destabilizing effect.
Types of Inductive Effect
- It is divided into 2 parts on the basis of electronegativity w.r.t. hydrogen atom:
- + I effect , - I effect
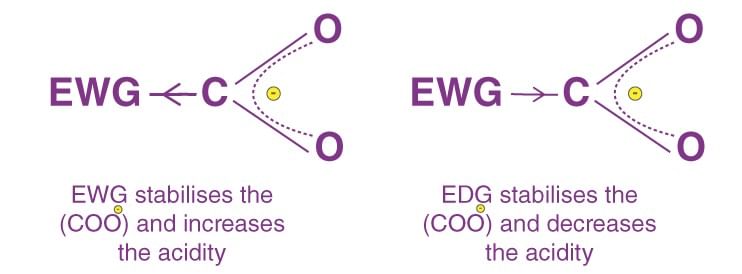
- If any atom or group having electronegativity greater than that of hydrogen, then it is considered as - I effect and vice-versa.
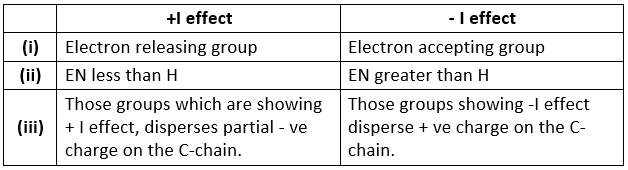
- Example:
1. CH3 – CH2 – Cl i.e. - I effect of Cl
2. CH3 – CH2 = CH2 i.e. - I effect of – CH2 and + I effect of – CH3 - Order of -I effect showing group:
- Order of+ I effect showing group:
Application of Inductive Effect
- To compare the stability of intermediates.
Intermediates: These are real separable species having measurable stability formed during the conversion of reactant to product. After bond cleavage and before bond formation. They are formed by homolytical and heterolytical cleavage. - 6 types of intermediates:
- Free radical
- Carbocation
- Carbanion
- Carbene
- Nitrene
- Benzyne
Electromeric Effect
- It involves the complete transfer of electrons of a multiple bond to one of the bonded atom in presence of an electron attacking reagent. It is called the E effect.
This effect is temporary and takes place only in the presence of a reagent. As soon as the reagent is removed, the molecule reverts back to its original position.
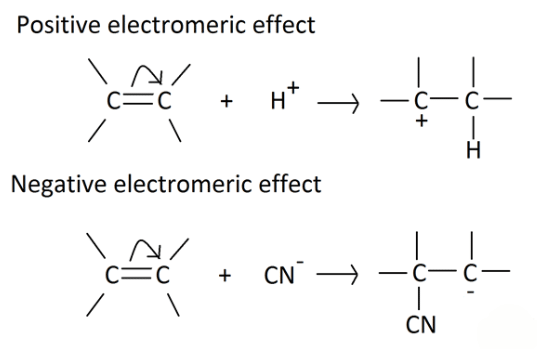
Types of Electromeric Effect
- +E effect: If the electrons of the π-bond are transferred to that atom of the double bond to which the reagent gets finally attached, the effect is called the +E effect. Example: Addition of acids to alkenes.
- -E Effect: If the electrons of the double bond are transferred to an atom of the double bonds other than the one to which the reagent gets finally attached the effect is called -E Effect. Example: Addition of Cyanide ion to the carbonyl group.
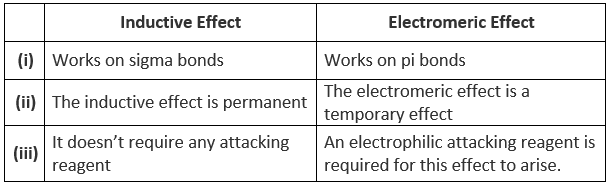
Differences between Inductive and Electromeric Effect
Resonance Effect
In many organic compounds, a single Lewis structure doesn't accurately predict properties. For example, benzene appears to have C-C and C=C bonds, but its behavior deviates. Resonance structures (hypothetical and not representing real molecules individually) help describe these compounds. The resonance hybrid, the true structure, is more stable and lower in energy than any individual resonance structure.
Factor Affecting Resonance Stability
- More covalent bonds
- Atoms with an octet of electrons (excluding hydrogen, which follows the duet rule)
- Separation of opposite charges
- Dispersal of charge
- A negative charge on more electronegative atoms and a positive charge on more electropositive atoms increase stability.
Resonance and Polarity
Resonance causes polarity by delocalizing π-electrons, either between two π-bonds or a π-bond and a lone pair. There are two main types:
- Positive Resonance Effect (+R effect): Electron density moves away from the attached group. Groups like –COOH, –CHO, >C=O, –CN, and –NO₂ contribute.
- Negative Resonance Effect (-R effect): Electron density moves towards the attached group. Groups like –COOH, –CHO, >C=O, –CN, and –NO₂ contribute.
Resonating Structure
- Hypothetical structure existing on paper.
- The energy difference b/w different resonating structure is very small.
- All Resonating Structure contribute towards the formation of resonance hybrid (Their contribution may be different).
- A single Resonanting Structure can't explain each & every property of that particular compound.
Resonating Structure of Chlorobenzene:
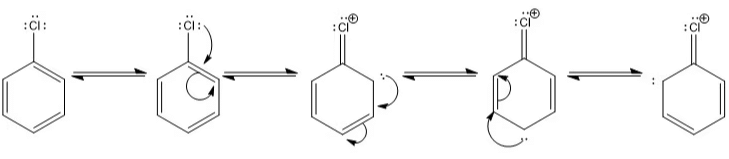
- Resonance hybrid: It is a real structure that explains all the properties of a compound formed by the contribution of different R.S.
It has got maximum stability as compared to any Resonating Structure. - Resonance Energy: It is the difference b/w theoretical value of H.O.H & experimental value. Or it can be defined as the difference b/w more stable Resonating Structure & Resonating Hybrid.
The more resonance energy, the more stable will be the molecule.
Resonance energy is an absolute term.
Fries Rule:
- Compounds with more benzenoid structures are more stable.
- As the Resonance energy is greater than those in which lesser number of benzenoid structures are present.
- If a double bond is participating in resonance then it will acquire a partial single bond character as a result of which bond length increases & bond strength decreases.
- If a single bond is involved in resonance then it will acquire partial double bond character. As a result of which bond length decreases & bond strength increase.
Mesomeric Effect (Resonance effect)
The mesomeric effect is valid only for the conjugated system.
Types of Mesomeric Effect
- It is divided into 2 parts:
+M effect (+R), - M Effect (-R) - Consider the following conjugated system:
Mesomeric Effect in the Compounds Having a Benzene Ring
- If the movement of electrons is towards the ring, it will show +M effect. This effect increases the electron density over the benzene ring.
- +M effect in phenol
- +M group increases the electron density of ring while - M decreases the electron density of benzene ring.
- If NO2 is present on the ortho or para position then along with its -I effect, It will also show -M effect.
Above compound have +M of -OH .
As we can easily see that -NO2 at meta position is not attracting e- density towards itself and that's why it will not show -M effect at m-position.
Hyperconjugation
Permanent polarisation caused by the displacement of s-electrons into p-molecular orbital is known as hyperconjugation. Hyper conjugation is called No-bond Resonance.
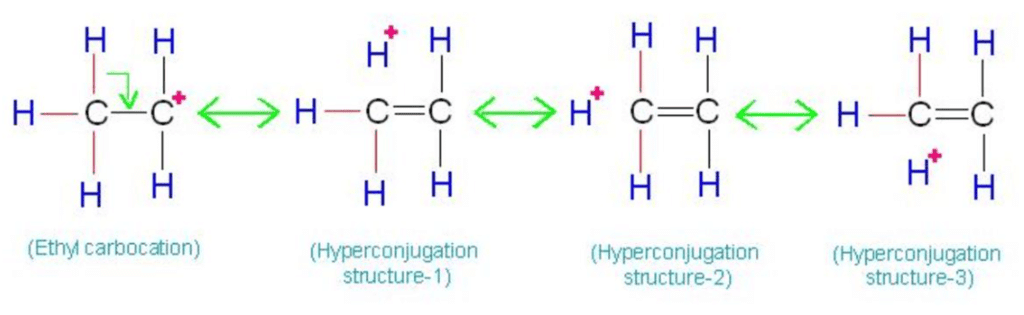
- More the C - H bond, more will be the no bond resonating structure (Hyperconjugation).
- More the (C - H) bond, the more will be the stability of free radicals.
Properties of Free Radical
- It is a neutral species.
- It has one unpaired electron, therefore, why paramagnetic in nature.
Structure
→ methyl free Radical
→ ethyl free radical
- Its hybridization is sp2 and triangular planar shape.
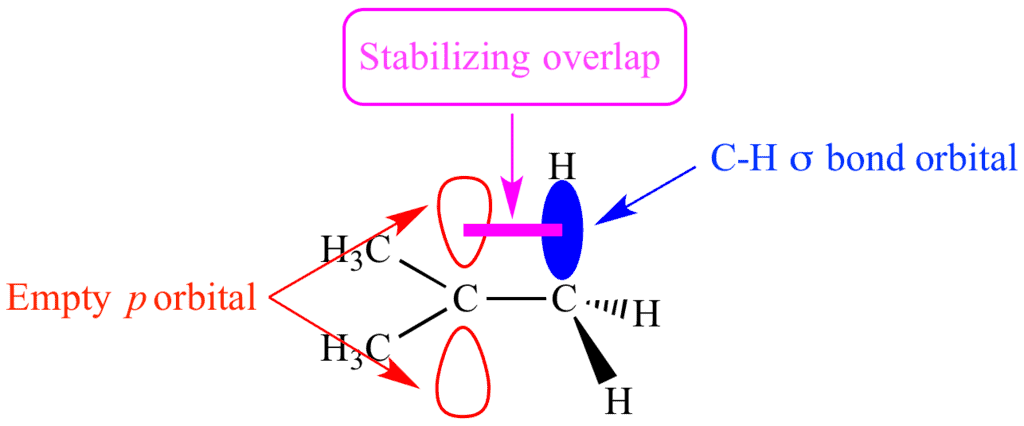
- Hyperconjugation occurs when electrons in adjacent C-H or C-C bonds overlap with an empty p-orbital (in carbocations) or a free radical orbital.
- Stabilizing effect: It spreads the electron density and stabilizes the molecule.
- More alkyl groups: The more alkyl groups attached to the carbon center, the greater the hyperconjugation effect, making the molecule more stable.
- Common in carbocations: This effect is especially prominent in tertiary carbocations, where three alkyl groups donate electron density.
Stability of Free Radical
The stability of free radicals is influenced by several factors:
- Hyperconjugation: The more alkyl groups adjacent to the free radical, the more stable it becomes due to the donation of electron density.
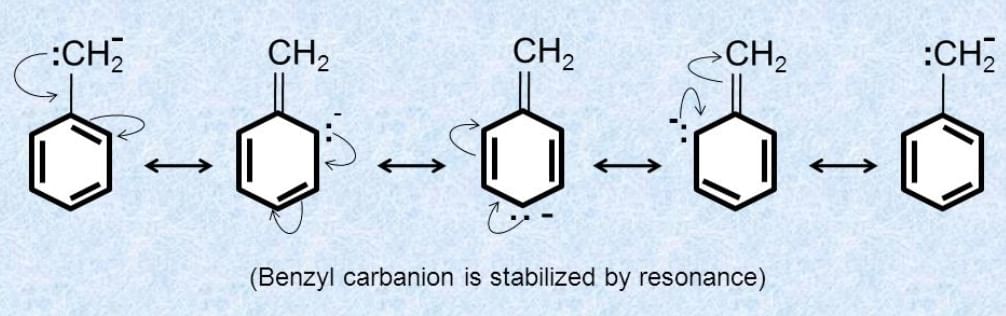
- Resonance: If the free radical's unpaired electron can be delocalized through resonance (e.g., in allyl or benzyl radicals), the radical is more stable.
- Inductive effects: Electron-donating groups, such as alkyl groups, increase radical stability by providing electron density to the unpaired electron.
- Radical type: Tertiary radicals are more stable than secondary and primary radicals due to the stabilizing effects of adjacent alkyl groups.
In general, the stability order of free radicals is: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl.
|
114 videos|263 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanism - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the difference between a carbocation and a carbanion? |  |
| 2. What are substrates and reagents in organic chemistry reactions? |  |
| 3. What is an electrophile, and how does it differ from a nucleophile? |  |
| 4. How do inductive and electromeric effects influence organic reactions? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of electron displacement effects in organic reaction mechanisms? |  |

















